|
Sierras Pampeanas
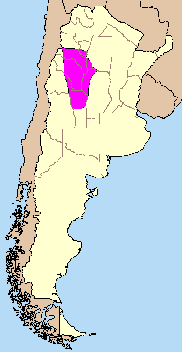
The Sierras Pampeanas (also called Central Sierras or Pampas Sierras) (English: Pampas Mountains) is a geographical region of Argentina. The Sierras Pampeanas are a chain of mountains that rise sharply from the surrounding pampa region of Northwest Argentina. They run parallel to the Andes Mountains and their crest line is some east of the Andes crest line (running from 29° to 35° S latitude at about 65° W longitude). They cross into seven Argentina provinces: Province of San Luis, San Luis, Province of San Juan (Argentina), San Juan, Córdoba Province (Argentina), Córdoba, La Rioja Province (Argentina), La Rioja, Catamarca Province, Catamarca, Santiago del Estero Province, Santiago del Estero and province of Tucumán, Tucumán. Geography The highest point of the Sierras Pampeanas is Cerro General Belgrano (6250 m above sea level) in La Rioja, in the Sierra de Famatina. Between the mountain ranges are several salt-filled depressions. The Salinas Grandes depression is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sierras Pampeanas1
Sierra is a Spanish language, Spanish word meaning mountain chain and saw, from Latin ''Serra (other), serra''. The corresponding word in Portuguese language, Portuguese, Catalan language, Catalan and Latin is ''serra''. This name is used for various mountain ranges in Spanish-speaking and other countries (with the word ''serra'' used in Portuguese-speaking countries). Sierra or Sierras may refer to: Argentina * Sierra de Córdoba, in the central region of the country * Antofagasta de la Sierra, a volcanic field * Sierra Nevada de Lagunas Bravas, on the border of Argentina and Chile * Sierra de la Ventana (mountains), Buenos Aires province Brazil * Serra do Mar, in the country's southeast Chile * Sierra Nevada (stratovolcano), La Araucanía Region * Sierra Nevada de Lagunas Bravas, on the border of Argentina and Chile Colombia * Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta * Sierra Nevada del Cocuy Ecuador * Sierra Negra (Galápagos), Galápagos Province, Ecuador Mexico * Sierra de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cave
Caves or caverns are natural voids under the Earth's Planetary surface, surface. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. Exogene caves are smaller openings that extend a relatively short distance underground (such as rock shelters). Caves which extend further underground than the opening is wide are called endogene caves. Speleology is the science of exploration and study of all aspects of caves and the cave environment. Visiting or exploring caves for recreation may be called Caving, ''caving'', ''potholing'', or ''spelunking''. Formation types The formation and development of caves is known as ''speleogenesis''; it can occur over the course of millions of years. Caves can range widely in size, and are formed by various geological processes. These may involve a combination of chemical processes, erosion by water, tectonic forces, microorganisms, pressure, and atmospheric influences. Isotopic dating techniques can be applied to cave sedime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologic Province
A geologic province or geological province is a spatial entity with common geologic attributes. A province may include a single dominant structural element such as a basin or a fold belt, or a number of contiguous related elements. Adjoining provinces may be similar in structure but be considered separate due to differing histories. Geologic provinces by origin Geologic provinces by resources Some studies classify provinces based upon mineral resources, such as mineral deposits. There are a particularly large number of provinces identified worldwide for petroleum and other mineral fuels, such as the Niger Delta petroleum province. See also * Physiographic province * Geomorphology * United States Geological Survey The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The agency was founded on Mar ... R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhyolitic
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals ( phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained groundmass. The mineral assemblage is predominantly quartz, sanidine, and plagioclase. It is the extrusive equivalent of granite. Its high silica content makes rhyolitic magma extremely viscous. This favors explosive eruptions over effusive eruptions, so this type of magma is more often erupted as pyroclastic rock than as lava flows. Rhyolitic ash-flow tuffs are among the most voluminous of continental igneous rock formations. Rhyolitic tuff has been used extensively for construction. Obsidian, which is rhyolitic volcanic glass, has been used for tools from prehistoric times to the present day because it can be shaped to an extremely sharp edge. Rhyolitic pumice finds use as an abrasive, in concrete, and as a soil amendment. Description Rhyo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gondwanide Orogeny
The Gondwanide orogeny was an orogeny active in the Permian that affected parts of Gondwana that are by current geography now located in southern South America, South Africa, Antarctica, Australia and New Guinea. The zone of deformation in Argentina extends as a belt south and west of the cratonic nucleus of Río de la Plata– Pampia. The deformation of the orogeny is visible in the Sierra de la Ventana mountains in Argentina and the Cape Fold Belt in South Africa. The Gondwanide orogeny might have been linked with the roughly contemporary San Rafael orogeny of western Argentina. The Gondwanide orogeny is the successor to the Neoproterozoic-Paleozoic Terra Australis orogeny in Gondwana. The Gondwanide orogeny was widespread across the southern hemisphere during the Late Permian-Early Triassic. Alexander du Toit described Gondwanide deformation as consisting of asymmetric folding, thrusting and cleavage formation. The uplift and erosion which followed is evidenced by an unco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precordillera Terrane
The Precordillera Terrane or Cuyania was an ancient microcontinent or terrane whose history affected many of the older rocks of Cuyo in Argentina. It was separated by oceanic crust from the Chilenia terrane which accreted into it at ~420-390 Ma when Cuyania was already amalgamated with Gondwana. The hypothesized Mejillonia Terrane in the coast of northern Chile is considered by some geologists to be a single block with Cuyania. The San Rafael Block crops out 200 km to the south of the other exposures of Cuyania and is the southern extension of the terrane. The Precordillera has been hypothesised to have been derived from Laurentia, the core of North America, which was attached to the western margin of South America during the Precambrian when virtually all continents formed a "proto-Gondwana" supercontinent known as Pannotia Pannotia (from Greek: ''wikt:pan-, pan-'', "all", ''wikt:νότος, -nótos'', "south"; meaning "all southern land"), also known as the Vendian superco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Famatinian Orogeny
The Famatinian orogeny () is an orogeny that predates the rise of the Andes and that took place in what is now western South America during the Paleozoic, leading to the formation of the Famatinian orogen also known as the Famatinian belt. The Famatinian orogeny lasted from the Late Cambrian to at least the Late Devonian and possibly the Early Carboniferous, with orogenic activity peaking about 490 to 460 million years ago. The orogeny involved metamorphism and deformation in the crust and the eruption and intrusion of magma along a Famatinian magmatic arc that formed a chain of volcanoes. The igneous rocks of the Famatinian magmatic arc are of calc-alkaline character and include gabbros, tonalites, granodiorites and trondhjemites. The youngest igneous rocks of the arc are granites. Part of the pegmatite dykes of the Pampean Pegmatite Province formed during the orogeny. These dykes are thought to be derived from S-type granitic melts. The relationship of the orogeny with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pan-African Orogeny
The Pan-African orogeny was a series of major Neoproterozoic orogenic events which related to the formation of the supercontinents Gondwana and Pannotia about 600 million years ago. This orogeny is also known as the Pan-Gondwanan or Saldanian Orogeny. The Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny are the largest known systems of orogenies on Earth. The sum of the continental crust formed in the Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny makes the Neoproterozoic the period of Earth's history that has produced most continental crust. History and terminology The term ''Pan-African'' was coined by for a tectono-thermal event at about 500 Ma when a series of mobile belts in Africa formed between much older African cratons. At the time, other terms were used for similar orogenic events on other continents, i.e. '' Brasiliano'' in South America; ''Adelaidean'' in Australia; and ''Beardmore'' in Antarctica. Later, when plate tectonics became generally accepted, the term ''Pan-A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brasiliano Orogeny
Brasiliano orogeny or Brasiliano cycle ( and ''Ciclo Brasiliano'') refers to a series of orogenies from the Neoproterozoic era, exposed chiefly in Brazil but also in other parts of South America. The Brasiliano orogeny is a regional name for the larger Pan-African/Brasiliano orogeny that extended not only in South America but across most of Gondwana Gondwana ( ; ) was a large landmass, sometimes referred to as a supercontinent. The remnants of Gondwana make up around two-thirds of today's continental area, including South America, Africa, Antarctica, Australia (continent), Australia, Zea .... In a wide sense the Brasiliano orogeny includes also the Pampean orogeny. Almeida ''et al''. coined the term Brasiliano Orogenic Cycle in 1973. The orogeny led to the closure of several oceans and aulacogens including the Adamastor Ocean, the Goianides Ocean, the Puncoviscana Ocean and the Peri-Franciscano Ocean. Attempts to correlate the South American Brasiliano belts with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pampean Orogeny
The Pampean orogeny () was an orogeny active in the Cambrian in the western margin of the ancient landmass of Gondwana. The orogen's remains can now be observed in central Argentina, in particular at the Sierras de Córdoba and other parts of the eastern Sierras Pampeanas. It is uncertain if the orogeny involved at some point a continental collision. The Pampean orogen can be considered both part of the larger Terra Australis orogen and of the Brasiliano orogeny. The Pampean orogeny was succeeded by the Famatinian orogeny further west. Magmatic belts The Pampean orogen contains a magmatic belt including granodiorites, monzogranites, and volcanic rocks, all of them of calc-alkaline chemistry. The igneous rocks of this belt formed at various times in over the period from 555 to 525 million years ago. From 525 million years ago onward another magmatic belt of peralumineous and mafic rocks developed further amidst gneiss, schist, amphibolites and carbonate rocks. The igneous rocks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gondwana
Gondwana ( ; ) was a large landmass, sometimes referred to as a supercontinent. The remnants of Gondwana make up around two-thirds of today's continental area, including South America, Africa, Antarctica, Australia (continent), Australia, Zealandia, Arabian Peninsula, Arabia, and the Indian subcontinent. Gondwana was formed by the Accretion (geology), accretion of several cratons (large stable blocks of the Earth's crust), beginning with the East African Orogeny, the collision of India and Geography of Madagascar, Madagascar with East Africa, and culminating in with the overlapping Brasiliano orogeny, Brasiliano and Kuunga orogeny, Kuunga orogenies, the collision of South America with Africa, and the addition of Australia and Antarctica, respectively. Eventually, Gondwana became the largest piece of continental crust of the Paleozoic Era, covering an area of some , about one-fifth of the Earth's surface. It fused with Laurasia during the Carboniferous to form Pan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sierras De Córdoba
The Sierras de Córdoba is a mountain range in central Argentina, located between the Pampas to the east and south and the Gran Chaco, Chaco to the north and east. Most of the range is located in Córdoba Province, Argentina, Córdoba Province, except for the southwestern margin which is in San Luis Province. The Sierras de Córdoba are part of the Sierras Pampeanas, a group of mountain ranges which extend north and south on the eastern side of the Andes. The Sierras de Córdoba are covered in dry forests, grasslands, woodlands, and shrublands, and are home to rare and endemic species of plants and animals. Parts of the Sierras have long been used for extensive cattle grazing, which has transformed the mountains' ecology. Other economic activities include tourism and viticulture, winegrowing. Geography The Sierras de Cordoba extend about 430 km from south to north, from 29º S to 33º 30’ S. They consist of four sub-ranges, the Sierras del Norte, Sierras Chicas, Sierra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |