|
Single-sideband Modulation
In radio communications, single-sideband modulation (SSB) or single-sideband suppressed-carrier modulation (SSB-SC) is a type of signal modulation used to transmit information, such as an audio signal, by radio waves. A refinement of amplitude modulation, it uses transmitter power and bandwidth more efficiently. Amplitude modulation produces an output signal the bandwidth of which is twice the maximum frequency of the original baseband signal. Single-sideband modulation avoids this bandwidth increase, and the power wasted on a carrier, at the cost of increased device complexity and more difficult tuning at the receiver. Basic concept Radio transmitters work by mixing a radio frequency (RF) signal of a specific frequency, the carrier wave, with the audio signal to be broadcast. In AM transmitters this mixing usually takes place in the final RF amplifier (high level modulation). It is less common and much less efficient to do the mixing at low power and then amplify it in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SSB Bandform
SSB may refer to: Organizations * Scandinavian School of Brussels * Social Security Board (other) * , the Society of Saint Bridget * Society of the Sisters of Bethany, an Anglican order of sisters * Society of Systematic Biologists * , a former public transport operator in Switzerland * Statistics Norway (), a Norwegian government statistics bureau * , a public transport operator in Germany * Sustainable South Bronx, an environmental justice organization * Swedish School Beijing, a former international school in China (1994–2015) * Smoke Signal Broadcasting, a defunct American computer company Military * Presidency of Defense Industries () of Turkey * SSB (militia), paramilitary clan militia that operates in the Sool, Sanaag and Togdheer regions of Somaliland * ''Sashastra Seema Bal'', Indian border patrol force, formerly called Special Service Bureau * Secret Service Bureau, of the United Kingdom, now called the Secret Intelligence Service * Services Selection Board, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rugby Transmitting Station
__NOTOC__ Rugby Radio Station was a large British government radio transmission facility just east of the Hillmorton area of the town of Rugby, Warwickshire in England. The site straddled the A5 trunk road, with most of it in Warwickshire, and part on the other side of the A5 in Northamptonshire. First opened in 1926, at its height in the 1950s it was the largest radio transmitting station in the world, with a total of 57 radio transmitters, covering an area of . Traffic slowly dwindled from the 1980s onwards, and the site was closed between 2003 and 2007. The tallest masts on the site were tall, and could be seen from up to away, making the site for many years a major local landmark. Since closure, part of the site has been used for a large housing development called Houlton, named after Houlton, Maine, USA the American town which received the first transatlantic phone call from the station in 1927. History Following the end of the First World War the British government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilbert Transform
In mathematics and signal processing, the Hilbert transform is a specific singular integral that takes a function, of a real variable and produces another function of a real variable . The Hilbert transform is given by the Cauchy principal value of the convolution with the function 1/(\pi t) (see ). The Hilbert transform has a particularly simple representation in the frequency domain: It imparts a phase shift of ±90° (/2 radians) to every frequency component of a function, the sign of the shift depending on the sign of the frequency (see ). The Hilbert transform is important in signal processing, where it is a component of the Analytic signal, analytic representation of a real-valued signal . The Hilbert transform was first introduced by David Hilbert in this setting, to solve a special case of the Riemann–Hilbert problem for analytic functions. Definition The Hilbert transform of can be thought of as the convolution of with the function , known as the Cauchy ker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IQ Modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) is the name of a family of digital modulation methods and a related family of analog modulation methods widely used in modern telecommunications to transmit information. It conveys two analog message signals, or two digital bit streams, by changing (''modulating'') the amplitudes of two carrier waves, using the amplitude-shift keying (ASK) digital modulation scheme or amplitude modulation (AM) analog modulation scheme. The two carrier waves are of the same frequency and are out of phase with each other by 90°, a condition known as orthogonality or quadrature. The transmitted signal is created by adding the two carrier waves together. At the receiver, the two waves can be coherently separated (demodulated) because of their orthogonality. Another key property is that the modulations are low-frequency/low-bandwidth waveforms compared to the carrier frequency, which is known as the narrowband assumption. Phase modulation (analog PM) and pha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-sideband Derivation
In radio communications, single-sideband modulation (SSB) or single-sideband suppressed-carrier modulation (SSB-SC) is a type of signal modulation used to transmit information, such as an audio signal, by radio waves. A refinement of amplitude modulation, it uses transmitter power and bandwidth more efficiently. Amplitude modulation produces an output signal the bandwidth of which is twice the maximum frequency of the original baseband signal. Single-sideband modulation avoids this bandwidth increase, and the power wasted on a carrier, at the cost of increased device complexity and more difficult tuning at the receiver. Basic concept Radio transmitters work by mixing a radio frequency (RF) signal of a specific frequency, the carrier wave, with the audio signal to be broadcast. In AM transmitters this mixing usually takes place in the final RF amplifier (high level modulation). It is less common and much less efficient to do the mixing at low power and then amplify it in a li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strategic Air Command
Strategic Air Command (SAC) was a United States Department of Defense Specified Command and a United States Air Force (USAF) Major Command responsible for command and control of the strategic bomber and intercontinental ballistic missile components of the United States military's strategic nuclear weapon, strategic nuclear forces from 1946 to 1992. SAC was also responsible for strategic reconnaissance aircraft; airborne command posts; and most of the USAF's aerial refueling aircraft. SAC primarily consisted of the Second Air Force (2AF), Eighth Air Force (8AF) and the Fifteenth Air Force (15AF), while SAC headquarters (HQ SAC) included Directorates for Operations & Plans, Intelligence, Command & Control, Maintenance, Training, Communications, and Personnel. At a lower echelon, SAC headquarters divisions included Aircraft Engineering, Missile Concept, and Strategic Communications. In 1992, as part of an overall post-Cold War reorganization of the U.S. Air Force, SAC was disesta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amateur Radio Operator
An amateur radio operator is someone who uses equipment at an amateur radio station to engage in two-way personal communications with other amateur operators on radio frequencies assigned to the amateur radio service. Amateur radio operators have been granted an amateur radio license by a governmental regulatory authority after passing an examination on applicable regulations, electronics, radio theory, and radio operation. As a component of their license, amateur radio operators are assigned a call sign that they use to identify themselves during communication. About three million amateur radio operators are currently active worldwide. Amateur radio operators are also known as radio amateurs or hams. The term "ham" as a nickname for amateur radio operators originated in a pejorative usage (like "ham actor") by operators in commercial and professional radio communities, and dates to wired telegraphy. The word was subsequently adopted by amateur radio operators. Demographic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), often described as being equivalent to one event (or Cycle per second, cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose formal expression in terms of SI base units is 1/s or s−1, meaning that one hertz is one per second or the Inverse second, reciprocal of one second. It is used only in the case of periodic events. It is named after Heinrich Hertz, Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (1857–1894), the first person to provide conclusive proof of the existence of electromagnetic waves. For high frequencies, the unit is commonly expressed in metric prefix, multiples: kilohertz (kHz), megahertz (MHz), gigahertz (GHz), terahertz (THz). Some of the unit's most common uses are in the description of periodic waveforms and musical tones, particularly those used in radio- and audio-related applications. It is also used to describe the clock speeds at which computers and other electronics are driven. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L-carrier
The L-carrier system was one of a series of carrier systems developed by AT&T for high-capacity transmission for long-distance communications. It was the first designed to handle hundreds of Voice frequency, voice frequency telephone lines, compared to earlier carrier systems which handled 12 or fewer channels. Over a period from the late 1930s to the 1970s, the system evolved in six significant phases of development, designated by Bell System engineers as L-1 through L-5, and L-5E. Coaxial cable was the principal transmission medium in all stages, initially lending the system another description i.e. the ''coaxial system''.E.L. Green, ''The Coaxial Cable System'', Bell Laboratories Record 15(9) p274 (May 1937) It was the successor to a series of previous carrier systems, typically identified by capital letters. In the 1960s, the system was hardened against the dangers of the Cold War using complete placement of all terminal and repeater equipment in hardened underground vaults. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
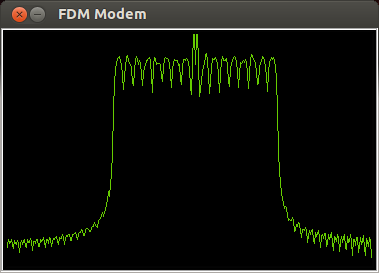
Frequency-division Multiplexing
In telecommunications, frequency-division multiplexing (FDM) is a technique by which the total bandwidth (signal processing), bandwidth available in a communication channel, communication medium is divided into a series of non-overlapping frequency bands, each of which is used to carry a separate signal. This allows a single transmission medium such as a microwave radio link, cable or optical fiber to be shared by multiple independent signals. Another use is to carry separate serial bits or segments of a higher rate signal in Parallel communication, parallel. The most common example of frequency-division multiplexing is radio and television broadcasting, in which multiple radio signals at different frequencies pass through the air at the same time. Another example is cable television, in which many television channels are carried simultaneously on a single cable. FDM is also used by telephone systems to transmit multiple telephone calls through high capacity trunklines, communi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telephone Line
A telephone line or telephone circuit (or just line or circuit industrywide) is a single-user circuit on a telephone communication system. It is designed to reproduce speech of a quality that is understandable. It is the physical wire or other signaling medium connecting the user's telephone apparatus to the telecommunications network, and usually also implies a single telephone number for billing purposes reserved for that user. Telephone lines are used to deliver consistent landline telephone service and digital subscriber line (DSL) phone cable service to the premises. Telephone overhead lines are connected to the public switched telephone network. The voltage at a subscriber's network interface is typically 48 V between the ring and tip wires, with tip near ground and ring at –48 V. In the United States In 1878, the Bell Telephone Company began using two-wire circuits, called the local loop, from each user's telephone to end offices, which performed a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |