|
Shirenzigou Culture
The Shirenzigou culture (, ca. 410–190 BCE), also referred to as Dongheigou (), or Heigouliang-Dongheigou (黑沟梁-东黑沟), is an archaeological culture from the Shirenzigou site in Barkol County, to the east of the Tarim Basin. Skeletal evidence from sites in Shirenzigou and Xigou in eastern Xinjiang indicate that by the fourth century BCE both horseback riding and mounted archery were practiced along China's northwest frontier. Genetic studies on Iron Age individuals of the Shirenzigou site dated to circa 200 BCE have shown a fairly balanced admixture between the West Eurasian and East Eurasian genetic pools. The West Eurasian component was Yamnaya-related, while the East Eurasian component was Northeast Asian-related. The Yamnaya component suggests a strong probability that the Shirenzigou populations were derived from the Afanasievo culture to the north, and spoke an Indo-European language. This reinforces an Afanasievo origin hypothesis for the Tocharians, often cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orange Dot (semi-transparent)
Orange most often refers to: *Orange (fruit), the fruit of the tree species '' Citrus'' × ''sinensis'' ** Orange blossom, its fragrant flower ** Orange juice *Orange (colour), the color of an orange fruit, occurs between red and yellow in the visible light spectrum *Some other citrus or citrus-like fruit, see ''list of plants known as orange'' *Orange (word), ''Orange'' (word), both a noun and an adjective in the English language Orange may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Films * Game of Life (film), ''Game of Life'' (film), a 2007 film originally known as ''Oranges'' * Orange (2010 film), ''Orange'' (2010 film), a Telugu-language film * The Oranges (film), ''The Oranges'' (film), a 2011 American romantic comedy starring Hugh Laurie * Orange (2012 film), ''Orange'' (2012 film), a Malayalam-language film * Orange (2015 film), ''Orange'' (2015 film), a Japanese film * Orange (2018 film), ''Orange'' (2018 film), a Kannada-language film Music Groups and labels * Ora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andronovo Culture
The Andronovo culture is a collection of similar local Late Bronze Age cultures that flourished 2000–1150 BC,Grigoriev, Stanislav, (2021)"Andronovo Problem: Studies of Cultural Genesis in the Eurasian Bronze Age" in Open Archaeology 2021 (7), p.3: "...By Andronovo cultures we may understand only Fyodorovka and Alakul cultures..."Parpola, Asko, (2020)"Royal 'Chariot' Burials of Sanauli near Delhi and Archaeological Correlates of Prehistoric Indo-Iranian Languages" in Studia Orientalia Electronica, Vol. 8, No. 1, Oct 23, 2020, p.188: "...the Alakul’ culture (c.2000–1700 BCE) in the west and the Fëdorovo culture (c.1850–1450 BCE) in the east..." spanning from the southern Urals to the upper Yenisei River in central Siberia and western Xinjiang in the east. In the south, the Andronovo sites reached Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. It is agreed among scholars that the Andronovo culture was Indo-Iranian languages, Indo-Iranian.: "Archaeologists are now generally agreed that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemurchek Culture
The Chemurchek culture (Ch:切木尔切克, ''Qièmùěrqièkè''; Ru: Чемурчекская культура), also called Khemtseg, Hemtseg, Qiemu’erqieke, Shamirshak (2750–1900 BCE), is a Bronze Age archaeological culture of western Mongolia and the borders of neighbouring countries, such as the Dzungarian Basin of Xinjiang and eastern Kazakhstan. It immediately follows the Afanasievo culture, and is contemporary with the early Tarim Mummies to the south and the Okunev culture to the north. The Chemurchek burials are characterized by large rectangular stone fences, built around collective tombs. The mortuary position of the deceased (supine position with flexed legs) is similar to that of the Afanasievo culture, but the Chemurchek culture is considered distinct. The name "Chemurchek culture" is derived from the Chemurchek cemetery in Altay City, Xinjiang, China. Chemurchek sites have been identified from western Mongolia to areas as far west as the Ili River, Ili valley ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yanbulaq Culture
The Yanbulaq culture (Ch: 焉不拉克文化 or 焉布拉克文化, Yanbulake wenhua, 1100–500 BCE) was an ancient culture based on the tombs of the Yanbulaq Cemetery (Chinese 焉不拉克古墓群, Pinyin Yānbùlākè gǔmùqún or焉不拉克墓地, Yānbùlākè mùdì , English Yanbulaq Cemetery) located on the northern hills of the Qumul Basin, in Yizhou District, Xinjiang, China. It was a Bronze Age culture, or an early Iron Age culture. The cemetery at Yanbulaq contained 29 mummies which dated from 1100 to 500 BCE, 21 of which are Asian—the earliest Asian mummies found in the Tarim Basin—and the remaining 8 are of the same Caucasian physical type as found at Qäwrighul. These later and eastern "Tarim mummies" represented both "Caucasoid" and "Mongoloid" remains, indicating contact between newly arrived western nomads and agricultural communities in the east. The Yuezhi may have been positionned around the Shirenzigou culture area, between the Subeshi culture to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subeshi Culture
The Subeshi culture (; 1100–100 BCE), also rendered as Subeishi culture or Subeixi culture, is an Iron Age culture from the area of Shanshan County, Turfan, Xinjiang, at the eastern edge of the Tarim Basin. The Subeshi culture contributes some of the later period Tarim Mummies. It might be associated with the Jushi Kingdom known from Chinese historical sources. The culture includes three closely related cemeteries: * the Subeshi cemetery * the Shengjindian cemetery, * the Yanghai cemetery. After 200 BCE, the Subeshi culture may have evolved into the later walled city-state culture of the Jushi Kingdom. Characteristics The origins of the Subeshi culture were influenced by the cultures of West Asia and Central Asia as far back as the late Neolithic period and the early Bronze Age, when bronze technology, pottery and ornamation styles were introduced from the west, before spreading further east to the early cultures of China, such as the Siba culture (about 2000–1600 BCE), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barkol Kazakh Autonomous County
Barkol Kazakh Autonomous County (sometimes Barkul or Balikul in English) is a part of Hami Prefecture in Xinjiang and has an area of . It forms part of the China–Mongolia border (bordering the Mongolian provinces of Khovd and Govi-Altai) on the county's north, while bordering Yizhou District to the south, Yiwu County to the east and Changji's Mori Kazakh Autonomous County to the west. Barkol was made an autonomous county on October 1, 1954. It is noted for camel breeding and horse breeding with the Barkol horse well known throughout China. Due to the large number of camels, which is unparalleled in China, the county is nicknamed the "county of ten thousand camels". History Barkol was a territory of Pulei country in ancient times. During the continuous Han–Xiongnu War, in 72 BC, Emperor Xuan of Han sent Zhao Chongguo as general of Pulei, together with Wusun to attack the Huns. After the Northern Wei dynasty, Rouran and Gaoche competed for the Pule grassland for a long tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuezhi
The Yuezhi were an ancient people first described in China, Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defeat at the hands of the Xiongnu in 176 BC, the Yuezhi split into two groups migrating in different directions: the Greater Yuezhi and Lesser Yuezhi. This started a complex domino effect that radiated in all directions and, in the process, set the course of history for much of Asia for centuries to come. The Greater Yuezhi initially migrated northwest into the Ili River, Ili Valley (on the modern borders of China and Kazakhstan), where they reportedly displaced elements of the Sakas. They were driven from the Ili Valley by the Wusun and migrated southward to Sogdia and later settled in Bactria. The Greater Yuezhi have consequently often been identified with peoples mentioned in classical European sources as having overrun the Greco-Bactrian K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pazyryk Culture
The Pazyryk culture ( ''Pazyrykskaya'' kul'tura) is a Saka (Central Asian Scythian cultures, Scythian) nomadic Iron Age archaeological culture (6th to 3rd centuries BC) identified by excavated artifacts and mummified humans found in the Siberian permafrost, in the Altay Mountains, Kazakhstan and Mongolia. The mummies are buried in long barrows (or ''kurgans'') similar to the tomb mounds of Scythian culture in Ukraine. The type site are the Pazyryk burials of the Ukok Plateau. Many artifacts and human remains have been found at this location, including the Siberian Ice Princess, indicating a flourishing culture at this location that benefited from the many trade routes and caravans of merchants passing through the area. The Pazyryk are considered to have had a war-like life. The Pazyryk culture was preceded by the "Arzhan culture" (Initial Scythian period, 8th - 7th century BC). Archaeology Other kurgan cemeteries associated with the culture include those of Bashadar, Tuekta, Ul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yanbulake Culture
The Yanbulaq culture (Ch: 焉不拉克文化 or 焉布拉克文化, Yanbulake wenhua, 1100–500 BCE) was an ancient culture based on the tombs of the Yanbulaq Cemetery (Chinese 焉不拉克古墓群, Pinyin Yānbùlākè gǔmùqún or焉不拉克墓地, Yānbùlākè mùdì , English Yanbulaq Cemetery) located on the northern hills of the Qumul Basin, in Yizhou District, Xinjiang, China. It was a Bronze Age culture, or an early Iron Age culture. The cemetery at Yanbulaq contained 29 mummies which dated from 1100 to 500 BCE, 21 of which are Asian—the earliest Asian mummies found in the Tarim Basin—and the remaining 8 are of the same Caucasian physical type as found at Qäwrighul. These later and eastern "Tarim mummies" represented both "Caucasoid" and "Mongoloid" remains, indicating contact between newly arrived western nomads and agricultural communities in the east. The Yuezhi may have been positionned around the Shirenzigou culture area, between the Subeshi culture to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
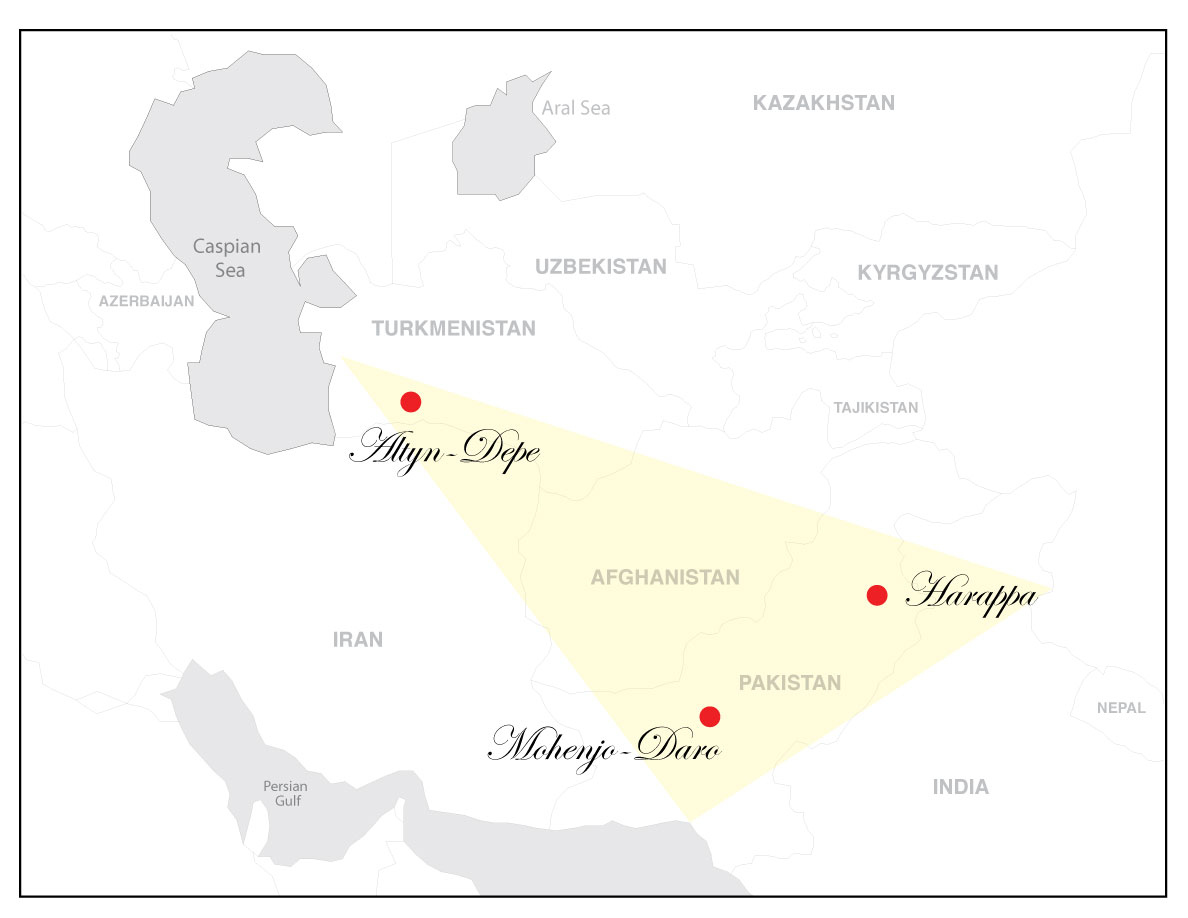
Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex
The Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex (BMAC) is the modern archaeological designation for a particular Middle Bronze Age civilisation of southern Central Asia, also known as the Oxus Civilization. The civilisation's urban phase or Integration Era was dated in 2010 by Sandro Salvatori to –1950 BC, but a different view is held by Nadezhda A. Dubova and Bertille Lyonnet, –1700 BC.Lyonnet, Bertille, and Nadezhda A. Dubova, (2020b)"Questioning the Oxus Civilization or Bactria- Margiana Archaeological Culture (BMAC): an overview" in Bertille Lyonnet and Nadezhda A. Dubova (eds.), ''The World of the Oxus Civilization'', Routledge, London and New York, p. 32.: "...Salvatori has often dated its beginning very early (ca. 2400 BC), to make it match with Shahdad where a large amount of material similar to that of the BMAC has been discovered. With the start of international cooperation and the multiplication of analyses, the dates now admitted by all place the Oxus Civilizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinjiang
Xinjiang,; , SASM/GNC romanization, SASM/GNC: Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Sinkiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the Northwest China, northwest of the country at the crossroads of Central Asia and East Asia. Being the List of Chinese administrative divisions by area, largest province-level division of China by area and the List of the largest country subdivisions by area, 8th-largest country subdivision in the world, Xinjiang spans over and has about 25 million inhabitants. Xinjiang Borders of China, borders the countries of Afghanistan, India, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia, Pakistan, Russia, and Tajikistan. The rugged Karakoram, Kunlun Mountains, Kunlun and Tian Shan mountain ranges occupy much of Xinjiang's borders, as well as its western and southern regions. The Aksai Chin and Trans-Karakoram Tract regions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tocharians
The Tocharians or Tokharians ( ; ) were speakers of the Tocharian languages, a group of Indo-European languages known from around 7,600 documents from the 6th and 7th centuries, found on the northern edge of the Tarim Basin (modern-day Xinjiang, China). The name "Tocharian" was given to these languages in the early 20th century by scholars who identified their speakers with a people known in ancient Greek sources as the ''Tokharistan, Tókharoi'' (), who inhabited Bactria from the 2nd century BC. This identification is now generally considered erroneous, but the name "Tocharian" remains the most common term for the languages and their speakers. Their Endonym and exonym, endonym is unknown, although they may have referred to themselves as the ''Karasahr, Agni'', ''Kucha, Kuči'', and ''Krorän'' or as the ''Agniya'' and ''Kuchiya'' known from Sanskrit texts. Agricultural communities first appeared in the oases of the northern Tarim circa 2000 BC. Some scholars have linked the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |