|
Single-lens Reflex Camera
In photography, a single-lens reflex camera (SLR) is a type of camera that uses a mirror and prism system to allow photographers to view through the lens and see exactly what will be captured. SLRs became the dominant design for professional and consumer-level cameras throughout the late 20th century, offering interchangeable lenses, through-the-lens (TTL) metering, and precise framing. Originating in the 1930s and popularized in the 1960s and 70s, SLR technology played a crucial role in the evolution of modern photography. Although digital single-lens reflex (DSLR) cameras succeeded film-based models, the rise of Mirrorless camera, mirrorless cameras in the 2010s has led to a decline in SLR use and production. With twin lens reflex and rangefinder cameras, the viewed image could be significantly different from the final image. When the shutter button is pressed on most SLRs, the mirror flips out of the light path and allows light to pass through to the light receptor and the im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
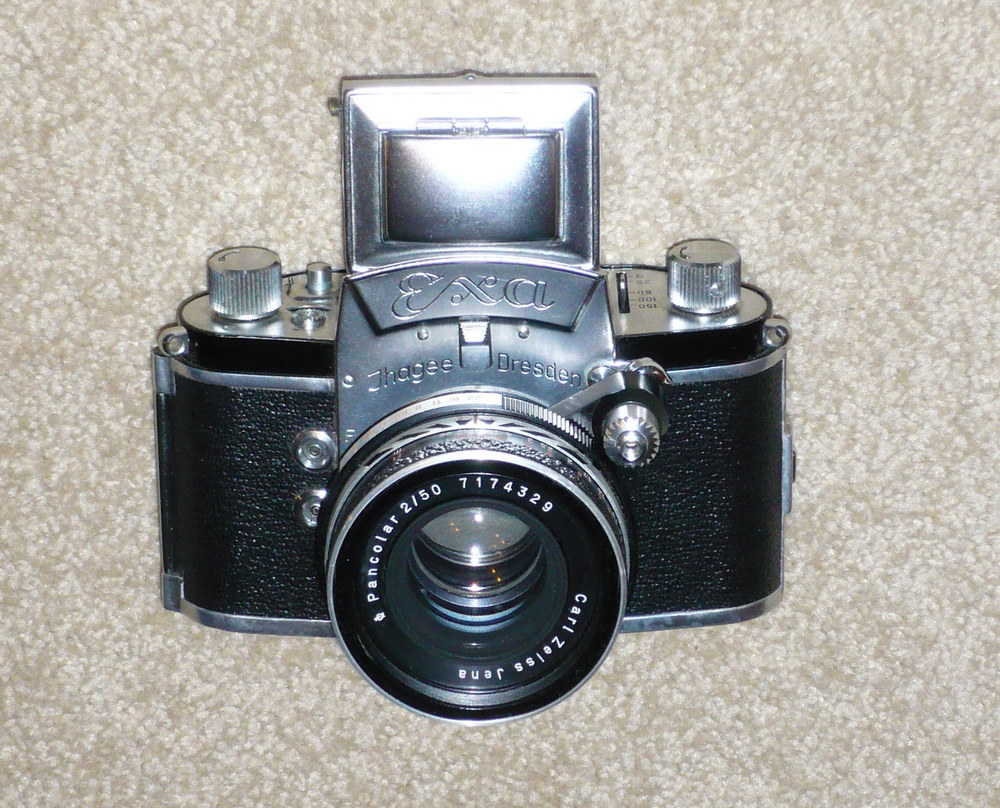
Exa Camera
A metric prefix is a unit prefix that precedes a basic unit of measure to indicate a multiple or submultiple of the unit. All metric prefixes used today are decadic. Each prefix has a unique symbol that is prepended to any unit symbol. The prefix ''kilo'', for example, may be added to ''gram'' to indicate ''multiplication'' by one thousand: one kilogram is equal to one thousand grams. The prefix '' milli'', likewise, may be added to ''metre'' to indicate ''division'' by one thousand; one millimetre is equal to one thousandth of a metre. Decimal multiplicative prefixes have been a feature of all forms of the metric system, with six of these dating back to the system's introduction in the 1790s. Metric prefixes have also been used with some non-metric units. The SI prefixes are metric prefixes that were standardised for use in the International System of Units (SI) by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) in resolutions dating from 1960 to 2022. Since 2009, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sony SLT Camera
Single-lens translucent (SLT) is a Sony proprietary designation for Sony Alpha cameras which employ a pellicle mirror, electronic viewfinder, and Autofocus#Phase detection, phase-detection autofocus system. They employ the same Minolta A-mount as Sony Alpha DSLR cameras. Sony SLT cameras have a semi-transparent fixed mirror which diverts a portion of incoming light to a sensor, while the remaining light strikes a motherboard. The image sensor feeds the electronic viewfinder and also records still images and video on command. The utility of the SLT design is to allow full-time phase-detection autofocus during electronic viewfinder, live view, and video recording operation. With the advent of digital image sensors with integrated phase-detection, the SLT design is no longer required to accomplish this goal, as evidenced by cameras such as the Sony NEX-5R, Fujifilm X-100s, and Nikon 1, although the SLT design avoids having pixels unavailable for image formation due to their space on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
35 mm Format
file:135film.jpg, 135 film. The film is wide. Each image is 24×36 mm in the most common "small film" format (sometimes called "double-frame" for its relationship to the "single-frame" 35 mm movie format or full frame after the introduction of 135 sized digital sensors; confusingly, "full frame" was also used to describe the Full frame (cinematography), full gate of the movie format half the size). file:LEI0060 186 Leica I Sn.5193 1927 Originalzustand Front-2 FS-15.jpg, Leica I, 1927, the first successful camera worldwide for 35 cine film 135 film, more popularly referred to as 35 mm film or 35 mm, is a format of photographic film with a film gauge of loaded into a standardized type of magazine (also referred to as a cassette or cartridge) for use in 135 film cameras. The term 135 was introduced by Kodak in 1934 as a designation for 35 mm film specifically for still photography, perforated with Kodak Standard perforations. It quickly grew in popularity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Sutton (photographer)
Thomas Sutton (c. 1819 – 19 March 1875, in Kensington) was an English photographer, author, and inventor. Life Thomas Sutton went to school in Newington Butts and studied architecture for four years before studying at Caius College, Cambridge graduating in 1846 as the 29th wrangler. He opened a photographic studio in Jersey the following year under the patronage of Prince Albert. In 1855 he set up a photographic company in Jersey with business partner Louis Désiré Blanquart-Evrard that produced prints from calotype negatives. The following year, Sutton and Blanquart-Evrard founded the journal ''Photographic Notes'', which Sutton edited for eleven years. A prolific author, Sutton wrote a number of books on the subject of photography, including the ''Dictionary of Photography'' in 1858. In 1859, Sutton developed the earliest panoramic camera with a wide-angle lens. The lens consisted of a glass sphere filled with water, which projected an image onto a curved plate. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Format
Large format photography refers to any imaging format of or larger. Large format is larger than "medium format", the or size of Hasselblad, Mamiya, Rollei, Kowa, and Pentax cameras (using 120 film, 120- and 220-roll film), and much larger than the frame of 135 film, 35 mm format. The main advantage of a large format, film or digital, is a higher resolution at the same pixel pitch, or the same resolution with larger pixels or grains which allows each pixel to capture more light enabling exceptional low-light capture. A 4×5 inch image (12.903 mm²) has about 15 times the area, and thus 15 times the total resolution, of a 35 mm frame (864 mm²). Large format cameras were some of the earliest photographic devices, and before enlargers were common, it was normal to just make 1:1 contact prints from a 4×5, 5×7, or 8×10-inch negative. Formats The most common large format is , which was the size used by cameras like the Graflex Speed Graphi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamut
In color reproduction and colorimetry, a gamut, or color gamut , is a convex set containing the colors that can be accurately represented, i.e. reproduced by an output device (e.g. printer or display) or measured by an input device (e.g. camera or visual system). Devices with a larger gamut can represent more colors. Similarly, gamut may also refer to the colors within a defined color space, which is not linked to a specific device. A trichromatic gamut is often visualized as a color triangle. A less common usage defines gamut as the subset of colors contained within an image, scene or video. Introduction The term ''gamut'' was adopted from the field of music, where the medieval Latin expression "gamma ut" meant the lowest tone of the G scale and, in time, came to imply the entire range of musical notes of which musical melodies are composed. William Shakespeare, Shakespeare's use of the term in ''The Taming of the Shrew'' is sometimes attributed to the author / musician Thom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
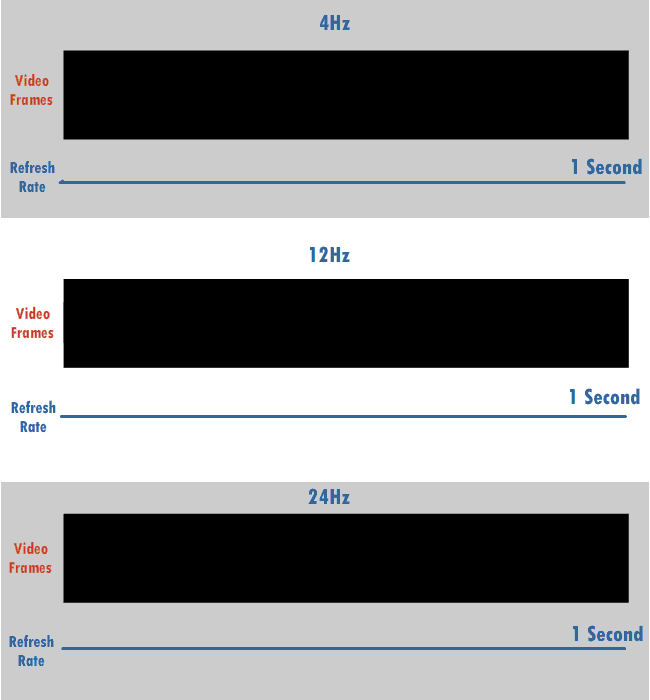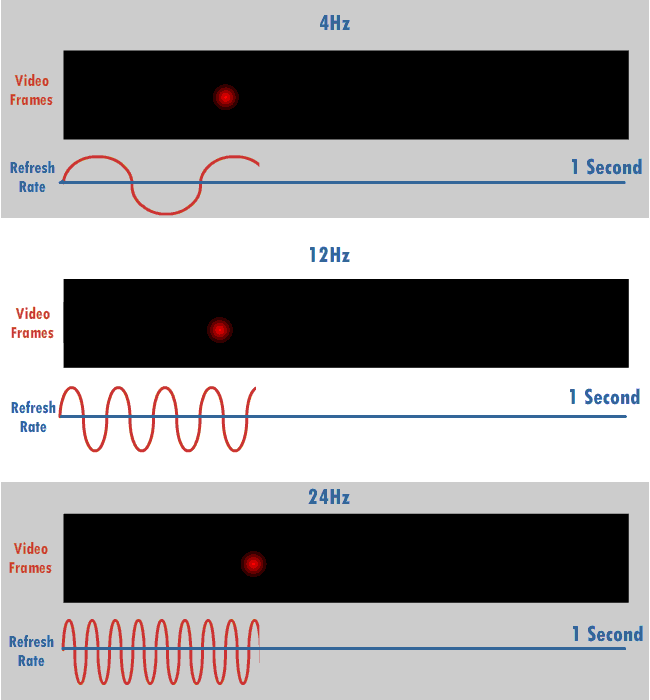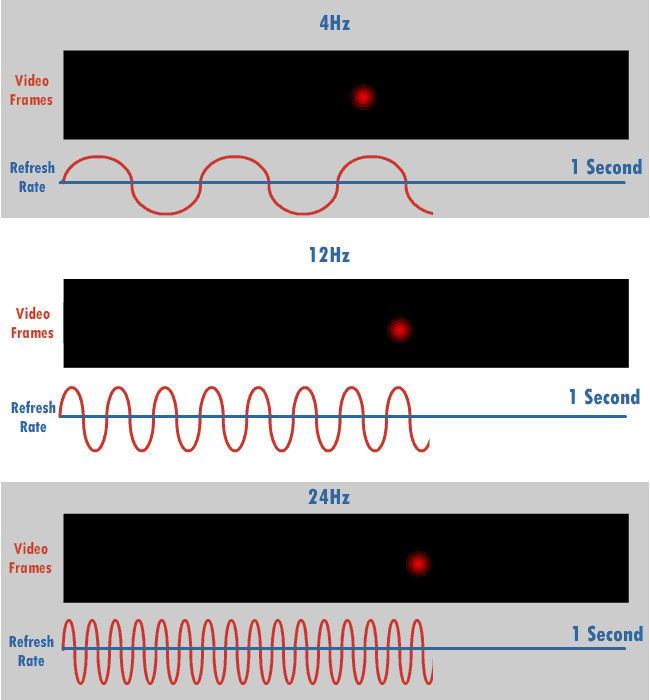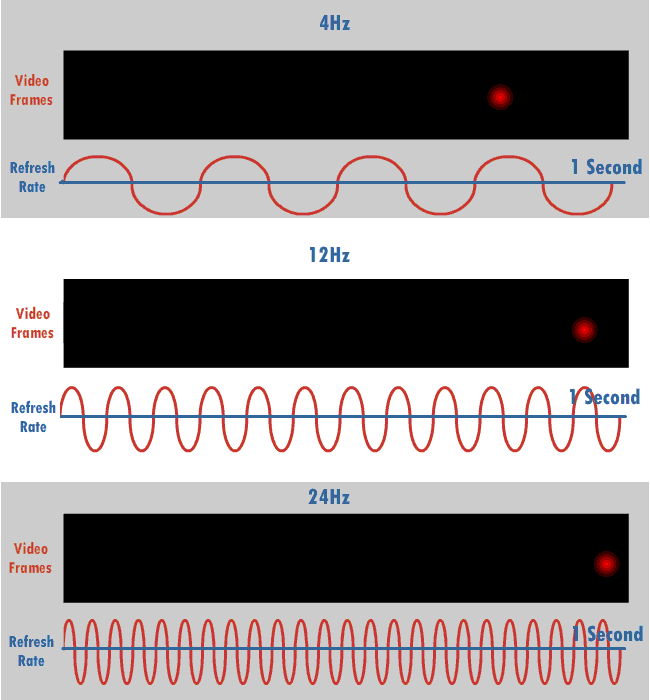
Refresh Rate
The refresh rate, also known as vertical refresh rate, vertical scan rate or vertical frequency in reference to terminology originating with the cathode-ray tubes (CRTs), is the number of times per second that a raster-based display device displays a new image. This is independent from frame rate, which describes how many images are stored or generated every second by the device driving the display. On CRT displays, higher refresh rates produce less flickering, thereby reducing eye strain. In other technologies such as liquid-crystal displays, the refresh rate affects only how often the image can potentially be updated. Non-raster displays may not have a characteristic refresh rate. Vector displays, for instance, do not trace the entire screen, only the actual lines comprising the displayed image, so refresh speed may differ by the size and complexity of the image data. For computer programs or telemetry, the term is sometimes applied to how frequently a datum is updated with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contrast Ratio
The contrast ratio (CR) is a property of a display system, defined as the ratio of the luminance of the brightest shade (white) to that of the darkest shade (black) that the system is capable of producing. A high contrast ratio is a desired aspect of any display. It has similarities with dynamic range. There is no official, standardized way to measure contrast ratio for a system or its parts, nor is there a standard for defining "Contrast Ratio" that is accepted by any standards organization so ratings provided by different manufacturers of display devices are not necessarily comparable to each other due to differences in method of measurement, operation, and unstated variables. Manufacturers have traditionally favored measurement methods that isolate the device from the system, whereas other designers have more often taken the effect of the room into account. An ideal room would absorb all the light reflecting from a projection screen or emitted by a cathode-ray tube, and the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a Raster graphics, raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, pixels are the smallest element that can be manipulated through software. Each pixel is a Sampling (signal processing), sample of an original image; more samples typically provide more accurate representations of the original. The Intensity (physics), intensity of each pixel is variable. In color imaging systems, a color is typically represented by three or four component intensities such as RGB color model, red, green, and blue, or CMYK color model, cyan, magenta, yellow, and black. In some contexts (such as descriptions of camera sensors), ''pixel'' refers to a single scalar element of a multi-component representation (called a ''photosite'' in the camera sensor context, although ''wikt:sensel, sensel'' is sometimes used), while in yet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shutter Lag
In photography, shutter lag is the delay between triggering the shutter and when the photograph is actually recorded, which includes all lag between when the shutter button is pressed and when the photo is taken, including metering and focus lag. it can be mitigated to an extent by pre-focusing and readying for action. Film cameras In film cameras, the delay is caused by the mechanism inside the camera that opens the shutter, exposing the film. Because the process is mechanical, however, and relatively brief, shutter lag in film cameras is often only noticeable (and of any concern) to professionals. SLRs have a slight additional lag due to the time it takes to move the mirror out of the way. Digital cameras Shutter lag is much more of a problem with digital cameras, although higher cost models tend to have less lag. The comet-tail artifact that early CCD sensors suffered from was significantly reduced by the invention of the pinned photodiode (PPD). It was invented by No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System Camera
A system camera or camera body is a camera with interchangeable components that constitutes the core of a system. Early representatives include Leica Camera, Leica I Schraubgewinde (1930), Exakta (1936) and the Nikon F (1959). System cameras are often Single-lens reflex camera, single-lens reflex (SLR) or Twin-lens reflex camera, twin-lens reflex (TLR) but can also be rangefinder cameras or, more recently, mirrorless interchangeable-lens cameras. Voice coil motors (VCMs) are used to control the lens movement to achieve fast and accurate autofocus. The VCM moves the lens elements to focus the light onto the sensor with high precision. Systems are usually named for the lens mount, such Nikon F-mount, Canon EF mount, and M42 lens mount, M42 mount (a non-proprietary mount using a screw thread). Even point-and-shoot cameras usually include a Tripod screw, tripod socket. A system camera includes at the very least a camera body and separate, interchangeable lenses, whence the alterna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focus (optics)
In geometrical optics, a focus, also called an image point, is a point where ray (optics), light rays originating from a point on the object vergence (optics), converge. Although the focus is conceptually a point, physically the focus has a spatial extent, called the circle of confusion, blur circle. This non-ideal focusing may be caused by optical aberration, aberrations of the imaging optics. Even in the absence of aberrations, the smallest possible blur circle is the Airy disc caused by diffraction from the optical system's aperture; diffraction is the ultimate limit to the light focusing ability of any optical system. Aberrations tend to worsen as the aperture diameter increases, while the Airy circle is smallest for large apertures. An image, or image point or region, is in focus if light from object points is converged almost as much as possible in the image, and defocus aberration, out of focus if light is not well converged. The border between these is sometimes define ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |