|
Shark Fin (other)
Mount Schwerdtfeger () is a peak, high on the ridge at the head of Renegar Glacier, south of Mount Kempe in the Royal Society Range, Victoria Land, Antarctica. Name Mount Schwerdtfeger was named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) (1994) after Werner Schwerdtfeger, senior meteorological researcher, University of Wisconsin, a driving force in the study of Antarctic meteorology. His specialty was the study of the barrier winds east of the Antarctic Peninsula. Nearby features Fisher Bastion . A high rectangular massif high between the upper reaches of Potter Glacier and Foster Glacier, southeast of Mount Huggins. Named by US-ACAN in 1994 after Commander Dwight David Fisher (Fisher Peak, q.v.), United States Navy Commanding Officer of NSFA, 1987-89. Mount Duvall An ice-covered mountain, high, standing close west of Fisher Bastion on the north side of Solomon Glacier. Named byUS-ACAN (1994) after Thomas L. Duvall, Jr., who conducted rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
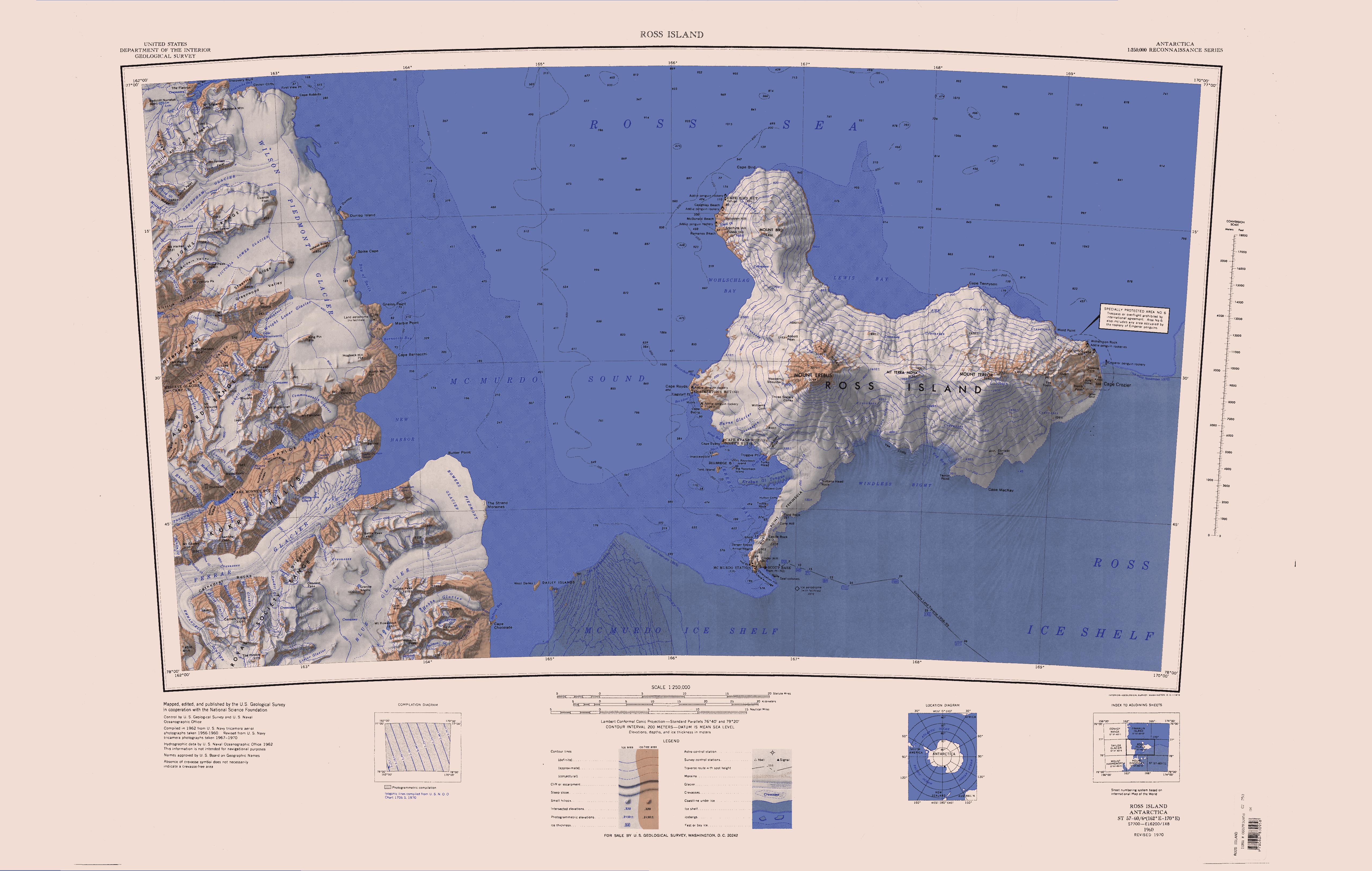
Victoria Land
Victoria Land is a region in eastern Antarctica which fronts the western side of the Ross Sea and the Ross Ice Shelf, extending southward from about 70°30'S to 78th parallel south, 78°00'S, and westward from the Ross Sea to the edge of the Antarctic Plateau. It was discovered by Captain James Clark Ross in January 1841 and named after Victoria of the United Kingdom, Queen Victoria. The rocky promontory of Minna Bluff is often regarded as the southernmost point of Victoria Land, and separates the Scott Coast to the north from the Hillary Coast of the Ross Dependency to the south. History Early explorers of Victoria Land include James Clark Ross and Douglas Mawson. In 1979, scientists discovered a group of 309 Meteorite, meteorites in Antarctica, some of which were found near the Allan Hills in Victoria Land. The meteorites appeared to have undergone little change since they were formed at what scientists believe was the birth of the Solar System. In 1981, Lichen, lichens fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Range
The Royal Society Range () is a majestic range of mountains in Victoria Land, Antarctica, rising to along the west shore of McMurdo Sound between the Koettlitz, Skelton and Ferrar Glaciers. They are south of the Kukri Hills, southeast of the Quartermain Mountains, and northeast of the Worcester Range. With its summit at , the massive Mount Lister forms the highest point in this range. Mount Lister is located along the western shore of McMurdo Sound between the Koettlitz, Skelton and Ferrar glaciers. Other notable local terrain features include Allison Glacier, which descends from the west slopes of the Royal Society Range into Skelton Glacier. Discovery and naming The range was probably first seen by Captain James Clark Ross in 1841. It was explored by the British National Antarctic Expedition (BrNAE; 1901–04) under Robert Falcon Scott, who named the range after the Royal Society and applied names of its members to many of its peaks. For example, Mount Lister was nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
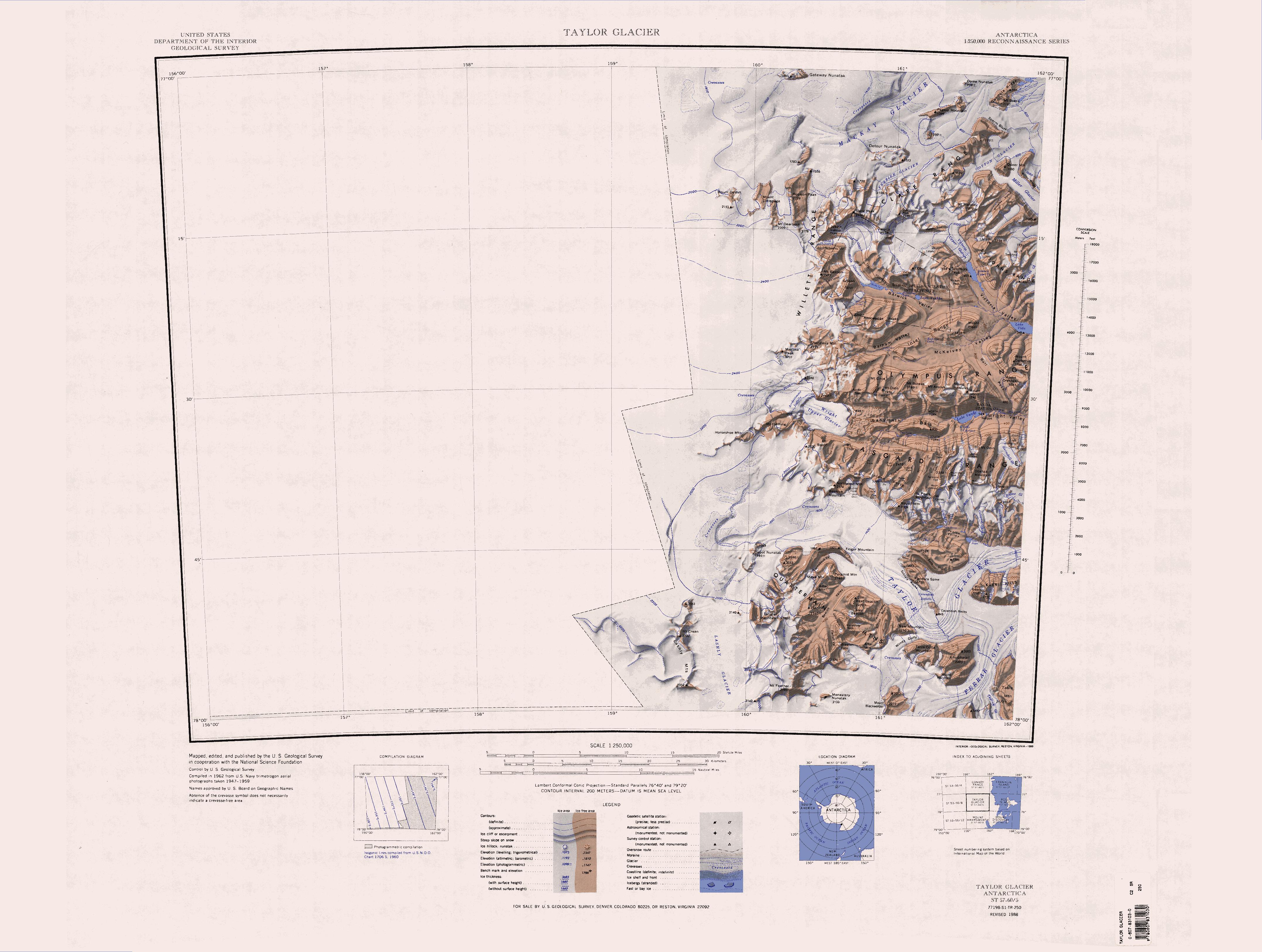
Renegar Glacier
Koettlitz Glacier () is a large Antarctic glacier lying west of Mount Morning and Mount Discovery in the Royal Society Range, flowing from the vicinity of Mount Cocks northeastward between Brown Peninsula and the mainland into the ice shelf of McMurdo Sound. Naming and exploration Koettlitz Glacier was discovered by the British National Antarctic Expedition (1901–04) which named it for Dr. Reginald Koettlitz, physician and botanist of the expedition. Glaciology The Koettlitz Glacier appears to have been smaller during the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) than it is today, while the Ross Ice Shelf was larger. There is evidence that during the LGM the mouth of the Pyramid Trough was blocked by grounded Ross Sea ice until at least 11,000 years ago. In the last 3,000 years the glacier has advanced, and today the mouth of ice-free Pyramid Trough is blocked by the Koettlitz Glacier. Under this hypothesis, the glacier may have been thicker at the coast due to buttressing, but may hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Kempe
Mount Dromedary () is a hump-shaped mountain, over high, standing east of Mount Kempe in the Royal Society Range of Victoria Land, Antarctica. First mapped by the BrNAE, 1901–04, but named by the BrAE, 1910–13. Named for the appearance of the mountain which resembles a dromedary's hump. Location Mount Dromedary is in the southeast of the Royal Society Range. The Pyramid, the southeast tip of the range, is to the southeast. The head of Renegar Glacier, a tributary of the Koettlitz Glacier, is to the south. Mount Kempe is to the east, connected to Mount Dromedary by a ridge that runs along the south side of the Kempe Glacier. Features to the north and east include Dismal Ridge, Glee Glacier, Roaring Valley, Lake Porkchop, Penny Lake, The Amphitheatre and Dromedary Glacier. Western features Nearby features to the west of Mount Dromedary include: Mount Kempe . A peak, high, midway between Mounts Muggins and Dromedary. Discovered by the British National Antarctic Expedit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potter Glacier
Skelton Glacier () is a large glacier flowing from the polar plateau into the Ross Ice Shelf at Skelton Inlet on the Hillary Coast, south of Victoria Land, Antarctica. Naming and exploration Skelton Glacier was named after the Skelton Inlet by the New Zealand party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (CTAE), 1956–58. The glacier was chosen in 1957 as the New Zealand party's route from the Ross Ice Shelf to the Antarctic Plateau. The Arctic Institute of North America organized two ground traverses in the antarctic summer of 1959–60 sponsored by the United States Antarctic Research Program. The first left New Zealand's Scott Base on 16 October 1959, crossed part of the Ross Ice Shelf, and on 27 October 1959 reached the foot of the Skelton Glacier. They traversed up the heavily crevassed glacier to a fuel cache deposited on the edge of the Victoria Land plateau by planes of the United States Navy and Air Force. From there they travelled more than to the end station ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foster Glacier
Koettlitz Glacier () is a large Antarctic glacier lying west of Mount Morning and Mount Discovery in the Royal Society Range, flowing from the vicinity of Mount Cocks northeastward between Brown Peninsula and the mainland into the ice shelf of McMurdo Sound. Naming and exploration Koettlitz Glacier was discovered by the British National Antarctic Expedition (1901–04) which named it for Dr. Reginald Koettlitz, physician and botanist of the expedition. Glaciology The Koettlitz Glacier appears to have been smaller during the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) than it is today, while the Ross Ice Shelf was larger. There is evidence that during the LGM the mouth of the Pyramid Trough was blocked by grounded Ross Sea ice until at least 11,000 years ago. In the last 3,000 years the glacier has advanced, and today the mouth of ice-free Pyramid Trough is blocked by the Koettlitz Glacier. Under this hypothesis, the glacier may have been thicker at the coast due to buttressing, but may have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Huggins
Mount is often used as part of the name of specific mountains, e.g. Mount Everest. Mount or Mounts may also refer to: Places * Mount, Cornwall, a village in Warleggan parish, England * Mount, Perranzabuloe, a hamlet in Perranzabuloe parish, Cornwall, England People * Mount (surname) * William L. Mounts (1862–1929), American lawyer and politician Computing and software * Mount (computing), the process of making a file system accessible * Mount (Unix), the utility in Unix-like operating systems which mounts file systems Books * ''Mount!'', a 2016 novel by Jilly Cooper Displays and equipment * Mount, a fixed point for attaching equipment, such as a hardpoint on an airframe * Mounting board, in picture framing * Mount, a hanging scroll for mounting paintings * Mount, to display an item on a heavy backing such as foamcore, e.g.: ** To pin a biological specimen, on a heavy backing in a stretched stable position for ease of dissection or display ** To prepare dead animal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Geographic Board
The New Zealand Geographic Board Ngā Pou Taunaha o Aotearoa (NZGB) is the authority over geographical and hydrographic names within New Zealand and its territorial waters. This includes the naming of small urban settlements, localities, mountains, lakes, rivers, waterfalls, harbours and natural features and may include researching local Māori names. It has named many geographical features in the Ross Sea region of Antarctica. It has no authority to alter street names (a local body responsibility) or the name of any country. The board was established by the New Zealand Geographic Board Act 1946, which has since been replaced by the New Zealand Geographic Board (Ngā Pou Taunaha o Aotearoa) Act 2008. Although an independent institution, it is responsible to the Minister for Land Information. The NZGB secretariat is part of Toitū Te Whenua Land Information New Zealand (LINZ) and provides the board with administrative and research assistance and advice. The New Zealand Geogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Victoria Land
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least above the surrounding land. A few mountains are inselberg, isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. mountain formation, Mountains are formed through tectonic plate, tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through Slump (geology), slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce Alpine climate, colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the Montane ecosystems, ecosystems of mountains: different elevations hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |