|
Sibirenauta Sibirica
''Sibirenauta sibirica'' is a species of small air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Physidae, a family which are sometimes known as the bladder snails. Taxonomy Swedish malacologist Carl Agardh Westerlund discovered and described this species under the name ''Physa sibirica'' in 1877.Vinarski M. V., Nekhaev I. O., Glöer P. & von Proschwitz T. (2013). "Type materials of freshwater gastropod species described by C.A. Westerlund and accepted in current malacological taxonomy: a taxonomic and nomenclatorial study". ''Ruthenica'' 23: 79–108. Starobogatov et al. moved this species to the genus ''Sibirenauta'' in 1989. Vinarski and colleagues designated the lectotype for ''Sibirenauta sibirica'' in 2013 and the lectotype is stored in the Swedish Museum of Natural History in Stockholm. The generic name ''Sibirenauta'' is feminine (according to original description), the correct species name should be ''Sibirenauta sibirica'' instead of '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Agardh Westerlund
Carl Agardh Westerlund (12 January 1831 – 28 February 1908 in Ronneby) was a Swedish malacologist. Biography Westerlund was born at Berga in Kalmar County, Sweden. He became a student in Uppsala University in 1853 and studied at Lund University where he received his bachelor's degree in 1860 and became a Ph.D. in 1862. He worked as a temporary teacher in Malmö in 1858–1859 and in Landskrona 1860–1862, and was a teacher at the high school in Ronneby from 1862 to 1893. in Nordisk Familjebok, vol. 32 (1921), col. 43-44 Westerlund contributed much to the knowledge of the land and freshwater molluscs of the |
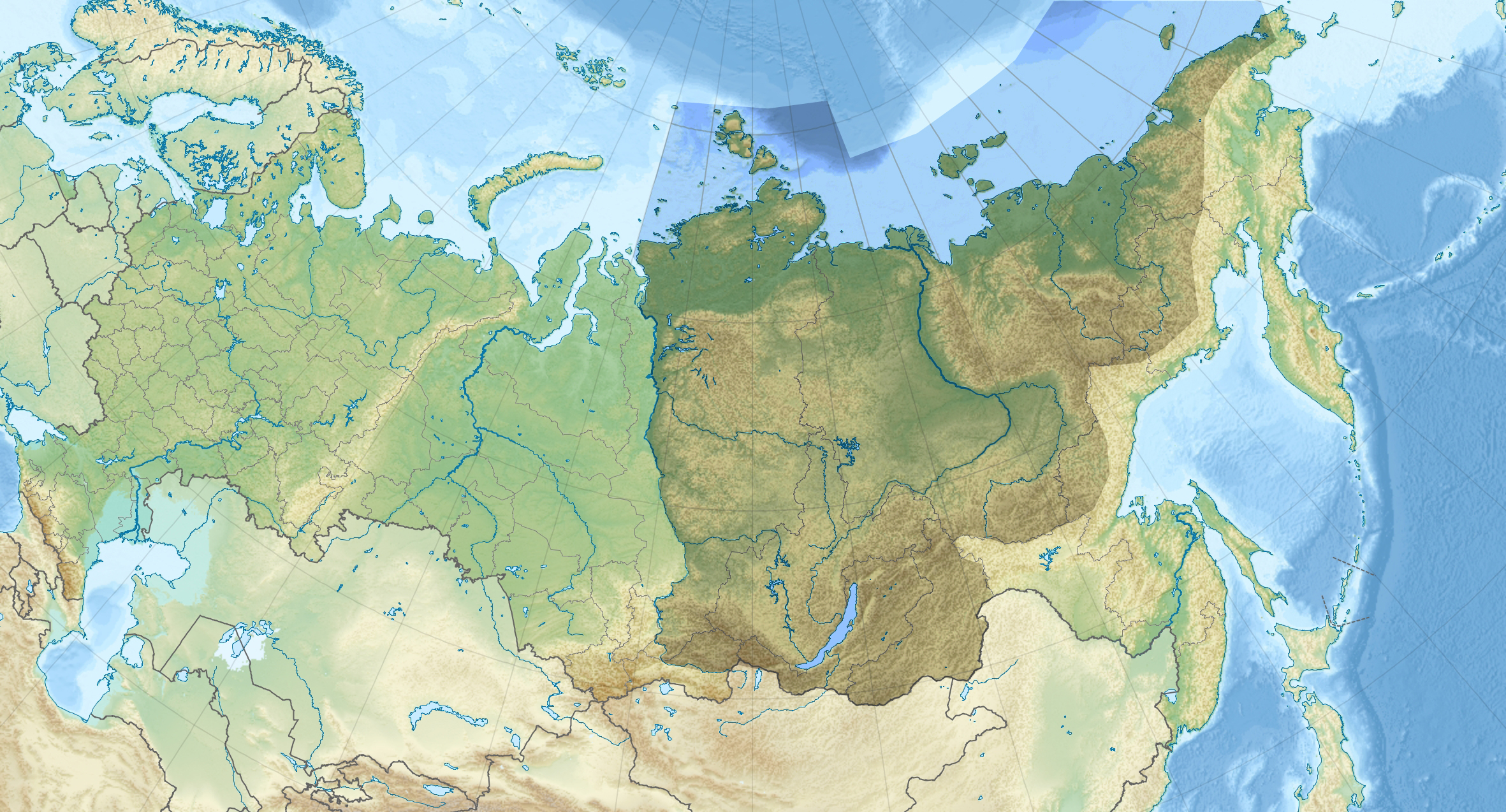
Eastern Siberia
Eastern Siberia is a part of Siberia that incorporates the territory located between the Yenisei River in the west and the Pacific Ocean divides in the east. Its area is equal to 7.2 million sq. km.Galina Samoylova (Г. С. Самойлова)ВОСТО́ЧНАЯ СИБИ́РЬ/ref> Most of Eastern Siberia is occupied by the Central Siberian Plateau, as well as by tundra in the north and mountain ranges in the south. The Eastern Siberian region consists of Yakutia, Buryatia, Tuva, Krasnoyarsk Krai, Irkutsk Oblast and Chita Oblast. The largest cities are Irkutsk and Krasnoyarsk. It considerably overlaps, but not coincides with, the Russian Far East, which stretches from Lake Baikal to the Pacific Ocean The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is .... References {{reflist Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whorl (mollusc)
A whorl is a single, complete 360° revolution or turn in the spiral or whorled growth of a mollusc shell. A spiral configuration of the shell is found in numerous gastropods, but it is also found in shelled cephalopods including ''Nautilus'', ''Spirula'' and the large extinct subclass of cephalopods known as the ammonites. A spiral shell can be visualized as consisting of a long Cone (geometry), conical tube, the growth of which is coiled into an overall Helix, helical or planispiral shape, for reasons of both strength and compactness. The number of whorls which exist in an adult shell of a particular species depends on mathematical factors in the geometric growth, as described in D'Arcy Wentworth Thompson's classic 1917 book ''On Growth and Form'', and by David Raup. The main factor is how rapidly the conical tube expands (or flares-out) over time. When the rate of expansion is low, such that each subsequent whorl is not that much wider than the previous one, then the adult s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastropod Shell
The gastropod shell is part of the body of many gastropods, including snails, a kind of mollusc. The shell is an exoskeleton, which protects from predators, mechanical damage, and dehydration, but also serves for muscle attachment and calcium storage. Some gastropods appear shell-less (slugs) but may have a remnant within the mantle, or in some cases the shell is reduced such that the body cannot be retracted within it (semi-slug). Some snails also possess an operculum that seals the opening of the shell, known as the Aperture (mollusc), aperture, which provides further protection. The study of mollusc shells is known as conchology. The biological study of gastropods, and other molluscs in general, is malacology. Shell morphology terms vary by species group. Shell layers The gastropod shell has three major layers secreted by the Mantle (mollusc), mantle. The calcareous central layer, ostracum, is typically made of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) precipitated into an organic matrix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taymyr Peninsula
The Taymyr Peninsula ( ) is a peninsula in the Far North of Russia, in the Siberian Federal District, that forms the northernmost part of the mainland of Eurasia. Administratively it is part of the Krasnoyarsk Krai Federal subject of Russia. Geography The Taymyr Peninsula lies between the Yenisei Gulf of the Kara Sea and the Khatanga Gulf of the Laptev Sea. Lake Taymyr and the Byrranga Mountains are located within the vast Taymyr Peninsula. Cape Chelyuskin, the northernmost point of the Eurasian continent, is located at the northern end of the Taymyr Peninsula. Etymology There are several theories about the origin of the name "Taimyr." The most widely accepted explanation is that it comes from the Evenki language, originating from the ancient Tungus word "tamura", which means "valuable, precious, rich." The Evenki people originally used this name for the Taimyr River, known for its abundance of fish. In the 19th century, thanks to the geographer and explorer Alexander ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yenisei River
The Yenisey or Yenisei ( ; , ) is the list of rivers by length, fifth-longest river system in the world, and the largest to drain into the Arctic Ocean. Rising in Mungaragiyn-gol in Mongolia, it follows a northerly course through Lake Baikal and the Krasnoyarsk Dam before draining into the Yenisey Gulf in the Kara Sea. The Yenisey divides the Western Siberian Plain in the west from the Central Siberian Plateau to the east; it drains a large part of central Siberia. Its delta is formed between the Gyda Peninsula and the Taymyr Peninsula. It is the central one of three large Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean (the other two being the Ob (river), Ob and the Lena River, Lena). The maximum depth of the Yenisey is and the average depth is . Geography The Yenisey proper, from the confluence of its source rivers the Great Yenisey and Little Yenisey at Kyzyl to its mouth in the Kara Sea, is long. From the source of its tributary the Selenga, it is long. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Locality (biology)
In biology, a type is a particular wikt:en:specimen, specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally associated. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes the defining features of that particular taxon. In older usage (pre-1900 in botany), a type was a taxon rather than a specimen. A taxon is a scientifically named grouping of organisms with other like organisms, a set (mathematics), set that includes some organisms and excludes others, based on a detailed published description (for example a species description) and on the provision of type material, which is usually available to scientists for examination in a major museum research collection, or similar institution. Type specimen According to a precise set of rules laid down in the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) and the ''International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants'' (ICN), the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Research
''Polar Research'' is a biannual peer-reviewed scientific journal covering natural and social scientific research on the polar regions. It is published by the Norwegian Polar Institute. It covers a wide range of fields from biology to oceanography, including socio-economic and management topics. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2014 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 1.141. References External links * Biology journals Ecology journals Geography journals Academic journals established in 1982 Biannual journals English-language journals 1982 establishments in Norway Antarctic research Glaciology journals {{glaciology-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Non-marine Molluscs Of Russia
The non-marine molluscs of Russia are a part of the molluscan fauna of Russia. A number of species of non-marine molluscs are found in the wild in Russia. Freshwater gastropods Valvatidae * '' Cincinna (Sibirovalvata) aliena'' (Westerlund, 1877)M. V. Vinarski & A. V. Karimov (2015). "Aquatic snails (Gastropoda) of the “Malaya Sos’va” Nature Reserve (Western Siberia)". Ruthenica 25(2): 25-35. * '' Cincinna (Sibirovalvata) confusa'' (Westerlund, 1897) * '' Cincinna (Sibirovalvata) sibirica'' (Middendorff, 1851) Lymnaeidae * '' Galba (Galba) truncatula'' (O. F. Müller, 1774) * '' Lymnaea (Lymnaea) stagnalis'' (Linnaeus, 1758) * '' Radix (Peregriana) balthica'' (Linnaeus, 1758) * '' Radix (Peregriana) dolgini'' (Gundrizer et Starobogatov, 1979) * '' Radix (Peregriana) intermedia'' (Lamarck, 1822) * '' Radix (Peregriana) peregra'' (O. F. Müller, 1774) * '' Stagnicola (Stagnicola) ventricosella'' (B. Dybowski, 1913) Physidae * '' Aplexa hypnorum'' (Linnaeus, 1758) Plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrangel Island
Wrangel Island (, ; , , ) is an island of the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia. It is the List of islands by area, 92nd-largest island in the world and roughly the size of Crete. Located in the Arctic Ocean between the Chukchi Sea and East Siberian Sea, the island lies astride the 180th meridian, 180th meridian (geography), meridian. The International Date Line is therefore displaced eastwards at this latitude to keep the island, as well as the Chukchi Peninsula on the Russian mainland, on the same day as the rest of Russia. The closest land to Wrangel Island is the tiny and rocky Herald Island (Arctic), Herald Island located to the east.Kosko, M.K., M.P. Cecile, J.C. Harrison, V.G. Ganelin, N.V., Khandoshko, and B.G. Lopatin, 1993Geology of Wrangel Island, Between Chukchi and East Siberian Seas, Northeastern Russia.Bulletin 461, Geological Survey of Canada, Ottawa Ontario, 101 pp. Its straddling the 180th meridian makes its north shore at that point both the northeasternmost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subarctic
The subarctic zone is a region in the Northern Hemisphere immediately south of the true Arctic, north of hemiboreal regions and covering much of Alaska, Canada, Iceland, the north of Fennoscandia, Northwestern Russia, Siberia, and the Cairngorms. Generally, subarctic regions fall between 50°N and 70°N latitude, depending on local climates. Precipitation is usually low, and vegetation is characteristic of the taiga. Daylight at these latitudes is quite extreme between summer and winter due to its high latitude. Near the summer solstice for instance, subarctic regions can experience an all-night period of either civil, nautical, or astronomical twilight (or in the northern reaches full daylight), since the sun never dips more than 18 degrees below the horizon. Noctilucent clouds are best observed within this range of latitude. Climate and soils Subarctic temperatures are above for at least one and at most three months of the year. Precipitation tends to be low due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |