|
Sideritis Remota
''Sideritis'', also known as ironwort, mountain tea, Greek tea and shepherd's tea, is a genus of flowering plants known for their use as herbal medicine, commonly as a herbal tea. They are abundant in Mediterranean regions, the Balkans, the Iberian Peninsula and Macaronesia, but can also be found in Central Europe and temperate Asia. History and etymology In Greek, "sideritis" ( Gr: σιδηρίτις) can be literally translated as "he who is made of iron". The plant was known to ancient Greeks, specifically Pedanius Dioscorides and Theophrastus. Although Dioscorides describes three species, only one (probably ''S. scordioides'') is thought to belong to ''Sideritis''. In ancient times "sideritis" was a generic reference for plants capable of healing wounds caused by iron weapons during battles. However, others hold that the name stems from the shape of the sepal, which resembles the tip of a spear. Taxonomy In 2002, molecular phylogenetic research found ''Sideritis'' and five ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was the son of a curate and was born in Råshult, in the countryside of Småland, southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecotype
Ecotypes are organisms which belong to the same species but possess different phenotypical features as a result of environmental factors such as elevation, climate and predation. Ecotypes can be seen in wide geographical distributions and may eventually lead to speciation. Definition In evolutionary ecology, an ecotype,Greek: ''οίκος'' = home and ''τύπος'' = type, coined by Göte Turesson in 1922 sometimes called ecospecies, describes a genetically distinct geographic variety, Population biology, population, or Race (biology), race within a species, which is genotypically Adaptation, adapted to specific environmental conditions. Typically, though ecotypes exhibit Phenotype, phenotypic differences (such as in Morphology (biology), morphology or physiology) stemming from environmental heterogeneity, they are capable of interbreeding with other geographically adjacent ecotypes without loss of fertility or vigor.''Ecology: From individuals to ecosystems'' by Begon, Townsen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
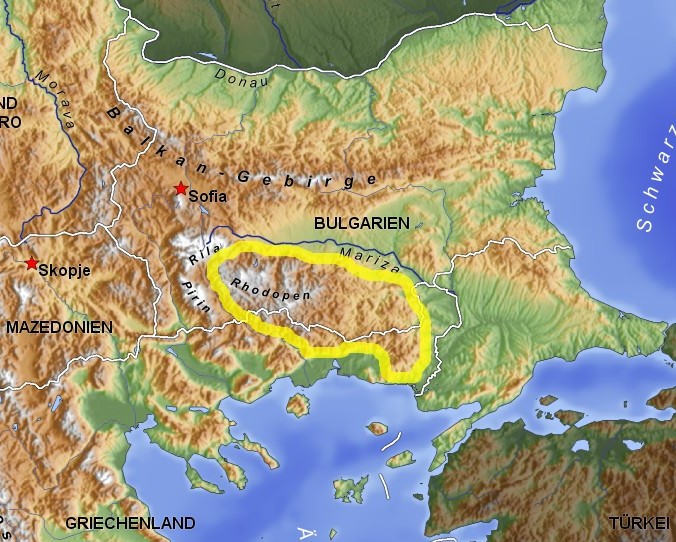
Rhodope Mountains
The Rhodopes (; , ; , ''Rodopi''; ) are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, and the largest by area in Bulgaria, with over 83% of its area in the southern part of the country and the remainder in Greece. Golyam Perelik is its highest peak at . The mountain range gives its name to the terrestrial ecoregion Rodope montane mixed forests that belongs in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome and the Palearctic realm. The region is particularly notable for its karst areas with their deep river gorges, large caves and specific sculptured forms, such as the Trigrad Gorge. A significant part of Bulgaria's hydropower resources are located in the western areas of the range. There are a number of hydro-cascades and dams used for electricity production, irrigation, and as tourist destinations. Name and mythology The name of the Rhodope Mountains is of Thracian origin. Rhod-ope (Род-oпа) is interpreted as the first name of a river, meaning "rusty/reddish river", wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
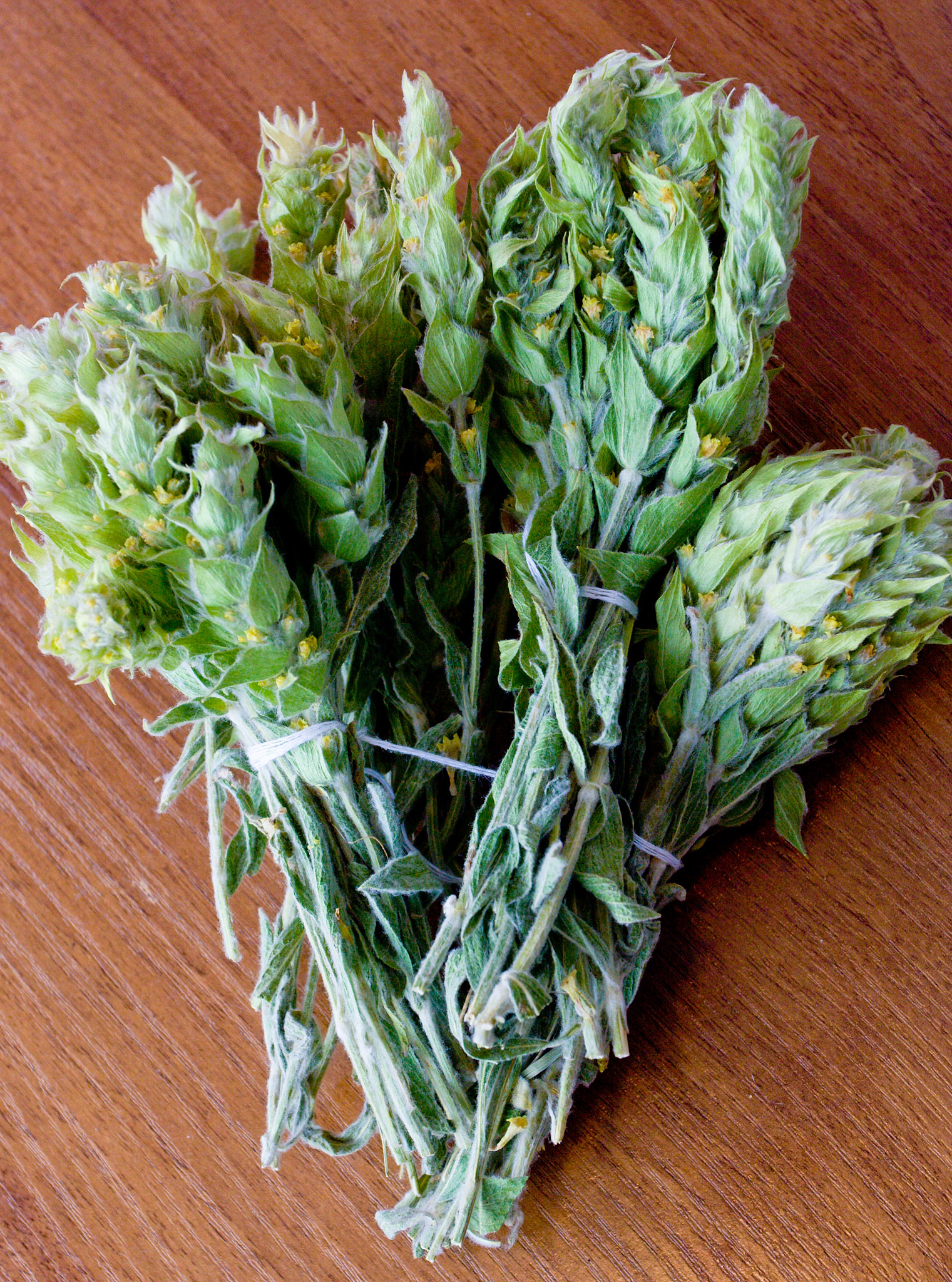
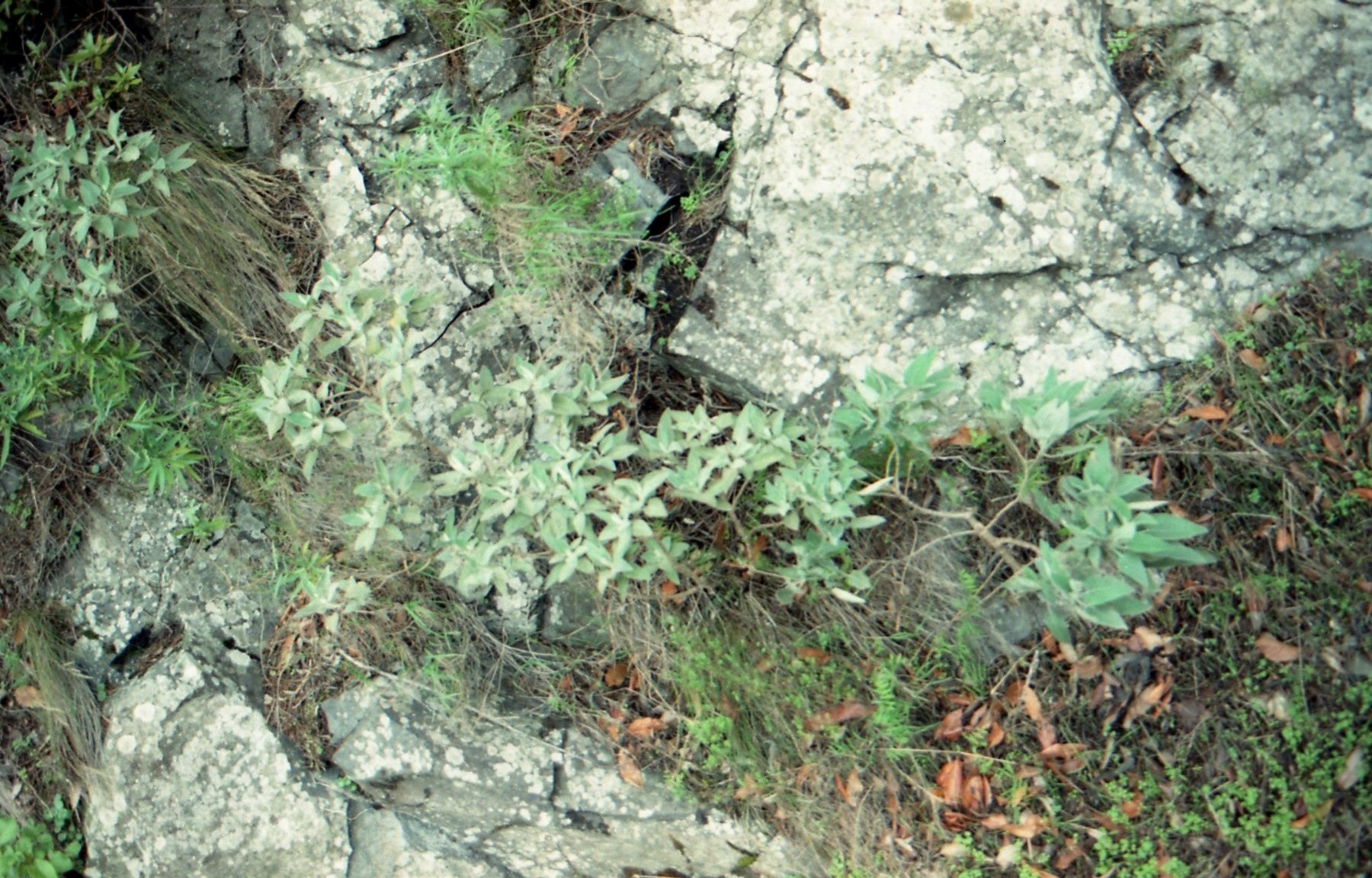
Sideritis Elica
''Sideritis elica'' is a plant species in the genus '' Sideritis'', endemic to Bulgaria. The species was discovered and described by Associate Prof. Ina Aneva and Senior Assistant Prof. Georgi Bonchev of the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, as well as by Prof. Petar Zhelev of the University of Forestry in Sofia. The molecular analysis supports the morphological data about the divergence between the more widespread '' Sideritis scardica'' and ''Sideritis elica''. The studied populations of the two taxa were found to be genetically distant. The species is only known from the northern foothills of the central Rhodope Mountains The Rhodopes (; , ; , ''Rodopi''; ) are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, and the largest by area in Bulgaria, with over 83% of its area in the southern part of the country and the remainder in Greece. Golyam Perelik is its highest peak ..., where it grows in the Chervenata Stena Reserve near Asenovgrad and Bachkovo Monastery. References {{Ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of islands in the Mediterranean, third largest and third most populous island in the Mediterranean, after Sicily and Sardinia. It is located southeast of Greece, south of Turkey, west of Syria and Lebanon, northwest of Israel and Palestine, and north of Egypt. Its capital and largest city is Nicosia. Cyprus hosts the British Overseas Territories, British military bases Akrotiri and Dhekelia, whilst the northeast portion of the island is ''de facto'' governed by the self-declared Northern Cyprus, Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus, which is separated from the Republic of Cyprus by the United Nations Buffer Zone in Cyprus, United Nations Buffer Zone. Cyprus was first settled by hunter-gatherers around 13,000 years ago, with farming communities em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sideritis Cypria
''Sideritis cypria'', the Cyprus ironwort, is a species of flowering plant in the family Lamiaceae. Erect perennial herb with a woody base, 60 cm high, with densely hairy tetragonal shoots. Leaves, opposite, simple, obscurely serrate, densely hairy, thick, oblanceolate, 3-12 x 1–5 cm. Flowers in verticillasters subtended by the cup-like bracts, zygomorphic, corolla bright yellow. Flowers from June to August. Fruit of 4 nutlets.The Endemic Plants of Cyprus, Texts: Takis Ch. Tsintides, Photographs: Laizos Kourtellarides, Cyprus Association of Professional Foresters, Bank of Cyprus Group, Nicosia 1998, Habitat South-facing, dry limestone cliffs, altitude 300–900 m. Distribution A very rare and vulnerable species endemic to Cyprus. Restricted to the Pentadaktylos Range: Buffavento, St. Hilarion, Halevga, Bellapais, Yaïla etc. Gallery File:Gardenology.org-IMG 2506 ucla09.jpg, File:Sideritis cypria 2 (Corse).jpg, References External links * * http://www.th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porto Santo Island
Porto Santo Island () is a Portuguese island and municipality northeast of Madeira Island in the North Atlantic Ocean; it is the northernmost and easternmost island of the archipelago of Madeira, located in the Atlantic Ocean west of Europe and Africa. The municipality of Porto Santo occupies the entire island and small neighbouring islands. It was elevated to city status on 6 August 1996. The sole parish of the municipality is also named Porto Santo. The population in 2011 was 5,483, in an area of 42.59 km2. The main settlement on the island is Vila Baleira. History It appears that some knowledge of Atlantic islands, such as Madeira, existed before the discovery and settlement of these lands, as the islands appear on maps as early as 1339. From a portolan dating to 1351, and preserved in Florence, Italy, it would appear that the islands of Madeira had been discovered long before being claimed by the Portuguese expedition of 1418. In '' Libro del Conocimiento'' (1348� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bugio Island
Bugio Island () — is one of the three islands of the Portuguese Desertas Islands archipelago, a small chain of islands in the Madeira, Madeira Islands Archipelago of Macaronesia. It is located in the Atlantic Ocean off the western coast of North Africa, and to the southeast of Madeira Island. The island is part of the Desertas Islands nature reserve, with no approach to the island closer than 100 m without a permit. The island has breeding Desertas petrels. See also *Deserta Grande Island *Ilhéu Chão — ''Chão islet''. External linksMadeirabirds.com: Desertas Islands boat trips Islands of the Autonomous Region of Madeira Uninhabited islands of Port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madeira
Madeira ( ; ), officially the Autonomous Region of Madeira (), is an autonomous Regions of Portugal, autonomous region of Portugal. It is an archipelago situated in the North Atlantic Ocean, in the region of Macaronesia, just under north of the Canary Islands, Spain, west of the Morocco and southwest of mainland Portugal. Madeira sits on the African Plate, African Tectonic Plate, but is culturally, politically and ethnically associated with Europe, with its population predominantly descended from Portuguese settlers. Its population was 251,060 in 2021. The capital of Madeira is Funchal, on the main island's south coast. The archipelago includes the islands of Madeira Island, Madeira, Porto Santo Island, Porto Santo, and the Desertas Islands, Desertas, administered together with the separate archipelago of the Savage Islands. Roughly half of the population lives in Funchal. The region has political and administrative autonomy through the Autonomous Regions of Portugal#Const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sideritis Candicans
''Sideritis candicans'' (''erva branca'', ''selvageira''). More or less white to greyish, densely tomentose shrub 45–100 cm. Leaves 2.5-12 x 1.5 x 7.5 cm, the lower ovate-lanceolate to ovate, acute to obtuse, rounded to cordate at base, weakly crenate to sub-entire, petiolate. Inflorescence up to 30 cm. Calyx 5–6.5 mm; teeth 1–1.5 mm. Corolla creamy yellow; tube 4–5.5 mm not exserted; upper lip 23–2.5 mm; lower lip 2.2-3.5 mm, the middle lobe shallowly notched. Nutlets 1.5 mm, ovoid. Flowers from March to July. Widespread in clearings and open sunny places mostly from 600 to 1700 m. Endemic to the islands of Madeira Madeira ( ; ), officially the Autonomous Region of Madeira (), is an autonomous Regions of Portugal, autonomous region of Portugal. It is an archipelago situated in the North Atlantic Ocean, in the region of Macaronesia, just under north of ..., Porto Santo and Bugio. References * Press, J. R. and M. J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Europe and the fourth-most populous European Union member state. Spanning across the majority of the Iberian Peninsula, its territory also includes the Canary Islands, in the Eastern Atlantic Ocean, the Balearic Islands, in the Western Mediterranean Sea, and the Autonomous communities of Spain#Autonomous cities, autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla, in mainland Africa. Peninsular Spain is bordered to the north by France, Andorra, and the Bay of Biscay; to the east and south by the Mediterranean Sea and Gibraltar; and to the west by Portugal and the Atlantic Ocean. Spain's capital and List of largest cities in Spain, largest city is Madrid, and other major List of metropolitan areas in Spain, urban areas include Barcelona, Valencia, Seville, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Palma
La Palma (, ), also known as ''La isla bonita'' () and historically San Miguel de La Palma, is the most northwesterly island of the Canary Islands, a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in Macaronesia in the North Atlantic Ocean. La Palma has an area of making it the fifth largest of the eight main Canary Islands. The total population at the start of 2023 was 84,338, of whom 15,522 lived in the capital, Santa Cruz de La Palma and 20,375 in Los Llanos de Aridane. Its highest mountain is the Roque de los Muchachos, at , being second among the peaks of the Canaries after the Teide massif on Tenerife. In 1815, the German geologist Leopold von Buch visited the Canary Islands. It was as a result of his visit to Tenerife, where he visited the Las Cañadas caldera, and then later to La Palma, where he visited the Taburiente caldera, that the Spanish word for cauldron or large cooking pot – "caldera" – was introduced into the geological vocabulary. In the center of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |