|
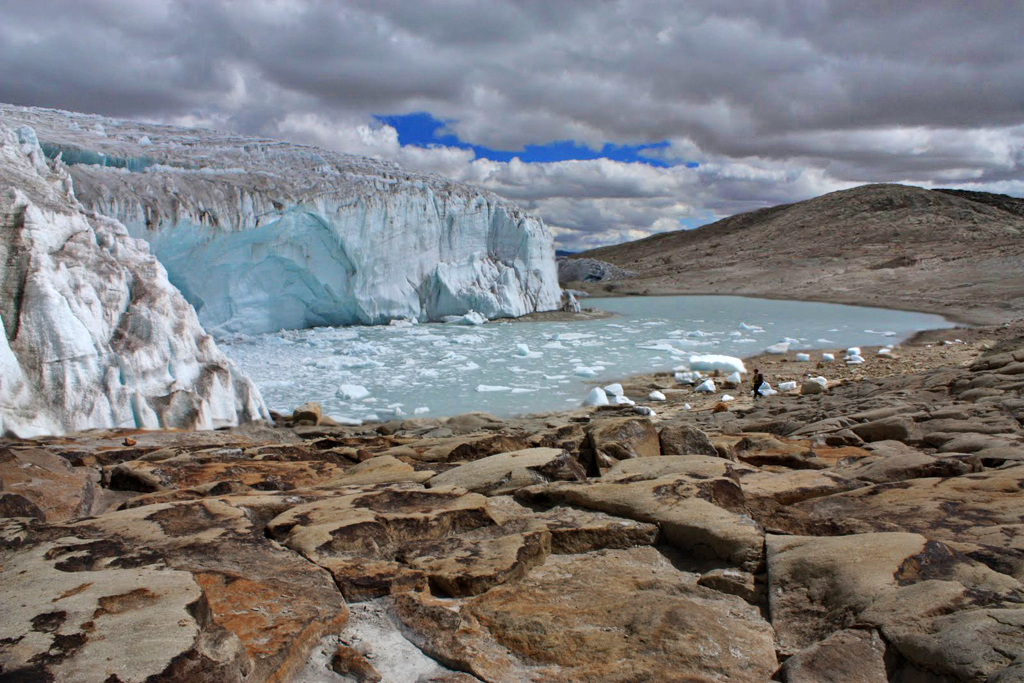
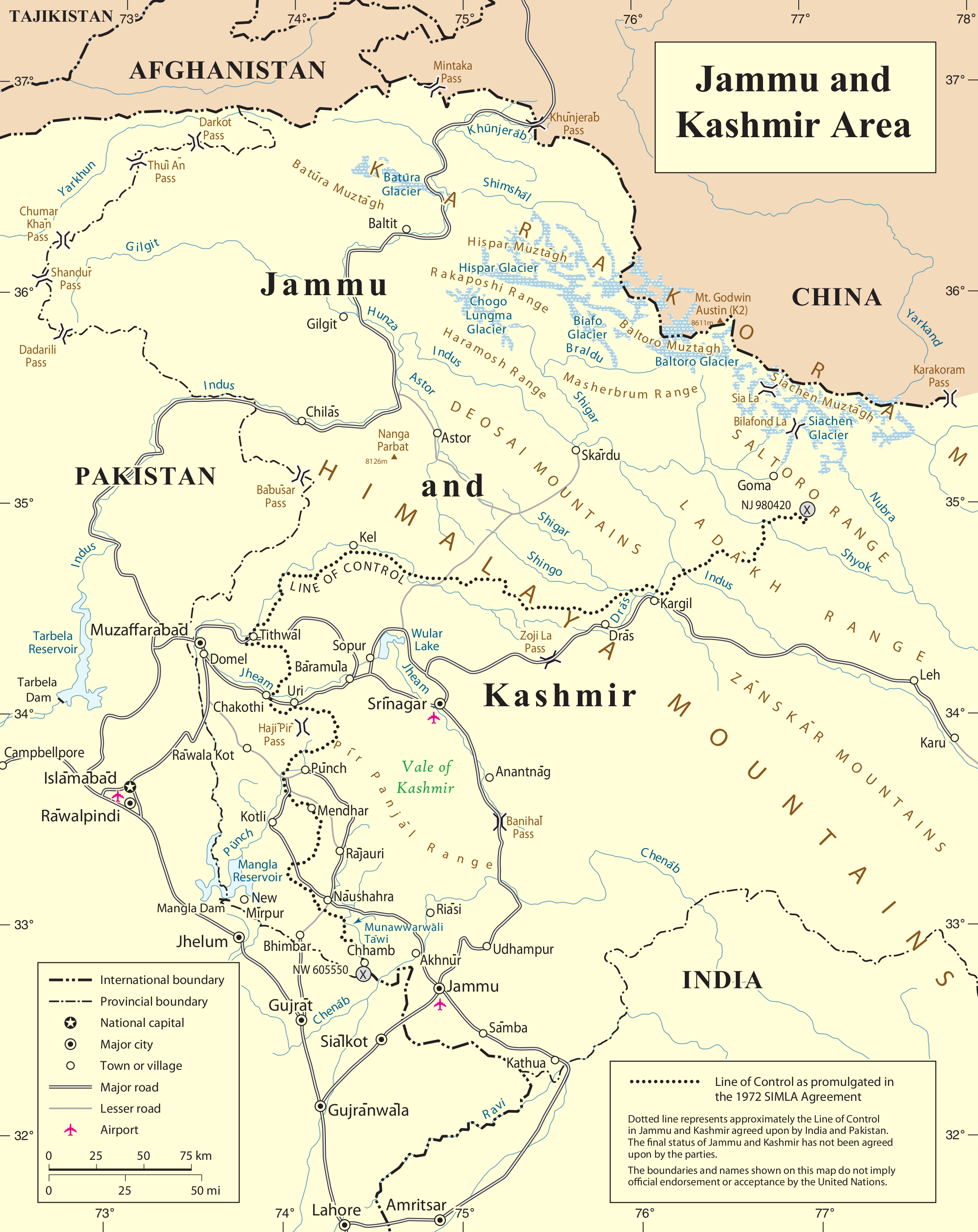
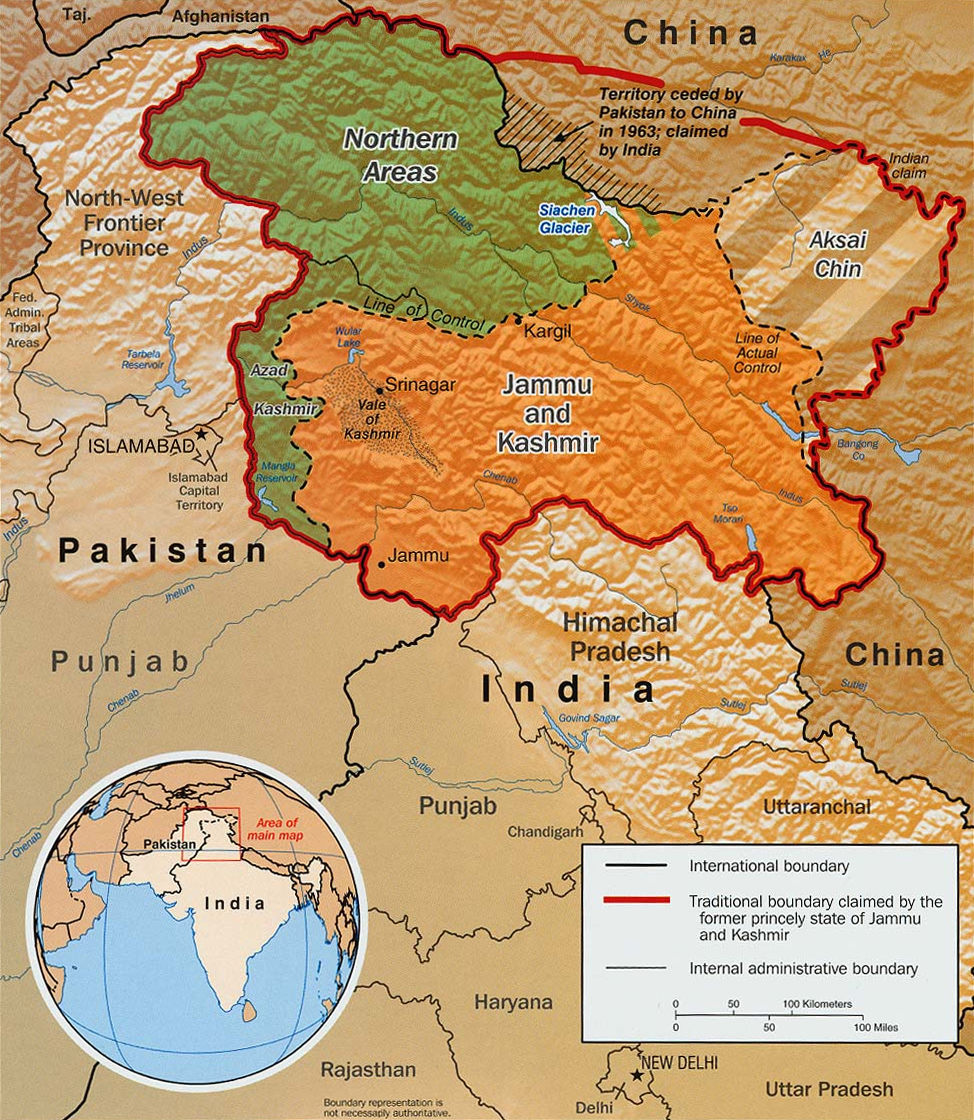
Siachen Glacier
The Siachen Glacier is a glacier located in the eastern Karakoram range of the Himalayas, just northeast of the point NJ9842 where the Line of Control between India and Pakistan ends in northeastern Kashmir. At long, it is the longest glacier in the Karakoram and List of glaciers#List of longest glaciers on Earth in non-polar regions, second-longest in the world's non-polar areas. It falls from an altitude of 5,753 m (18,875 ft) above sea level at its head at Indira Col on the India–China border down to 3,620 m (11,875 ft) at its glacier terminus, terminus. The entire Siachen Glacier, with all major passes, has been under the administration of India as part of the union territory of Ladakh Operation Meghdoot, since 1984. Pakistan maintains a territorial claim over the Siachen Glacier and controls the region west of Saltoro Ridge, lying west of the glacier, with Pakistani posts located 1 km below more than 100 Indian posts on the ridge. The Siachen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilafond La
Bilafond La (meaning "Pass of the Butterflies" in Balti language), also known as the Saltoro Pass, is a mountain pass situated on Saltoro Ridge, sitting immediately west of the vast Siachen Glacier, some directly north of map point NJ 980420 which defined the end of the 1972 Line of Control between Pakistan and India as part of the Simla Agreement. Bilafond La is on the ancient Silk Route linking the Indian Subcontinent and China. The Saltoro Mountains Range, of which western slopes are held by Pakistan and separated by the Actual Ground Position Line (AGPL) the higher peaks and passes are held by India all of which remain snowbound throughout the year, provides access to Siachen Glacier to its east through five passes, i.e., listed from south to north are Chulung La (5,800m), Yarma La (6,100m), Gyong La (5,640m), Bilafond La (6,160m) - also called Saltoro La, and Sia La (7,300m).Ghazanfar Ali and Hassan Akhtar Ghani, Siachen-The world's highest battlefield; Military ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indira Col
__NOTOC__ Indira Col West () is a mountain pass at altitude on the Indira Ridge of Siachen Muztagh in Karakoram Range. It is on the border between Indian-controlled Siachen Glacier and the Chinese-controlled Trans-Karakoram Tract (both in the disputed Kashmir region), close to the tripoint of India, Pakistan, and China. The India-Pakistan Actual Ground Position Line (AGPL) in the Siachen area ends near the pass. It is possible to ascend the pass from both the north and south sides controlled by China and India respectively. Indira Col East (Coord ), also ''Main Indira Col'' or just ''Indira Col'' (Hindi: इन्दिरा कोल), is another col on Indira Ridge which lies 2.4 km further east of Indira Col West at ) altitude. It is more difficult to ascend or descend on the north side controlled by China, but easier to do so from the south side controlled by India. India Saddle (Coord ), a geographical saddle, connects the Indira Col East and Indira Col West. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacier
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as crevasses and seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land“Glacier, N., Pronunciation.” Oxford English Dictionary, Oxford UP, June 2024, https://doi.org/10.1093/OED/7553486115. Accessed 25 Jan. 2025. and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water. On Earth, 99% of glacial ice is contained within vast ice sheets (also known as "continental glaciers") in the polar regions, but glaciers may be found in mountain ranges on ever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacier Terminus
A glacier terminus, toe, or snout, is the end of a glacier at any given point in time. Although glaciers seem motionless to the observer, in reality they are in endless Glacier#Motion, motion and the glacier terminus is always either advancing or retreating. The location of the terminus is often directly related to glacier mass balance, which is based on the amount of snowfall which occurs in the accumulation zone of a glacier, as compared to the amount that is melted in the ablation zone. The position of a glacier terminus is also impacted by localized or regional temperature change over time. Tracking Tracking the change in location of a glacier terminus is a method of monitoring a glacier's movement. The end of the glacier terminus is measured from a fixed position in neighboring bedrock periodically over time. The difference in location of a glacier terminus as measured from this fixed position at different time intervals provides a record of the glacier's change. A similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snowfall
Snow consists of individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes. It consists of frozen crystalline water throughout its life cycle, starting when, under suitable conditions, the ice crystals form in the atmosphere, increase to millimeter size, precipitate and accumulate on surfaces, then metamorphose in place, and ultimately melt, slide, or Sublimation (phase transition), sublimate away. Snowstorms organize and develop by feeding on sources of atmospheric moisture and cold air. Snowflakes Nucleation, nucleate around particles in the atmosphere by attracting supercooling, supercooled water droplets, which Freezing, freeze in hexagonal-shaped crystals. Snowflakes take on a variety of shapes, basic among these are platelets, needles, columns, and Hard rime, rime. As snow accumulates into a snowpack, it may blow into drifts. Over time, accumulated snow m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyong La
Gyong La is a mountain pass situated on Saltoro Ridge southwest of the vast Siachen Glacier, some directly north of map point NJ9842 which defined the end of the 1972 Line of Control between India and Pakistan. With Pakistan controlling areas just to the west along Chumik Glacier, the immediate Gyong La area has been under India's control since 1989. The Saltoro Mountains Range, of which western slopes are held by Pakistan and separated by the Actual Ground Position Line (AGPL) the higher peaks and passes are held by India all of which remain snowbound throughout the year, provides access to Siachen Glacier to its east through five passes, i.e., listed from south to north are Chulung La (5,800m), Yarma La (6,100m), Gyong La (5,640m), Bilafond La (6,160m) - also called Saltoro La, and Sia La (7,300m).Ghazanfar Ali and Hassan Akhtar Ghani, Siachen-The world's highest battlefield; Military Technology; Bonn Vol. 22, Iss. 3, (Mar 1998): S15-S17. Dozens of Indian military tent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sia La
Sia La is a mountain pass situated on Saltoro Ridge, in Gilgit Baltistan, Pakistan some north-northwest of map point NJ9842 which defined the end of the 1972 Line of Control between India and Pakistan as part of the Simla Agreement. Sia La sits near the Chinese border and immediately northwest of the upper part of the vast Siachen Glacier, connecting that glacier to the Pakistani-controlled Kondus Glacier and valley to the west. The Saltoro Mountains Range, of which western slopes are held by Pakistan and separated by the Actual Ground Position Line (AGPL) the higher peaks and passes are held by India all of which remain snowbound throughout the year, provides access to Siachen Glacier to its east through five passes, i.e., listed from south to north are Chulung La (5,800m), Yarma La (6,100m), Gyong La (5,640m), Bilafond La (6,160m) - also called Saltoro La, and Sia La (7,300m).Ghazanfar Ali and Hassan Akhtar Ghani, Siachen-The world's highest battlefield; Military Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sia Kangri
Sia Kangri (7,422 m, 24,350 ft) is a mountain in the Baltoro Muztagh in the Karakoram. Its summit lies on the border of Pakistan and China. About a kilometer southeast of the Sia Kangri summit is the tri point where territories controlled by India, Pakistan and China meet. Territories on all sides are disputed. The land immediately to the southwest of the peak is claimed by both Pakistan and India and controlled by Pakistan. The land to the northeast is part of the Trans-Karakoram Tract, controlled by China under a 1963 border agreement with Pakistan but claimed by India. The land to the southeast is claimed by Pakistan and India, but controlled by India, as a part of Ladakh. Sia Kangri is the 63rd highest mountain in the world, and the 25th highest in Pakistan. The peak is on the watershed between the Indus River basin and the Tarim Basin. Indira Col which is 3 km to the east is the northernmost point under India's control. Sia Kangri was first climbed in 1934 by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Pole
The Third Pole, also known as the Hindu Kush-Karakoram- Himalayan system (HKKH), is a mountainous region located in the west and south of the Tibetan Plateau. Part of High-Mountain Asia, it spreads over an area of more than across nine countries, i.e. Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Myanmar, Nepal, Pakistan and Tajikistan, bordering ten countries. The area is nicknamed the "Third Pole" because its mountain glaciers and snowfields store more frozen water than anywhere else in the world after the Arctic and Antarctic polar caps. With the world's loftiest mountains, comprising all 14 peaks above , it is the source of 10 major rivers and forms a global ecological buffer. The Third Pole area is rich with natural resources and consists of all or some of four global biodiversity hotspots. The mountain resources administer a wide range of ecosystem benefits and are the base for the drinking water, food production and livelihoods of the 220 million inhabitants of the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaciers
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as crevasses and seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land“Glacier, N., Pronunciation.” Oxford English Dictionary, Oxford UP, June 2024, https://doi.org/10.1093/OED/7553486115. Accessed 25 Jan. 2025. and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water. On Earth, 99% of glacial ice is contained within vast ice sheets (also known as "continental glaciers") in the polar regions, but glaciers may be found in mountain ranges on every c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakistan. (subscription required) Although the terms "Indian subcontinent" and "South Asia" are often also used interchangeably to denote a wider region which includes, in addition, Bhutan, the Maldives, Nepal and Sri Lanka, the "Indian subcontinent" is more of a geophysical term, whereas "South Asia" is more geopolitical. "South Asia" frequently also includes Afghanistan, which is not considered part of the subcontinent even in extended usage.Jim Norwine & Alfonso González, ''The Third World: states of mind and being'', pages 209, Taylor & Francis, 1988, Quote: ""The term "South Asia" also signifies the Indian Subcontinent""Raj S. Bhopal, ''Ethnicity, race, and health in multicultural societies'', pages 33, Oxford University Press, 2007, ; Q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |