|
Signor–Lipps Effect
The Signor–Lipps effect is a paleontological principle proposed in 1982 by Philip W. Signor and Jere H. Lipps which states that, since the fossil record of organisms is never complete, neither the first nor the last organism in a given taxon will be recorded as a fossil. The Signor–Lipps effect is often applied specifically to cases of the youngest-known fossils of a taxon failing to represent the last appearance of an organism. The inverse, regarding the oldest-known fossils failing to represent the first appearance of a taxon, is alternatively called the Jaanusson effect after researcher Valdar Jaanusson, or the Sppil–Rongis effect (''Signor–Lipps'' spelled backwards). One famous example is the coelacanth, which was thought to have become extinct in the very late Cretaceous—until a live specimen was caught in 1938. The animals known as " Burgess Shale-type fauna" are best known from rocks of the Early and Middle Cambrian periods. Since 2006, though, a few fossils ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian period at million years ago (Megaannum, Ma), to the beginning of the succeeding Carboniferous period at Ma. It is the fourth period of both the Paleozoic and the Phanerozoic. It is named after Devon, South West England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant evolutionary radiation of history of life#Colonization of land, life on land occurred during the Devonian, as free-spore, sporing land plants (pteridophytes) began to spread across dry land, forming extensive coal forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of vascular plants had evolved leaf, leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants (Pteridospermatophyta, pteridospermatophyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Extinction
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and recover. As a species' potential Range (biology), range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxon, Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the Fossil, fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. Over five billion species are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryotes globally, possibly many times more if microorganisms are included. Notable extinct animal species include Dinosaur, non-avian dinosaurs, Machairodontinae, saber-toothed cats, and mammoths. Through evolution, species arise through the process of specia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Sampling Bias
In statistics, sampling bias is a bias (statistics), bias in which a sample is collected in such a way that some members of the intended statistical population, population have a lower or higher sampling probability than others. It results in a biased sample of a population (or non-human factors) in which all individuals, or instances, were not equally likely to have been selected. If this is not accounted for, results can be erroneously attributed to the phenomenon under study rather than to the method of sampling (statistics), sampling. Medical sources sometimes refer to sampling bias as ascertainment bias. Ascertainment bias has basically the same definition, but is still sometimes classified as a separate type of bias. Distinction from selection bias Sampling bias is usually classified as a subtype of selection bias, sometimes specifically termed sample selection bias, but some classify it as a separate type of bias. A distinction, albeit not universally accepted, of samplin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
German Tank Problem
German(s) may refer to: * Germany, the country of the Germans and German things **Germania (Roman era) * Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language ** For citizenship in Germany, see also German nationality law **Germanic peoples (Roman era) * German diaspora * German language * German cuisine, traditional foods of Germany People * German (given name) * German (surname) * Germán, a Spanish name Places * German (parish), Isle of Man * German, Albania, or Gërmej * German, Bulgaria * German, Iran * German, North Macedonia * German, New York, U.S. * Agios Germanos, Greece Other uses * German (mythology), a South Slavic mythological being * Germans (band), a Canadian rock band * "German" (song), a 2019 song by No Money Enterprise * ''The German'', a 2008 short film * "The Germans", an episode of ''Fawlty Towers'' * ''The German'', a nickname for Congolese rebel André Kisase Ngandu See also * Germanic (di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Lazarus Taxon
In paleontology, a Lazarus taxon (plural ''taxa'') is a taxon that disappears for one or more periods from the fossil record, only to appear again either in later fossil records, or as actual living organisms, and often in isolated, obscure, or otherwise very specialized habitats. Likewise in conservation biology and ecology, it can refer to species or populations that were mistakenly thought to be extinct, and are rediscovered to be still living. The term Lazarus taxon was coined by Karl W. Flessa and David Jablonski in 1983 and was then expanded by Jablonski in 1986. Paul Wignall and Michael Benton defined Lazarus taxa as, "At times of biotic crisis many taxa go extinct, but others only temporarily disappeared from the fossil record, often for intervals measured in millions of years, before reappearing unchanged". Earlier work also supports the concept though without using the name Lazarus taxon, like work by Christopher R. C. Paul. The term refers to the story in the Christ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Genera
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. '' Panthera leo'' (lion) and '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus '' Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should clearly demonstrate both monophyly and validity as a separate lineag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Chicxulub Crater
The Chicxulub crater is an impact crater buried underneath the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico. Its center is offshore, but the crater is named after the onshore community of Chicxulub Pueblo (not the larger coastal town of Chicxulub Puerto). It was formed slightly over 66 million years ago when an asteroid, about in diameter, struck Earth. The crater is estimated to be in diameter and in depth. It is believed to be the second largest impact structure on Earth, and the only one whose peak ring is intact and directly accessible for scientific research. The crater was discovered by Antonio Camargo and Glen Penfield, geophysicists who had been looking for petroleum in the Yucatán Peninsula during the late 1970s. Penfield was initially unable to obtain evidence that the geological feature was a crater and gave up his search. Later, through contact with Alan R. Hildebrand in 1990, Penfield obtained samples that suggested it was an impact feature. Evidence for the crater's imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutionary history, evolution of dinosaurs is a subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrates after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event 201.3 mya and their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The fossil record shows that birds are feathered dinosaurs, Evolution of birds, having evolved from earlier Theropoda, theropods during the Late Jurassic epoch, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—birds—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds. Dinosaurs are varied from taxonomy (biology), taxonomic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Cretaceous–Paleogene Extinction Event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event, also known as the K–T extinction, was the extinction event, mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth approximately 66 million years ago. The event caused the extinction of all non-avian dinosaurs. Most other tetrapods weighing more than also became extinct, with the exception of some ectothermic species such as sea turtles and crocodilians. It marked the end of the Cretaceous period, and with it the Mesozoic era, while heralding the beginning of the current era, the Cenozoic. In the geologic record, the K–Pg event is marked by a thin layer of sediment called the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary, K–Pg boundary or K–T boundary, which can be found throughout the world in marine and terrestrial rocks. The boundary clay shows unusually high levels of the metal iridium, which is more common in asteroids than in the Earth's crust. As originally proposed in 1980 by a team of scientists le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Mass Extinction
An extinction event (also known as a mass extinction or biotic crisis) is a widespread and rapid decrease in the biodiversity on Earth. Such an event is identified by a sharp fall in the diversity and abundance of multicellular organisms. It occurs when the rate of extinction increases with respect to the background extinction rate and the rate of speciation. Estimates of the number of major mass extinctions in the last 540 million years range from as few as five to more than twenty. These differences stem from disagreement as to what constitutes a "major" extinction event, and the data chosen to measure past diversity. The "Big Five" mass extinctions In a landmark paper published in 1982, Jack Sepkoski and David M. Raup identified five particular geological intervals with excessive diversity loss. They were originally identified as outliers on a general trend of decreasing extinction rates during the Phanerozoic, but as more stringent statistical tests have been applie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
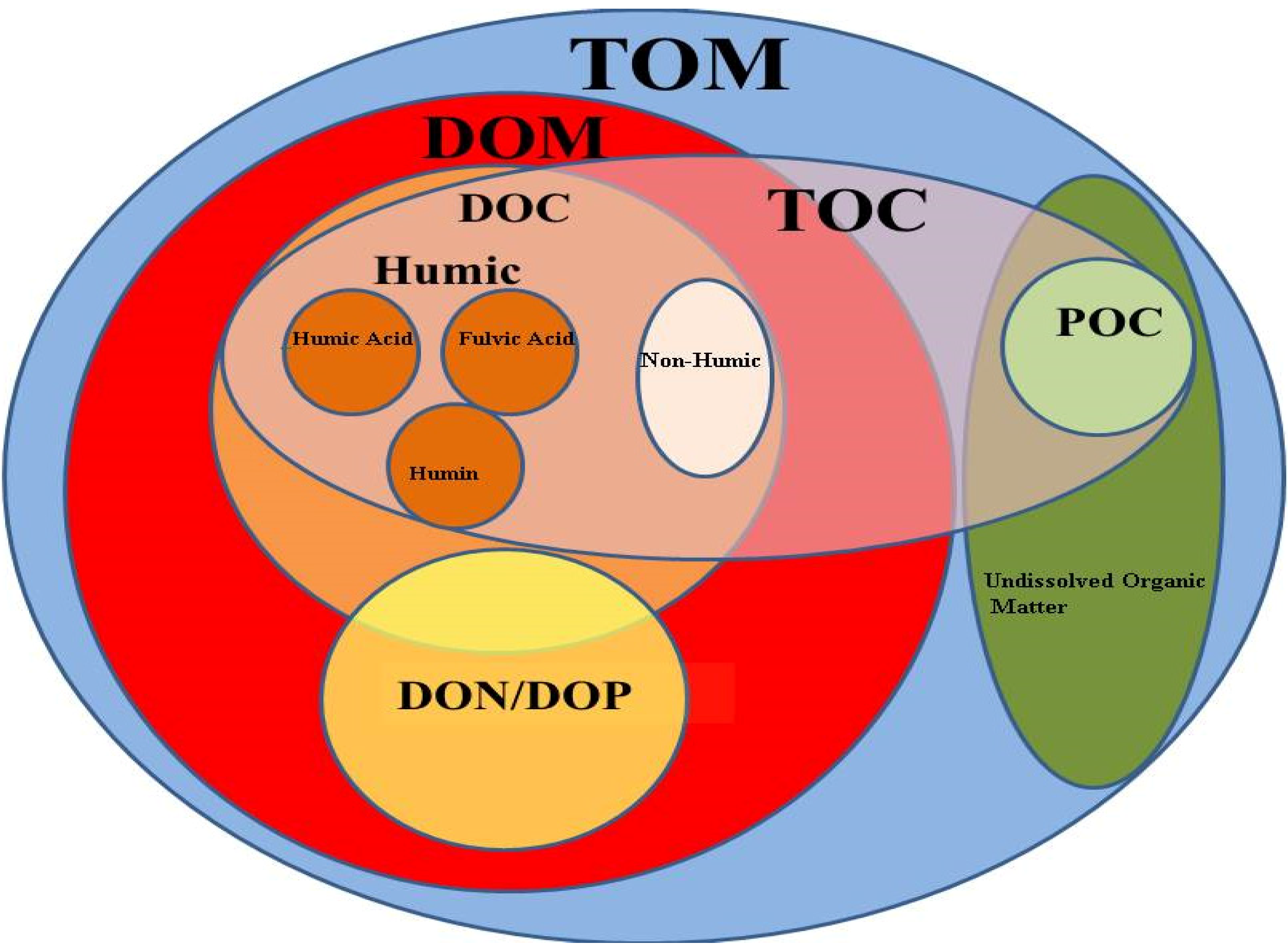 |
Ocean Chemistry
Marine chemistry, also known as ocean chemistry or chemical oceanography, is the study of the chemical composition and processes of the world’s oceans, including the interactions between seawater, the atmosphere, the seafloor, and marine organisms. This field encompasses a wide range of topics, such as the cycling of elements like carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus, the behavior of trace metals, and the study of gases and nutrients in marine environments. Marine chemistry plays a crucial role in understanding global biogeochemical cycles, ocean circulation, and the effects of human activities, such as pollution and climate change, on oceanic systems. It is influenced by plate tectonics and seafloor spreading, turbidity, currents, sediments, pH levels, atmospheric constituents, metamorphic activity, and ecology. The impact of human activity on the chemistry of the Earth's oceans has increased over time, with pollution from industry and various land-use practices significantly aff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |