|
Sicels
The Sicels ( ; or ''Siculī'') were an Indo-European tribe who inhabited eastern Sicily, their namesake, during the Iron Age. They spoke the Siculian language. After the defeat of the Sicels at the Battle of Nomae in 450 BC and the death of Sicel leader Ducetius in 440 BC, the Sicel state broke down and the Sicel culture merged into Magna Graecia. History Archaeological excavation has shown some Mycenean influence on Bronze Age Sicily. The earliest literary mention of Sicels is in the '' Odyssey''. Homer also mentions Sicania, but makes no distinctions: "they were (from) a faraway place and a faraway people and apparently they were one and the same" for Homer, Robin Lane Fox notes. It is possible that the Sicels and the Sicani of the Iron Age had consisted of an Illyrian population who (as with the Messapians) had imposed themselves on a native, Pre-Indo-European ("Mediterranean") population. Thucydides and other classical writers were aware of the traditions accordi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magna Graecia
Magna Graecia refers to the Greek-speaking areas of southern Italy, encompassing the modern Regions of Italy, Italian regions of Calabria, Apulia, Basilicata, Campania, and Sicily. These regions were Greek colonisation, extensively settled by Greeks beginning in the 8th century BC. Initially founded by their ''metropoleis'' (mother cities), the settlements evolved into independent and powerful Greek city-states (''poleis''). The settlers brought with them Ancient Greece, Hellenic civilization, which over time developed distinct local forms due to both their distance from Greece and the influence of the indigenous peoples of southern Italy. This interaction left a lasting imprint on Italy, including on Ancient Rome, Roman culture. The Greek settlers also influenced native groups such as the Sicels and the Oenotrians, many of whom adopted Greek culture and became Hellenization, Hellenized. In areas like architecture and urban planning, the colonies sometimes surpassed the achievem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicania
The Sicani or Sicanians were one of three ancient peoples of Sicily present at the time of Phoenician and Greek colonization. The Sicani dwelt east of the Elymians and west of the Sicels, having, according to Diodorus Siculus, the boundary with the last in the ancient Himera river (Salso) after a series of battles between these tribes. History The Sicani are the oldest inhabitants of Sicily with a recorded name. In the 5th century BCE, the Greek historian Thucydides, claims that the Sicani originated on the Iberian Peninsula, from around a river they called "Sicanus" and had migrated to Sicily following an invasion by the Ligurians. (The name Sicanus has been linked to the river known in modern Spanish as the Júcar.) Thucydides' source is unknown, although he often draws on the Sicilian historian Antiochus of Syracuse. Conversely, Timaeus of Tauromenium (writing c. 300 BCE) considers the Sicani to be indigenous to Sicily. A third theory, put forward by some modern scholars, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicani
The Sicani or Sicanians were one of three ancient peoples of Sicily present at the time of Phoenician and Greek colonization. The Sicani dwelt east of the Elymians and west of the Sicels, having, according to Diodorus Siculus, the boundary with the last in the ancient Himera river ( Salso) after a series of battles between these tribes. History The Sicani are the oldest inhabitants of Sicily with a recorded name. In the 5th century BCE, the Greek historian Thucydides, claims that the Sicani originated on the Iberian Peninsula, from around a river they called "Sicanus" and had migrated to Sicily following an invasion by the Ligurians. (The name Sicanus has been linked to the river known in modern Spanish as the Júcar.) Thucydides' source is unknown, although he often draws on the Sicilian historian Antiochus of Syracuse. Conversely, Timaeus of Tauromenium (writing c. 300 BCE) considers the Sicani to be indigenous to Sicily. A third theory, put forward by some modern schola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4.7 million inhabitants, including 1.2 million in and around the capital city of Palermo, it is both the largest and most populous island in the Mediterranean Sea. Sicily is named after the Sicels, who inhabited the eastern part of the island during the Iron Age. Sicily has a rich and unique culture in #Art and architecture, arts, Music of Sicily, music, #Literature, literature, Sicilian cuisine, cuisine, and Sicilian Baroque, architecture. Its most prominent landmark is Mount Etna, the tallest active volcano in Europe, and one of the most active in the world, currently high. The island has a typical Mediterranean climate. It is separated from Calabria by the Strait of Messina. It is one of the five Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicily Prehellenic Topographic Map
Sicily (Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy. With 4.7 million inhabitants, including 1.2 million in and around the capital city of Palermo, it is both the largest and most populous island in the Mediterranean Sea. Sicily is named after the Sicels, who inhabited the eastern part of the island during the Iron Age. Sicily has a rich and unique culture in arts, music, literature, cuisine, and architecture. Its most prominent landmark is Mount Etna, the tallest active volcano in Europe, and one of the most active in the world, currently high. The island has a typical Mediterranean climate. It is separated from Calabria by the Strait of Messina. It is one of the five Italian autonomous regions and is generally considered part of Southern Italy. The earliest archaeological record of human activity on the island is from around 14, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ducetius
Ducetius () (died 440 BCE) was a Hellenized leader of the Sicels and founder of a united Sicilian state and numerous cities.LiviusDucetius of Sicily Retrieved on 25 April 2006. It is thought he may have been born around the town of Mineo. His story is told through the Greek historian Diodorus Siculus in the 1st century BCE, who drew on the work of Timaeus. He was a native Sicilian, but his education was Greek and was very much influenced by Greek civilization in Sicily. He is sometimes known by the Hellenized name of Douketios. The Sicel revolt Sicily at this time was under the tyranny of Gelo and his brother Hiero. After the death of Hiero in 467 BCE, Syracuse became a democracy. There were however, troubles in the aftermath of the tyranny's collapse. War had broken out between Syracuse and its former colony Catana in 460 BCE. Ducetius assisted Syracuse because Catana had occupied Sicel land, and together defeated them. Ducetius went on to found the city of Menai (today M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Nomae
The Battle of Nomae was fought in 450 BCE between a united Sicel army under the command of Ducetius and a Greek army of Syracuse. Ducetius was defeated and his Sicel state broke up soon after. Background The Sicels were one of the original inhabitants of Sicily but their territory was slowly shrinking due to the expansion of the Greek colonies on the island, mainly Syracuse and Akragas. However, in the 450s BCE they had grown in power under a leader named Ducetius, who had united the Sicel territory under his rule. He was originally an ally of Syracuse, helping them in a war against Catana. However, as he grew in power, and also began to expand into Greek territory, Syracuse became concerned. When Ducetius attacked the other major Sicilian Greek power Akragas, the city asked Syracuse for help and Syracuse agreed.Ray 2011, p.116 Fielding 6,000 men along with 900 cavalry, the united Greek force commanded by Bolcon of Syracuse advanced towards Ducetius's army, which was besiegi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e.g., Tajikistan and Afghanistan), Armenia, and areas of southern India. Historically, Indo-European languages were also spoken in Anatolia. Some European languages of this family—English language, English, French language, French, Portuguese language, Portuguese, Russian language, Russian, Spanish language, Spanish, and Dutch language, Dutch—have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, including Albanian language, Albanian, Armenian language, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic languages, Celtic, Germanic languages, Germanic, Hellenic languages, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian languages, Indo-Iranian, and Italic languages, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siculian
Siculian (or Sicel) is an extinct Indo-European language spoken in central and eastern Sicily by the Sicels. It is attested in fewer than thirty inscriptions in eastern Sicily from the late 6th century to 4th century BCE, and in around twenty-five glosses from ancient writers. Classification Ancient sources state that Siculians entered Sicily from the Italian Peninsula either around the 13th century or the middle of the 11th century BCE (or in two waves), driving the prior inhabitants, the Sicanians and Elymians, to the west of the island. Due to its limited attestation, it is difficult to determine much about this language beyond that it was Indo-European. The prevalent modern view is that Siculian was an Italic language, although the scarcity of sources and the difficulties in interpreting inscriptions and glosses make it impossible to come to a definitive conclusion. Some inscriptions may reveal Italic elements, such as ''geped'' ('had'), which is comparable to the Oscan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
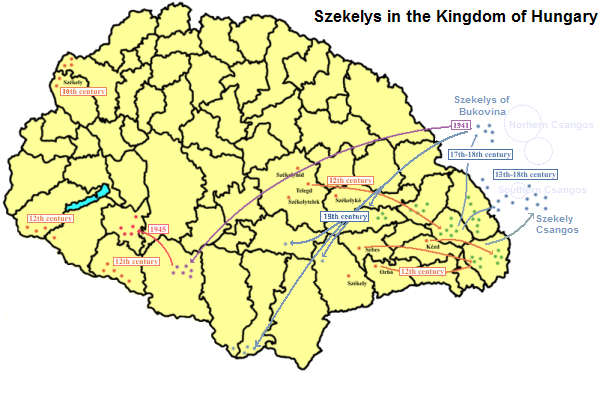
Székelys
The Székelys (, Old Hungarian script, Székely runes: ), also referred to as Szeklers, are a Hungarians, Hungarian subgroup living mostly in the Székely Land in Romania. In addition to their native villages in Suceava County in Bukovina, a significant population descending from the Székelys of Bukovina currently lives in Tolna County, Tolna and Baranya County, Baranya counties in Hungary and certain districts of Vojvodina, Serbia. In the Middle Ages, the Székelys played a role in the defense of the Kingdom of Hungary#Middle Ages, Kingdom of Hungary against the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans in their posture as guards of the eastern border. With the Treaty of Trianon of 1920, Transylvania (including the Székely Land) became part of Romania, and the Székely population was a target of Romanianization efforts. In 1952, during the Socialist Republic of Romania, communist rule of Romania, the former counties with the highest concentration of Székely population – Mureș County#His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umbrian
Umbrian is an extinct Italic language formerly spoken by the Umbri in the ancient Italian region of Umbria. Within the Italic languages it is closely related to the Oscan group and is therefore associated with it in the group of Osco-Umbrian languages, a term generally replaced by Sabellic in modern scholarship. Since that classification was first formulated, a number of other languages in ancient Italy were discovered to be more closely related to Umbrian. Therefore, a group, the Umbrian languages, was devised to contain them. Corpus Umbrian is known from about 30 inscriptions dated from the 7th through 1st centuries BC. The largest cache by far is the Iguvine Tablets, sevenThe tradition born in the 17th century that the tablets were originally nine, and that two, sent to Venice, never came back, must be considered spurious. Paolucci (1966), p. 44 inscribed bronze tablets found in 1444 near the village of Scheggia or, according to another tradition, in an underground c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabine
The Sabines (, , , ; ) were an Italic people who lived in the central Apennine Mountains (see Sabina) of the ancient Italian Peninsula, also inhabiting Latium north of the Anio before the founding of Rome. The Sabines divided into two populations just after the founding of Rome, which is described by Roman legend. The division, however it came about, is not legendary. The population closer to Rome transplanted itself to the new city and united with the preexisting citizenry, beginning a new heritage that descended from the Sabines but was also Latinized. The second population remained a mountain tribal state, coming finally to war against Rome for its independence along with all the other Italic tribes. Afterwards, it became assimilated into the Roman Republic. Etymology The Sabines derived directly from the ancient Umbrians and belonged to the same ethnic group as the Samnites and the Sabelli, as attested by the common ethnonyms of ''Safineis'' (in ancient Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |