|
Side Carving
Side carving () is a form of traditional Chinese seal art, seal carving techniques that originated in Chinese culture, ancient China. It was later introduced to other countries in East Asia and has gained popularity among contemporary seal artists from regions including Hong Kong, South Korea, Japan, Singapore, etc. It mainly focuses on developing pattern design skills and techniques applied to the carving of side surfaces of a seal, which distinguishes itself as a unique carving technique from knob carving (head part) and seal carving, face carving (bottom part). It decorates the side surfaces of seals with literal or pictorial imagery. History The history of this art can be traced back as early as the Western Zhou, Late Zhou and Qin dynasty, Qin dynasties when government or official seals had short notations on their side surfaces indicating the owner of the seal (by engraving the owner's name), the maker of the seal (by engraving the craftsman's name), and/or the date of manufa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Seal Art
In the Sinosphere, seals (stamps) can be applied on objects to establish personal identification. They are commonly applied on items such as personal documents, office paperwork, contracts, and art. They are used similarly to signatures in the West. Unlike in the West, where wax seals are common, Sinosphere seals are used with ink. Of Chinese origin, the process soon spread beyond China and across East and Southeast Asia. Various countries in these regions currently use a mixture of seals and hand signatures, and, increasingly, electronic signatures. Chinese seals are typically made of stone, sometimes of metals, wood, bamboo, plastic, or ivory, and are typically used with red ink or cinnabar paste ( zh, c=朱砂, p=zhūshā). The word 印 ("yìn" in Mandarin, "in" in Japanese and Korean, "ấn" and "in" in Vietnamese) specifically refers to the imprint created by the seal, as well as appearing in combination with other morphemes in words related to any printing, as in the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sha Menghai
Sha Menghai (, June 11, 1900 – October 10, 1992), born Shi Wenruo (沙文若), was a great master of calligraphy in China. He also was a master of Chinese seal carving (中国篆刻艺术), a theoretician of traditional Chinese art, and a master of Shanghai School art. Sha Wenhan is his brother. Sha was born in Sha village in Yinxian, Zhejiang. He was a professor in National Zhongshan University (from 1929), National Zhejiang University (from 1949), and China Academy of Art (from 1963). References *Zhu, Guantian"Sha Menghai" ''Encyclopedia of China The ''Encyclopedia of China'' () is the first large-entry modern encyclopedia in the Chinese language. The compilation began in 1978. Published by the Encyclopedia of China Publishing House, the encyclopedia was issued one volume at a time, be ...'', 1st ed. External links * 1900 births 1992 deaths Chinese seal artists Artists from Ningbo Academic staff of Zhejiang University China Academy of Art 20th- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhao Zhiqian
Zhao Zhiqian (; 1829–1884) was a Chinese calligrapher, seal carver and painter in the late Qing Dynasty, "the leading scholar-artist of his day." Zhao's seal carving had profound influence on the later masters, such as Wu Changshuo and Qi Baishi. He is also known under the courtesy name of Yifu (益甫) and his pseudonym (''hào'') of Lengjun (冷君), which he changed to Huishu (撝叔) and Bei'an (悲盦) respectively later in his life. Biography Zhao was born in 1829 in Shaoxing, Zhejiang Province into a merchant family. He became a Xiucai at the age of 20, and obtained the title Juren in 1859 in Zhejiang provincial exam. With the outbreak of Taiping Rebellion in the following year, his political ambition was hindered. During the rebellion, his family shattered, and a number of his art works as well as his collections were lost. Later, he went to Beijing for the national exams. After repeated failures, he gave up his dream of becoming a government official. He submitted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu Changshuo
Wu Changshuo (, September 12, 1844 – November 29, 1927, also romanised as Wu Changshi, ), born Wu Junqing (), was a Chinese calligrapher, painter, and seal artist of the late Qing Period. Life Wu was born into a scholarly family in Huzhou, Zhejiang. In his twenties, Wu moved to Jiangsu Province and settled down in Suzhou. Prior to the collapse of the Great Qing, he served as an imperial official in Liaoning. Initially, he devoted himself to poetry and calligraphy with a strong interest in early scripts. He also led the Xiling Seal Art Society, an academic organisation for Hangzhou-based seal artists. Wu started painting in his thirties. Only later did he consider himself a painter associated with the " Shanghai School." As a painter, he was noted for helping to rejuvenate the art of painting flowers and birds. He considered carving seals and doing paintings to be integrated to each other. His work garnered him fame and he was highly regarded in Japan. After his de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deng Shiru
Deng Shirú (Teng Shih-ju, traditional: 鄧石如, simplified: 邓石如); c. 1739/1743–1805 was a Chinese calligrapher during the Qing Dynasty (1644–1912). Deng was born in Huaining 懷寧 in the Anhui 安徽 province. His style name was 'Wanbo' 顽伯 and his sobriquet A sobriquet ( ) is a descriptive nickname, sometimes assumed, but often given by another. A sobriquet is distinct from a pseudonym in that it is typically a familiar name used in place of a real name without the need for explanation; it may beco ...s were 'Wanbai shanren 皖白山人, Wan bai 完白, Guhuan, Gu wanzi 故浣子, Youji daoren 游笈道人, Fengshui yuzhang 鳳水漁長, and Longshan qiaozhang 龍山樵長'. Deng studied at the Shen Chun Academy. He later learned the art of Seal cutting. References * External links {{DEFAULTSORT:Deng, Shiru 18th-century births 1805 deaths Artists from Anhui People from Huaining County ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Painting
Painting is a Visual arts, visual art, which is characterized by the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called "matrix" or "Support (art), support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush. Other implements, such as palette knives, sponges, airbrushes, the artist's fingers, or even a dripping technique that uses gravity may be used. One who produces paintings is called a painter. In art, the term "painting" describes both the act and the result of the action (the final work is called "a painting"). The support for paintings includes such surfaces as walls, paper, canvas, wood, glass, lacquer, pottery, leaf, copper and concrete, and the painting may incorporate other materials, in single or multiple form, including sand, clay, paper, cardboard, newspaper, plaster, gold leaf, and even entire objects. Painting is an important form of visual arts, visual art, bringing in elements such as drawing, Composition (visual art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird-and-flower Painting
Bird-and-flower painting, called () in chinese language, Chinese, is a kind of Chinese painting with a long tradition in China and is considered one of the treasures of Chinese culture. The was named after its subject matter. It originated in the Tang dynasty where it gained popularity, matured by the end of that period and during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, and fully reached its peak during the Song dynasty. Most paintings belong to the scholar-artist style of Chinese painting. In the coming centuries, the genre gained popularity and spread throughout the East Asian cultural sphere. It also had an influence on Iranian painting in the ' genre of illustration for book covers and illuminated manuscripts. Intended purpose and cultural significance According to Chinese tradition, the covers "flowers, birds, fish, and insects" (); thus, it can deal with a wide range of natural topics, including flowers, fish, insects, birds, pets (dogs, cats), etc. The paintin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shan Shui
''Shan shui'' (; pronounced ) refers to a style of traditional Chinese painting that involves or depicts scenery or natural landscapes, using a brush and ink rather than more conventional paints. Mountains, rivers and waterfalls are common subjects of ''shan shui'' paintings. History ''Shan shui'' painting first began to develop in the 5th century, in the Liu Song dynasty.''Textual Evidence for the Secular Arts of China in the Period from Liu Sung through Sui'' (1967) by Alexander Soper It was later characterized by a group of landscape painters such as Zhang Zeduan, most of them already famous, who produced large-scale landscape paintings. These landscape paintings usually centered on mountains. Mountains had long been seen as sacred places in China, which were viewed as the homes of immortals and thus, close to the heavens. Philosophical interest in nature, or in mystical connotations of naturalism, could also have contributed to the rise of landscape painting. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picture
An image or picture is a visual representation. An image can be two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be displayed through other media, including a projection on a surface, activation of electronic signals, or digital displays; they can also be reproduced through mechanical means, such as photography, printmaking, or photocopying. Images can also be animated through digital or physical processes. In the context of signal processing, an image is a distributed amplitude of color(s). In optics, the term ''image'' (or ''optical image'') refers specifically to the reproduction of an object formed by light waves coming from the object. A ''volatile image'' exists or is perceived only for a short period. This may be a reflection of an object by a mirror, a projection of a camera obscura, or a scene displayed on a cathode-ray tube. A ''fixed image'', also called a hard copy, is one that has bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
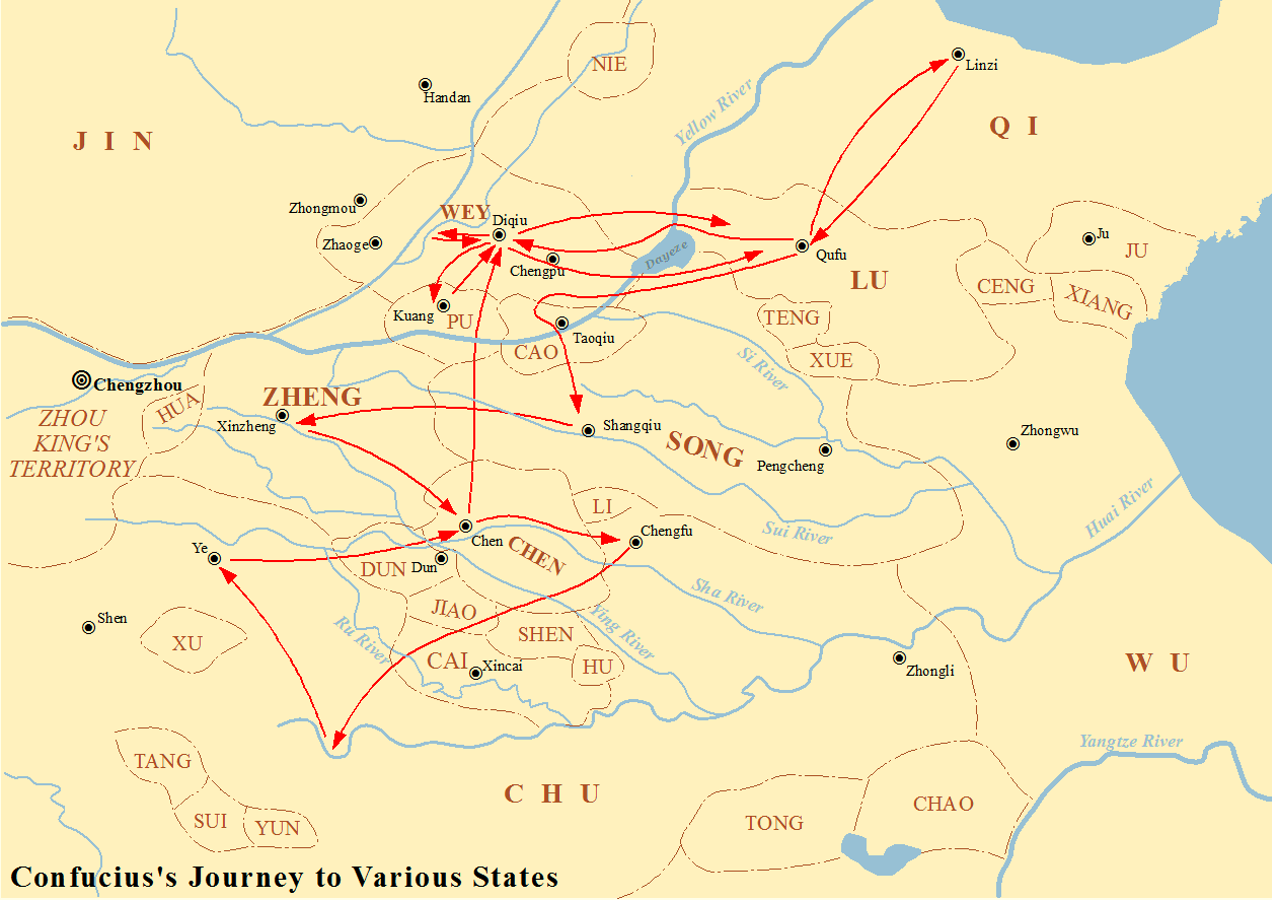
Confucius
Confucius (; pinyin: ; ; ), born Kong Qiu (), was a Chinese philosopher of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. Much of the shared cultural heritage of the Sinosphere originates in the philosophy and teachings of Confucius. His philosophical teachings, called Confucianism, emphasized personal and governmental morality, harmonious social relationships, righteousness, kindness, sincerity, and a ruler's responsibilities to lead by virtue. Confucius considered himself a transmitter for the values of Ancient China, earlier periods which he claimed had been abandoned in his time. He advocated for filial piety, endorsing strong family loyalty, Ancestor veneration in China, ancestor veneration, the respect of elders by their children and of husbands by their wives. Confucius recommended a robust family unit as the cornerstone for an ideal government. He championed the Silver Rule, or a negative form of the Golden Rule, advising, "Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |