|
Shan State Langur
The Shan State langur (''Trachypithecus melamera'') is a species of primate in the family Cercopithecidae. It is found in eastern Myanmar and southwest China. It had been generally considered a subspecies In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ... or even a synonym of Phayre's leaf monkey (''T. phayrei'') until Roos, et al., elevated it to species status in 2020. References Trachypithecus Mammals of Myanmar Mammals of China Primates of Southeast Asia Taxa named by Daniel Giraud Elliot Taxobox binomials not recognized by IUCN Mammals described in 1909 {{primate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Giraud Elliot
Daniel Giraud Elliot (March 7, 1835 – December 22, 1915) was an American zoologist and the founder of the American Ornithologist Union. Life He was born in New York City on March 7, 1835, to George and Rebecca Elliot. In 1858, he married Ann Eliza Henderson. From 1869 to 1879, he was in London and established strong links to British ornithologists and naturalists. Elliot used his wealth to publish a series of sumptuous color-plate books on birds and other animals. Elliot wrote the text himself and commissioned artists such as Joseph Wolf and Joseph Smit, both of whom had worked for John Gould, to provide the illustrations. The books included ''A Monograph of the Phasianidae (Family of the Pheasants)'' (1870–72), ''A Monograph of the Paradiseidae or Birds of Paradise'' (1873), ''A Monograph of the Felidae or Family of Cats'' (1878) and ''Review of the Primates'' (1913). In 1890, he was President of the American Ornithologists' Union. Elliot became the first curator of zool ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primate
Primates are a diverse order (biology), order of mammals. They are divided into the Strepsirrhini, strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the Haplorhini, haplorhines, which include the Tarsiiformes, tarsiers and the Simiiformes, simians (monkeys and apes, the latter including humans). Primates arose 85–55 million years ago first from small Terrestrial animal, terrestrial mammals, which adapted to living in the trees of tropical forests: many primate characteristics represent adaptations to life in this challenging environment, including large brains, visual acuity, color vision, a shoulder girdle allowing a large degree of movement in the shoulder joint, and dextrous hands. Primates range in size from Madame Berthe's mouse lemur, which weighs , to the eastern gorilla, weighing over . There are 376–524 species of living primates, depending on which classification is used. New primate species continue to be discovered: over 25 species were d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cercopithecidae
Old World monkey is the common English name for a family of primates known taxonomically as the Cercopithecidae (). Twenty-four genera and 138 species are recognized, making it the largest primate family. Old World monkey genera include baboons (genus ''Papio''), red colobus (genus '' Piliocolobus'') and macaques (genus '' Macaca''). Common names for other Old World monkeys include the talapoin, guenon, colobus, douc (douc langur, genus '' Pygathrix''), vervet, gelada, mangabey (a group of genera), langur, mandrill, surili (''Presbytis''), patas, and proboscis monkey. Phylogenetically, they are more closely related to apes than to New World monkeys. They diverged from a common ancestor of New World monkeys around 45 to 55 million years ago. The smallest Old World monkey is the talapoin, with a head and body 34–37 cm in length, and weighing between 0.7 and 1.3 kg. The largest is the male mandrill, around 70 cm in length, and weighing up to 50 kg. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explains, the English spellings of both Myanmar and Burma assume a non-rhotic variety of English, in which the letter r before a consonant or finally serves merely to indicate a long vowel: �mjænmɑː, ˈbɜːmə So the pronunciation of the last syllable of Myanmar as ɑːror of Burma as ɜːrməby some speakers in the UK and most speakers in North America is in fact a spelling pronunciation based on a misunderstanding of non-rhotic spelling conventions. The final ''r'' in ''Myanmar'' was not intended for pronunciation and is there to ensure that the final a is pronounced with the broad ''ah'' () in "father". If the Burmese name my, မြန်မာ, label=none were spelled "Myanma" in English, this would be pronounced at the end by al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
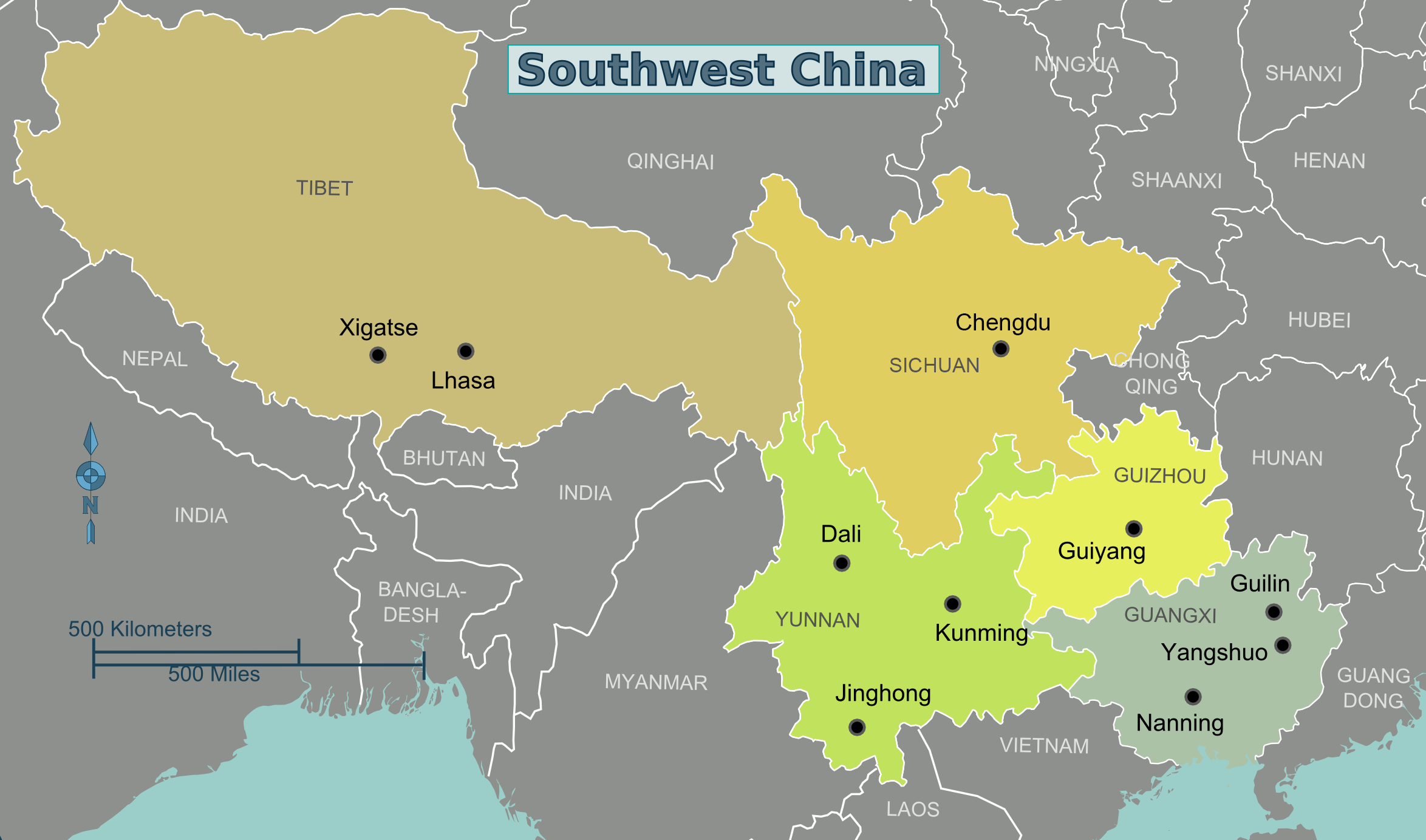
Southwest China
Southwest China () is a region in the south of the People's Republic of China. Geography Southwest China is a rugged and mountainous region, transitioning between the Tibetan Plateau to the west and the Chinese coastal hills (东南丘陵) and plains to the east. Key geographic features in the region include the Hengduan Mountains in the west, the Sichuan Basin in the northeast, and the karstic Yungui Plateau in the east. The majority of the region is drained by the Yangtze River which forms the Three Gorges in the northeast of the region. The narrowest concept of Southwest China consists of Sichuan, Chongqing, Yunnan, and Guizhou, while wider definitions often include Guangxi and western portions of Hunan. The official government definition of Southwest China includes the core provinces of Sichuan, Chongqing, Yunnan, and Guizhou, in addition to the Tibet Autonomous Region. History Portions of Southwest China were incorporated in the 3nd century BCE into the Qin dyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics ( morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species have subspecies, but for those that do there must be at least two. Subspecies is abbreviated subsp. or ssp. and the singular and plural forms are the same ("the subspecies is" or "the subspecies are"). In zoology, under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, the subspecies is the only taxonomic rank below that of species that can receive a name. In botany and mycology, under the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants, other infraspecific ranks, such as variety, may be named. In bacteriology and virology, under standard bacterial nomenclature and virus nomenclature, there are recommendations but not strict requirements for recognizing other important infraspecific ranks. A taxonomist decides w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phayre's Leaf Monkey
Phayre's leaf monkey (''Trachypithecus phayrei''), also known as Phayre's langur, is a species of lutung native to South and Southeast Asia, namely India, Bangladesh, and Myanmar. Populations from further east are now thought to belong to other species. It is listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List and is threatened by hunting and loss of habitat. The species epithet commemorates Arthur Purves Phayre. Taxonomy The scientific name ''Presbytis phayrei'' was used by Edward Blyth in 1847 for two young individuals captured alive in the Arakan Mountains in Myanmar. Phayre's langur is one of the most widespread members of the genus, but its actual distribution and intraspecific taxonomy remain controversial. Previously, three subspecies were recognized, namely ''T. p. crepusculus'', ''T. p. phayrei'' and ''T. p. shanicus''. Three separate species ''T. phayrei'', ''T. melamera'' (formerly ''T. p. shanicus''), and '' T. popa sp. nov.'' have been proposed based on mitochondrial genom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trachypithecus
The lutungs, langurs, or leaf monkeys are a group of Old World monkeys in the genus ''Trachypithecus'' (derived from Greek , meaning "rough" and , meaning "monkey"). Their range is much of Southeast Asia (northeast India, Vietnam, southern China, Borneo, Thailand, Java, and Bali). The name "lutung" comes from the Sundanese language meaning "blackness", ultimately from Proto-Austronesian *''luCuŋ'' (which originally referred to the Formosan rock macaque); it is preferred in one paper because the authors wanted the name langurs to only refer to monkeys in the genus '' Semnopithecus'', although some "lutungs" are now "langurs" again. Evolution Genetic analysis indicates that the ancestors of the modern species of lutung first differentiated from one another a little over 3 million years ago, during the late Pliocene. The various species alive today then diverged during the Pleistocene, presumably driven by habitat changes during the Ice Ages. The oldest fossils clearly iden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals Of Myanmar
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla (cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together with S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals Of China
This is a list of the mammal species recorded in China. There are 495 mammal species in China, of which thirteen are critically endangered, twenty-four are endangered, forty-seven are vulnerable, and seven are near threatened. One of the species listed for China can no longer be found in the wild. The following tags are used to highlight each species' conservation status as assessed by the International Union for Conservation of Nature: Some species were assessed using an earlier set of criteria. Species assessed using this system have the following instead of near threatened and least concern categories: Order: Sirenia (manatees and dugongs) Sirenia is an order of fully aquatic, herbivorous mammals that inhabit rivers, estuaries, coastal marine waters, swamps, and marine wetlands. All four species are endangered. *Family: Dugongidae **Genus: ''Dugong'' ***Dugong, ''D. dugon'' Order: Proboscidea (elephants) The elephants comprise three living species and are the lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primates Of Southeast Asia
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians (monkeys and apes, the latter including humans). Primates arose 85–55 million years ago first from small terrestrial mammals, which adapted to living in the trees of tropical forests: many primate characteristics represent adaptations to life in this challenging environment, including large brains, visual acuity, color vision, a shoulder girdle allowing a large degree of movement in the shoulder joint, and dextrous hands. Primates range in size from Madame Berthe's mouse lemur, which weighs , to the eastern gorilla, weighing over . There are 376–524 species of living primates, depending on which classification is used. New primate species continue to be discovered: over 25 species were described in the 2000s, 36 in the 2010s, and three in the 2020s. Primates have larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Daniel Giraud Elliot
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)