|
Siege Of Jerusalem (637)
Siege of Jerusalem, fall of Jerusalem, or sack of Jerusalem may refer to: Battles * Siege of Jebus (1010 BC), a siege by David, king of the United Kingdom of Israel, from biblical narrative * Sack of Jerusalem (925 BC), by Pharaoh Shishak, from biblical narrative * Siege of Jerusalem, during the Syro-Ephraimite War (736–732 BCE) * Assyrian siege of Jerusalem (701 BCE) by Sennacherib, king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire * Siege of Jerusalem (597 BC) by Nebuchadnezzar II of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, during Judah's first revolt against Babylon * Siege of Jerusalem (587 BC) and destruction of the city and the First Temple by Nebuchadnezzar II, during Judah's second revolt against Babylon * Siege of Jerusalem (168 BC) by Seleucid king Antiochus IV Epiphanes after revolt by Jason (High Priest), Jason * Siege of Jerusalem (162 BC) by Seleucid general Lysias (Syrian chancellor), Lysias * Siege of Jerusalem (134 BC) by Seleucid king Antiochus VII Sidetes during the reign of John Hyrcanus#Sie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Jebus
The siege of Jebus is described in passages of the Hebrew Bible as having occurred when the Israelites, led by King David, besieged and conquered the Canaanite city of Jerusalem, then known as ''Jebus'' (, , ). The Israelites gained access to the city by conducting a surprise assault, and Jebus (or Jerusalem) was subsequently installed as the capital city of the Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), United Kingdom of Israel under its initial name as the City of David (historic), City of David. The identification of Jebus with Jerusalem has been challenged. Danes, Danish biblical scholar Niels Peter Lemche notes that every non-biblical mention of Jerusalem found in the ancient Near East refers to the city with the name of Jerusalem, offering as an example the Amarna letters, which are dated to the 14th century BCE and refer to Jerusalem as . He states that "There is no evidence of Jebus and the Jebusites outside of the Old Testament. Some scholars reckon Jebus to be a different plac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sasanian Conquest Of Jerusalem
The Sasanian conquest of Jerusalem in early 614 was a significant event in the Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628. After the conquest of Jerusalem and the defeat of the Byzantines, Khosrow II ordered to transfer the true cross to Tisophon. Amidst the conflict, Sasanian king Khosrow II had appointed Shahrbaraz, his '' spahbod'' (army chief), to lead an offensive into the Diocese of the East of the Byzantine Empire. Under Shahrbaraz, the Sasanian army had secured victories at Antioch as well as at Caesarea Maritima, the administrative capital of Palaestina Prima. By this time, the grand inner harbour had silted up and was useless, but the city continued to be an important maritime hub after Byzantine emperor Anastasius I Dicorus ordered the reconstruction of the outer harbour. Successfully capturing the city and the harbour had given the Sasanian Empire strategic access to the Mediterranean Sea. The Sasanians' advance was accompanied by the outbreak of a Jewish revolt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerusalem Attack (other)
Jerusalem Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ... attack may refer to: * 1947 Jerusalem riots * 1969 PFLP bombings in Jerusalem *1989 Tel Aviv–Jerusalem bus 405 suicide attack * 2008 Jerusalem bulldozer attack * 2008 Jerusalem BMW attack * 2011 Jerusalem bus stop bombing * 2014 Jerusalem synagogue attack * 2014 Jerusalem unrest *August 2014 Jerusalem tractor attack * October 2014 Jerusalem vehicular attack * November 2014 Jerusalem vehicular attack * 2015 Jerusalem bus attack * 2016 Jerusalem bus bombing * 2016 Jerusalem shooting attack * 2017 Jerusalem Light Rail stabbing * 2017 Jerusalem truck attack * June 2017 Jerusalem attack * 2017 Temple Mount shooting * 2021 Jerusalem shooting * 2022 Jerusalem bombings * 2023 East Jerusalem synagogue shooting * 2023 Givat Shaul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Siege Of Jerusalem
''The Siege of Jerusalem, 70 A.D.'' is a board wargame published by Historical Perspectives in 1976 that simulates the Roman attack on Jerusalem by Cestius Gallus. The game was subsequently bought by Avalon Hill, revised and republished in 1989. Description ''The Siege of Jerusalem'' is a two-player game in which one player controls the besieging Roman army, and the other player controls the Jewish defenders. Components The 1st edition ziplock bag holds: * a four-piece 29" x 45" cardboard hex grid map of the walled city * 800 die-cut counters representing infantry, archers, cavalry, ladders, siege engines and towers, ramps, wall damage, and wall breaches *Rulebook * Game Rulebook *Five scenario books: Rebellion, Assault on the Temple, Assault of Gallus, Night Attack, and Full Siege, which is a combination of the previous four *Loss & Replacement Record *Time Record *Terrain Effects Chart *Conference Map *Errata Sheet *Two sets of charts Gameplay The Roman player's main obje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Jerusalem (poem)
''Siege of Jerusalem'' is the title commonly given to an anonymous Middle English epic poem created in the second half of the 14th century (possibly ca. 1370–1390). The poem is composed in the alliterative manner popular in medieval English poetry, especially during the period known as the "alliterative revival", and is known from nine surviving manuscripts, an uncommonly high number for works of this time. The siege described in the poem is that of 70 AD. The poem relies on a number of secondary sources—including ''Vindicta salvatoris'', Roger Argenteuil's ''Bible en François'', Ranulf Higdon's '' Polychronicon'', and the ''Destruction of Troy''—and on Josephus’ '' The Jewish War'', which was itself a source for the ''Polychronicon''. The destruction of Jerusalem is ahistorically portrayed as divinely ordained vengeance by the Romans Vespasian and Titus for the death of Jesus Christ. The poem also describes the tumultuous succession of emperors in Rome in the late 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
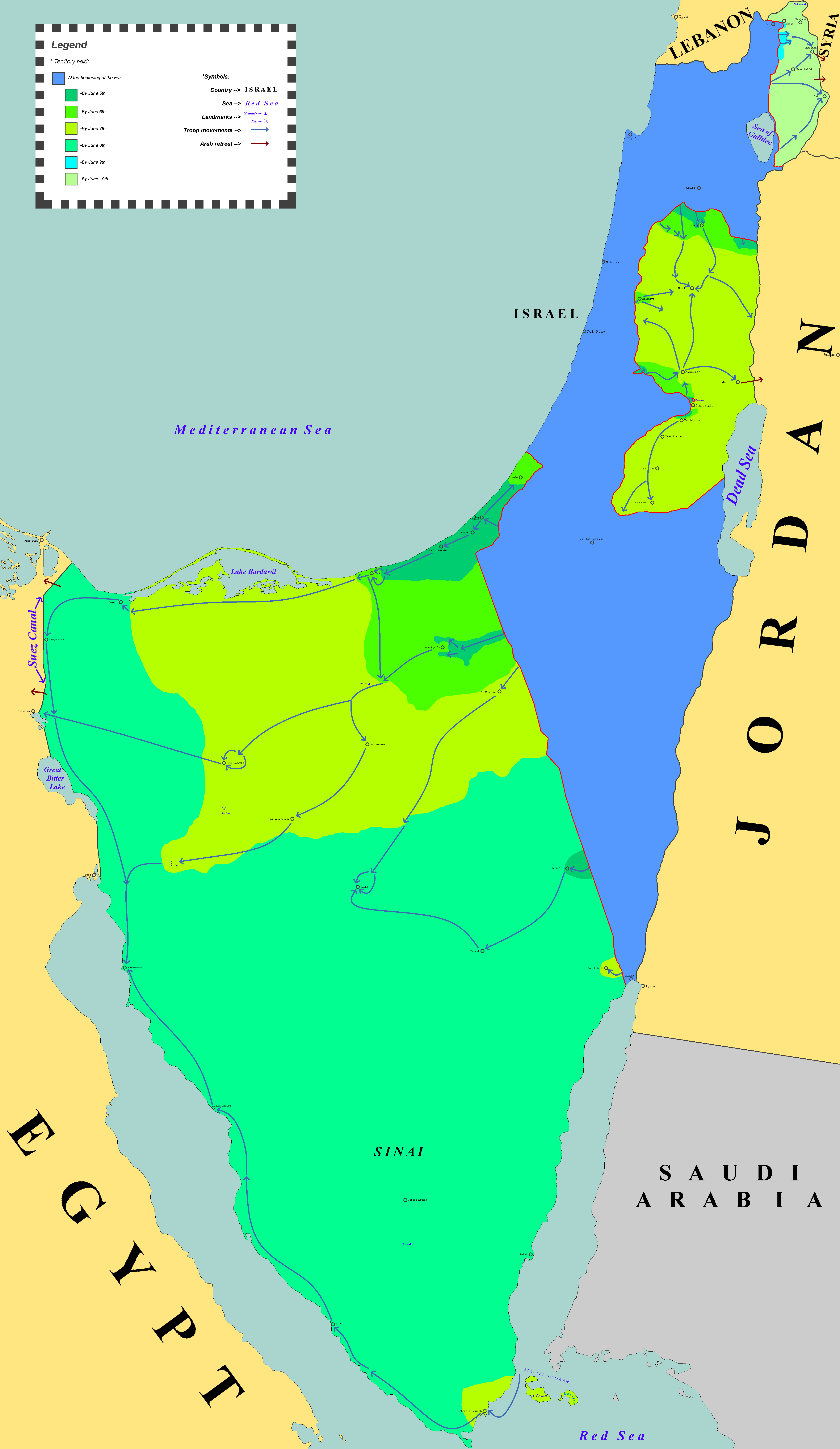
Six-Day War
The Six-Day War, also known as the June War, 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states, primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan from 5 to 10June 1967. Military hostilities broke out amid poor relations between Israel and its Arab neighbors, which had been observing the 1949 Armistice Agreements signed at the end of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, First Arab–Israeli War. In 1956, regional tensions over the Straits of Tiran (giving access to Eilat, a port on the southeast tip of Israel) escalated in what became known as the Suez Crisis, when Israel invaded Egypt over the Israeli passage through the Suez Canal and Straits of Tiran, Egyptian closure of maritime passageways to Israeli shipping, ultimately resulting in the re-opening of the Straits of Tiran to Israel as well as the deployment of the United Nations Emergency Force (UNEF) along the Borders of Israel#Border with Egypt, Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle For Jerusalem
The Battle for Jerusalem took place during the 1947–1948 civil war in Mandatory Palestine, 1947–1948 civil war phase of the 1947–1949 Palestine war. It saw Jewish and Arab militias in Mandatory Palestine, and later the militaries of Israel and Jordan, Transjordan, fight for control over the city of Jerusalem. Under the 1947 United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine, Jerusalem was to be a Corpus separatum (Jerusalem), ''corpus separatum'' () administered by an international body. Fighting nevertheless immediately broke out in the city between Jewish and Arab militias, with bombings and other attacks being carried out by both sides. Beginning in February 1948, Arab militias under Abd al-Qadir al-Husayni blockaded Jerusalem corridor, the corridor from Tel Aviv to Jerusalem, preventing essential supplies from reaching the Jewish population. This blockade was broken in mid-April of that year by Jewish militias who carried out Operation Nachshon and Battles of Latrun (1948), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Jerusalem
The Battle of Jerusalem also known as the Fall of Jerusalem occurred during the British Empire's "Jerusalem Operations" against the Ottoman Empire, in World War I, when fighting for the city developed from 17 November, continuing after the surrender until 30 December 1917, to secure the final objective of the Southern Palestine Offensive during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of World War I. Before Jerusalem could be secured, two battles were recognised by the British as being fought in the Judean Hills to the north and east of the Hebron–Junction Station line. These were the Battle of Nebi Samwill from 17 to 24 November and the Defence of Jerusalem from 26 to 30 December 1917. They also recognised within these Jerusalem Operations, the successful second attempt on 21 and 22 December 1917 to advance across the Nahr el Auja, as the Battle of Jaffa, although Jaffa had been occupied as a consequence of the Battle of Mughar Ridge on 16 November.Battles Nomenclature Committe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Jerusalem (1834)
The siege of Jerusalem of 1834 took place during the Peasants' revolt in Palestine, which erupted following the entry of Egyptian general Ibrahim Pasha into Ottoman Syria and his subsequent military conscription demand upon the Arab villagers of the region. The siege was engaged by local Arab peasant rebels upon an Egyptian garrison of about 2,000 soldiers, beginning from May 21 until the arrival of Ibrahim Pasha's main force on June 7. The crushing defeat of rebel reinforcements took place on June 9, led by Ibrahim Pasha. Background During the spring of 1834 discontent in Hebron and Nablus had begun to mount over Ibrahim Pasha's plans to conscript local men into his army. On 18 May, fighting broke out in Hebron and on 21 May a large rebel force dispatched on Jerusalem. The siege Arrival of rebel forces Nearly 6-7,000 rebels marched on Jerusalem from Hebron, aiming to capture it from the Egyptians. At the time, the city had a garrison of some 2,000 men, while Ibrahim P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Jerusalem (1244)
The siege of Jerusalem of 1244 took place after the Sixth Crusade, when a Khwarazmian army conquered the city on July 15, 1244. Prelude Emperor Frederick II of the Holy Roman Empire led the Sixth Crusade from 1228 to 1229 and claimed the title of King of Jerusalem as the husband of Isabella II of Jerusalem, queen since 1212. The army brought by the emperor and his reputation in the Muslim world were enough to recover Jerusalem, Bethlehem, Nazareth and several strongholds without fighting, as signed by a treaty with the Ayyubid Sultan al-Kamil. However, Jerusalem did not remain in the hands of Christians for long, as, despite further territorial gains a few years earlier in the Barons' Crusade, the latter did not control the surroundings of the city sufficiently to be able to ensure an effective defense. The Khwarazmian army consisted of 10,000 cavalry, comprising both some of the remnants of the predominantly Kipchak army of the last Khwarazmshah, Jalal al-Din Mangbu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Jerusalem (1187)
The siege of Jerusalem lasted from 20 September to 2 October 1187, when Balian of Ibelin surrendered the city to Saladin. Earlier that summer, Saladin had defeated the kingdom's army and conquered several cities. Balian was charged with organizing a defense. The city was full of refugees but had few soldiers. Despite this fact the defenders managed to repulse several attempts by Saladin's army to take the city by storm. Balian bargained with Saladin to buy safe passage for many, and the city was peacefully surrendered with limited bloodshed. Though Jerusalem fell, it was not the end of the Kingdom of Jerusalem, as the capital shifted first to Tyre and later to Acre after the Third Crusade. Latin Christians responded in 1189 by launching the Third Crusade led by Richard the Lionheart, Philip Augustus, and Frederick Barbarossa separately. In Jerusalem, Saladin restored Muslim holy sites and generally showed tolerance towards Christians; he allowed Orthodox and Eastern Christia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Jerusalem (1099)
The siege of Jerusalem marked the successful end of the First Crusade, whose objective was the recovery of the city of Jerusalem and the Church of the Holy Sepulchre from Islamic control. The five-week siege began on 7 June 1099 and was carried out by the Christian forces of the First Crusade, Christian forces of Western Europe mobilized by Pope Urban II after the Council of Clermont in 1095. The city had been out of Christian control since the Muslim conquest of the Levant in 637 and had been held for a century first by the Seljuk Turks and later by the Fatimid Caliphate, Egyptian Fatimids. One of the root causes of the Crusades#Background, Crusades was the hindering of Christian Christian pilgrimage#Holy Land, pilgrimages to the Holy Land which began in the 4th century. A number of eyewitness accounts of the battle were recorded, including in the anonymous chronicle ''Gesta Francorum''. After Jerusalem was captured on 15 July 1099, thousands of Muslims and Jews were massacred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |