|
Simeon Of Poland
Simeon of Poland (, ; ; 1584–1639) was a Polish-Armenian traveler known for his travelogue on his visit to the Ottoman domains as well as Italy from 1608 to 1619. Background With the consecutive invasions of the Armenian highlands by the Seljuks and Mongols during the 11th and 13th centuries, respectively, some Armenians fled far away from their homeland to regions such as Galicia and Volhynia in Eastern Europe, which housed a small Armenian community at the time. The fall of the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia in the 14th century, Ottoman conquest of parts of Crimea in the 15th century, and the Celali rebellions in the 16–17th centuries prompted more Armenians to pour out of Anatolia and Crimea, many of whom also settled in modern-day Western Ukraine and Poland, giving rise to around thirty Armenian settlements by the 17th century. Mostly composed of artisans and merchants, Armenians of Eastern Europe were concentrated in the cities of Kamianets-Podilskyi and Lvov. They ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zamość
Zamość (; ; ) is a historical city in southeastern Poland. It is situated in the southern part of Lublin Voivodeship, about from Lublin, from Warsaw. In 2021, the population of Zamość was 62,021. Zamość was founded in 1580 by Jan Zamoyski, Chancellor (Poland), Grand Chancellor of Poland, who envisioned an ideal city. The historical centre of Zamość was added to the UNESCO UNESCO World Heritage Site, World Heritage List in 1992, following a decision of the sixteenth ordinary session of the World Heritage Committee, held between 7 and 14 December 1992 in Santa Fe, New Mexico, United States; it was recognized for being "a unique example of a Renaissance in Poland, Renaissance town in Central Europe". Zamość is about from the Roztocze National Park. History Zamość was founded in 1580 by the Kanclerz, Chancellor and Hetman (head of the army of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth), Jan Zamoyski, on the trade route linking western and northern Europe with the Black Sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Kingdom Of Cilicia
The Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia, also known as Cilician Armenia, Lesser Armenia, Little Armenia or New Armenia, and formerly known as the Armenian Principality of Cilicia, was an Armenian state formed during the High Middle Ages by Armenian refugees fleeing the Seljuk invasion of Armenia., pp. 630–631. Located outside the Armenian Highlands and distinct from the Kingdom of Armenia of antiquity, it was centered in the Cilicia region northwest of the Gulf of Alexandretta. The kingdom had its origins in the principality founded by the Rubenid dynasty, an alleged offshoot of the larger Bagratuni dynasty, which at various times had held the throne of Armenia. Their capital was originally at Tarsus, and later moved to Sis. Cilicia was a strong ally of the European Crusaders, and saw itself as a bastion of Christendom in the East. It also served as a focal point for Armenian cultural production, since Armenia proper was under foreign occupation at the time. Cilicia's si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkic Languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of more than 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and West Asia. The Turkic languages originated in a region of East Asia spanning from Mongolia to Northwest China, where Proto-Turkic language, Proto-Turkic is thought to have been spoken, from where they Turkic migration, expanded to Central Asia and farther west during the first millennium. They are characterized as a dialect continuum. Turkic languages are spoken by some 200 million people. The Turkic language with the greatest number of speakers is Turkish language, Turkish, spoken mainly in Anatolia and the Balkans; its native speakers account for about 38% of all Turkic speakers, followed by Uzbek language, Uzbek. Characteristic features such as vowel harmony, agglutination, subject-object-verb order, and lack of grammatical gender, are almost universal within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kipchak Languages
The Kipchak languages (also known as the Kypchak, Qypchaq, Qypshaq or the Northwestern Turkic languages) are a sub-branch of the Turkic language family spoken by approximately 30 million people in much of Central Asia and Eastern Europe, spanning from Romania to China. Some of the most widely spoken languages in this group are Kazakh, Kyrgyz, and Tatar. Linguistic features The Kipchak languages share a number of features that have led linguists to classify them together. Some of these features are shared with other Common Turkic languages; others are unique to the Kipchak family. Shared features *Change of Proto-Turkic *d to (e.g. *''hadaq'' > ''ajaq'' "foot") *Loss of initial *h, see above example Unique features Family-specific *Extensive labial vowel harmony (e.g. ''olor'' vs. ''olar'' "them") *Frequent fortition (in the form of assibilation) of initial (e.g. ''*etti'' > ''etti'' "seven") *Diphthongs from syllable-final and (e.g. *''taɡ'' > ''taw'' "mountain", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
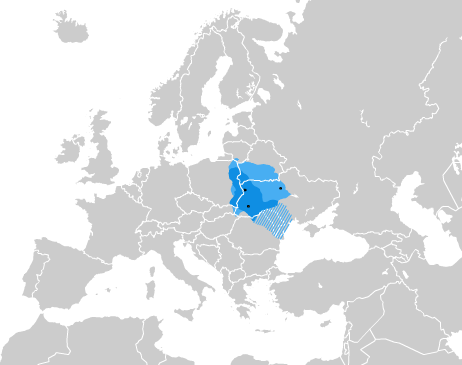
Armeno-Kipchak
Armeno-Kipchak (''Xıpçaχ tili'', ''Tatarça'') was a Turkic language belonging to the Kipchak branch of the family that was spoken in Crimea during the 14–15th centuries. The language has been documented from the literary monuments of 16–17th centuries written in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth (modern day Ukraine) in the Armenian script. Armeno-Kipchak resembles the language of ''Codex Cumanicus'', which was compiled in the 13th century. Speakers of the Armeno-Kipchak are considered to be linguistically assimilated Armenians. Armeno-Kipchak-speakers generally identified as Armenian. See also * Crimean Tatar language * Karaim language * Krymchak language * Urum language * Armenians in Ukraine * Armenians in Poland Armenians in Poland (; ) are one of nine legally recognized national minorities in Poland, their historical presence is going back to the Middle Ages. According to the Polish census of 2021 there are 6,772 ethnic Armenians in Poland. They are s ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Language
Armenian (endonym: , , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language and the sole member of the independent branch of the Armenian language family. It is the native language of the Armenians, Armenian people and the official language of Armenia. Historically spoken in the Armenian highlands, today Armenian is also widely spoken throughout the Armenian diaspora. Armenian is written in its own writing system, the Armenian alphabet, introduced in 405 AD by Saint Mesrop Mashtots. The estimated number of Armenian speakers worldwide is between five and seven million. History Classification and origins Armenian is an independent branch of the Indo-European languages. It is of interest to linguists for its distinctive phonological changes within that family. Armenian exhibits Centum and satem languages, more satemization than centumization, although it is not classified as belonging to either of these subgroups. Some linguists tentatively conclude that Armenian, Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Cathedral Of Lviv
The Armenian Cathedral of the Assumption of Mary (; ; ) in Lviv, Ukraine is located in the city's Old Town, north of the market square. Until 1945 it was the cathedral of the Armenian Catholic Archdiocese of Lviv. Since 2000 it has served as the cathedral of the Armenian Diocese of Ukraine. History 1363–1945 A small Armenian church was built between 1363 and 1370, founded by an Armenian merchant from Caffa. Established as the mother church of an eparchy, it was modelled on the Cathedral of Ani, the ancient Armenian capital. In 1437, the cathedral was surrounded with an arcade gallery; the southern part is preserved, and the northern portion has been rebuilt into a sacristy. In 1527, the cathedral was damaged by fire. A a new stone bell tower was erected in 1571. In 1630 the main nave; it was extended when it was rebuilt in 1723. From the 17th century until 1945, the cathedral belonged to the Armenian Catholic archdiocese of Lviv, when bishop Mikołaj (Nicolas) Torosowic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casimir III The Great
Casimir III the Great (; 30 April 1310 – 5 November 1370) reigned as the King of Poland from 1333 to 1370. He also later became King of Ruthenia in 1340, retaining the title throughout the Galicia–Volhynia Wars. He was the last Polish king from the Piast dynasty. Casimir inherited a kingdom weakened by war and under his rule it became relatively prosperous and wealthy. He reformed the Polish army and doubled the size of the kingdom. He reformed the judicial system and introduced several undying codified statutes, gaining the title "the Polish Justinian I, Justinian". Casimir built extensively and founded the Jagiellonian University (back then simply called the University of Krakow),Saxton, 1851, p. 535 the oldest List of universities in Poland, Polish university and List of oldest universities in continuous operation, one of the oldest in the world. He also confirmed privileges and protections previously granted to Jews and encouraged them to settle in Poland in great numbers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lvov
Lviv ( or ; ; ; see #Names and symbols, below for other names) is the largest city in western Ukraine, as well as the List of cities in Ukraine, fifth-largest city in Ukraine, with a population of It serves as the administrative centre of Lviv Oblast and Lviv Raion, and is one of the main Ukrainian culture, cultural centres of Ukraine. Lviv also hosts the administration of Lviv urban hromada. It was named after Leo I of Galicia, the eldest son of Daniel of Galicia, Daniel, King of Ruthenia. Lviv (then Lwów) emerged as the centre of the historical regions of Red Ruthenia and Galicia (Eastern Europe), Galicia in the 14th century, superseding Halych, Chełm, Belz, and Przemyśl. It was the capital of the Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia from 1272 to 1349, when it went to King Casimir III the Great of Kingdom of Poland, Poland in a Galicia–Volhynia Wars, war of succession. In 1356, Casimir the Great granted it town rights. From 1434, it was the regional capital of the Ruthenian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamianets-Podilskyi
Kamianets-Podilskyi (, ; ) is a city on the Smotrych River in western Ukraine, western Ukraine, to the north-east of Chernivtsi. Formerly the administrative center of Khmelnytskyi Oblast, the city is now the administrative center of Kamianets-Podilskyi Raion within the oblast. It hosts the administration of Kamianets-Podilskyi urban hromada. Population: Kamianets-Podilskyi is a historical center of Podolia region, serving as a capital of the Duchy of Podolia, Podolian Voivodeship, Podolia Eyalet, Podolia Governorate, and Podolian District. During the Ukrainian–Soviet War, the city officially served as the temporary capital of the Ukrainian People's Republic from 1919 to 1920. Name Originally known as Kamianec, its name was changed to the current following the partitions of Poland and occupation by the Russian Empire in 1795. The first part of the city's dual name originates from ' () or ', meaning 'stone' in Old East Slavic, Old Slavic. The second part of its name relate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Ukraine
Western Ukraine or West Ukraine (, ) refers to the western territories of Ukraine. There is no universally accepted definition of the territory's boundaries, but the contemporary Ukrainian administrative regions ( oblasts) of Chernivtsi, Ivano-Frankivsk, Lviv, Ternopil and Zakarpattia (which were part of the former Austro-Hungarian Empire) are typically included. In addition, Volyn and Rivne oblasts (parts of the territory annexed from the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth during its Third Partition) are also usually included. In modern sources, Khmelnytskyi Oblast is often included because of its geographical, linguistic and cultural association with Western Ukraine, although this can not be confirmed from a historical and political point of view. It includes several historical regions such as Carpathian Ruthenia, Halychyna including Pokuttia (the eastern portion of Eastern Galicia), most of Volhynia, northern Bukovina and the Hertsa region, and Podolia. Western Ukraine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimea
Crimea ( ) is a peninsula in Eastern Europe, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukraine. To the east, the Crimean Bridge, constructed in 2018, spans the Strait of Kerch, linking the peninsula with Krasnodar Krai in Russia. The Arabat Spit, located to the northeast, is a narrow strip of land that separates the Syvash lagoons from the Sea of Azov. Across the Black Sea to the west lies Romania and to the south is Turkey. The population is 2.4 million, and the largest city is Sevastopol. The region, internationally recognized as part of Ukraine, has been under Russian occupation of Crimea, Russian occupation since 2014. Called the Tauric Peninsula until the early modern period, Crimea has historically been at the boundary between the Classical antiquity, classical world and the Pontic–Caspian steppe, steppe. Greeks in pre-Rom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |