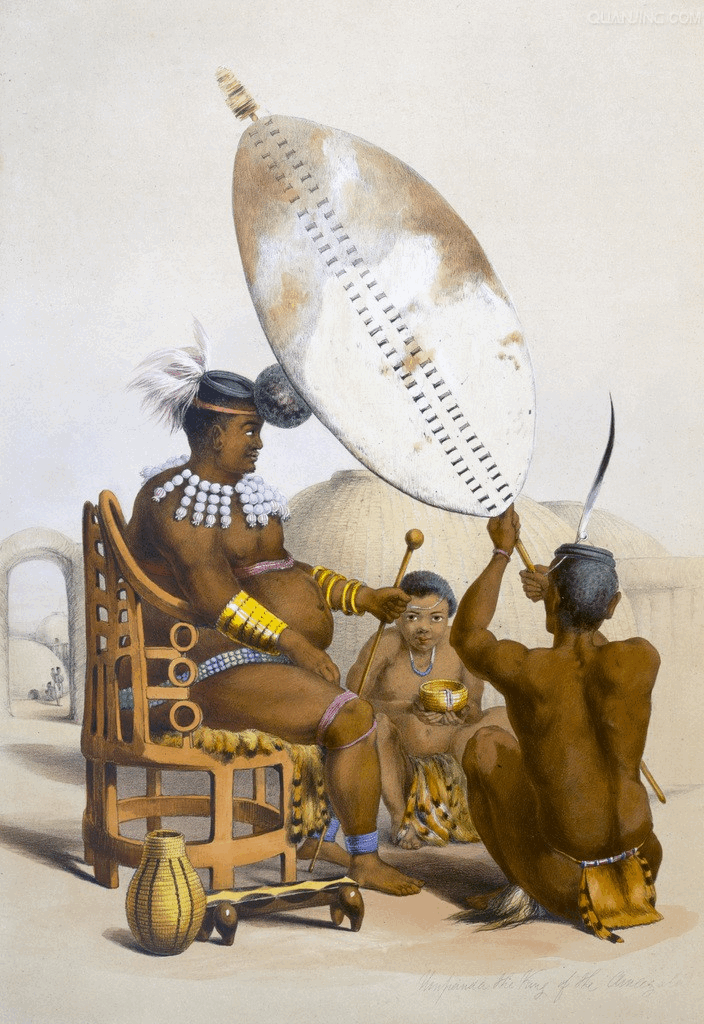|
Shaka
Shaka kaSenzangakhona (–24 September 1828), also known as Shaka (the) Zulu () and Sigidi kaSenzangakhona, was the king of the Zulu Kingdom from 1816 to 1828. One of the most influential monarchs of the Zulu, he ordered wide-reaching reforms that reorganized the military into a formidable force. King Shaka was born in the lunar month of ''uNtulikazi'' (July) in 1787, in Mthonjaneni, KwaZulu-Natal Province, South Africa. The son of the Zulu King Senzankakhona kaJama, he was spurned as an illegitimate son. Shaka spent part of his childhood in his mother's settlements, where he was initiated into an '' ibutho lempi'' (fighting unit/regiment), serving as a warrior under Inkosi Dingiswayo. King Shaka refined the ''ibutho'' military system with the Mthethwa Paramountcy's support over the next several years. He forged alliances with his smaller neighbours to counter Ndwandwe raids from the north. The initial Zulu maneuvers were primarily defensive, as King Shaka preferred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impi
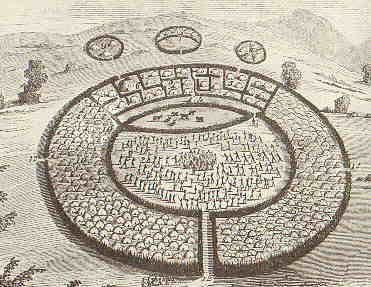
is a Nguni word meaning war or combat and by association any body of men gathered for war, for example is a term denoting an army. were formed from regiments () from large militarised homesteads (). In English is often used to refer to a Zulu regiment, which is called an in Zulu, or the army of the Zulu Kingdom. Its beginnings lie far back in historic local warfare customs, when groups of armed men called battled. They were systematised radically by the Zulu king Shaka, who was then only the exiled illegitimate son of king Senzangakhona kaJama, but already showing much prowess as a general in the army () of Mthethwa king Dingiswayo in the Ndwandwe–Zulu War of 1817–1819. Genesis The Zulu impi is popularly identified with the ascent of Shaka, ruler of the relatively small Zulu tribe before its explosion across the landscape of southern Africa, but its earliest shape as an instrument of statecraft lies in the innovations of the Mthethwa chieftain Dingiswayo, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dingiswayo
King Dingiswayo () ( – 1817) was a king of the Mthethwa Kingdom, well known in history for his mentorship over a young Zulu general, Shaka kaSenzangakhona, who rose to become the greatest of the Zulu Kings. His father was the Mthethwa King, Jobe kaKayi. It was under King Dingiswayo that the Mthethwa rose to prominence, mostly employing diplomacy and assimilation of nearby chiefdoms to strengthen his power base. According to Mthethwa (1995), the Mthethwas are descended from the Nguni peoples of northern Natal and the Lubombo Mountains, whose modern identity dates back some 700 years. Lineage Dingiswayo's lineage can be traced back to Mthethwa the first. It is possible that Dingiswayo and Zwide kaLanga shared the same lineage through Xaba KaMadungu. Zwide was the king of the Ndwandwe, Khumalo, Msene, and Jele peoples. (There does not appear to be a direct family link between Zwide kaLanga and Soshangane kaZikode of the Nxumalo people). Dingiswayo's Mthethwa famil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senzangakhona KaJama
Senzangakhona kaJama (c. 1762 – 1816) was the king of the Zulu Kingdom, and primarily notable as the father of three Zulu kings who ruled during the period when the Zulus achieved prominence, led by his oldest son King Shaka. Biography His father was chief Jama kaNdaba and his mother was Mthaniya Sibiya. He succeeded on his father's death. During the chieftaincy of Senzangakhona, the Zulus were a small clan in the Mthethwa confederation which was ruled by Dingiswayo. Senzangakhona’s name is derived from the Zulu word meaning "he who acts with a good reason". Although the Zulus practised ritual circumcision, the practice was slowly dying out. Senzangakhona and Shaka were not circumcised, marking this trend in Zulu culture. Glyn Charles Hewson. 1970. ''Shaka's kingship and the rise of the Zulu state, 1795-1828'', page 67. University of Wisconsin--Madison. Wives and children Senzangakhona married at least sixteen women by which he had fourteen known sons. His d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nandi (mother Of Shaka)
Nandi KaBhebhe (c. 1760 – October 10, 1827) was a daughter of Bhebhe, a past Elangeni chief and the mother of Shaka kaSenzangakhona, King of the Zulus. Birth Queen Nandi Bhebhe was born in Melmoth in 1760. Her father was a chief of the Elangeni (Mhlongo) people. Personal life Nandi Bhebhe was impregnated out of wedlock by Jama's son, Senzangakhona. The Mhlongo people demanded Senzangakhona pay damages for his non-traditional act. The Mhlongo approached the Jamas to settle the matter. Nandi was on the fore-front of this case and discussion. She personally demanded 55 head of cattle as payment for damages done to her and the herd was delivered to the Mhlongo people. The Jamas and Senzangakhona agreed to pay the damages demanded by Mhlongo people so as to avoid war. On the other hand, Senzangakhona did truly love Nandi. After Nandi gave birth to her son, Shaka, she initially spent some time at Senzangakhona's kraal before her relationship with Senzangakhona deteriorated, forcin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zulu People
Zulu people (; ) are a native people of Southern Africa of the Nguni people, Nguni. The Zulu people are the largest Ethnic groups in South Africa, ethnic group and nation in South Africa, living mainly in the province of KwaZulu-Natal. They originated from Nguni communities who took part in the Bantu migrations over millennia. As the clans integrated, the rulership of Shaka brought success to the Zulu nation due to his improved military tactics and organization. Zulus take pride in their ceremonies such as the Umhlanga (ceremony)#South Africa, Umhlanga, or Reed Dance, and their various forms of beadwork. The art and skill of beadwork take part in the identification of Zulu people and act as a form of communication and dedication to the nation and specific traditions. Today, the Zulu people are predominantly Christian, but have created a Religious syncretism, syncretic religion that is combined with the Zulu's prior belief systems. History of the people of Zulu Origins Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KwaDukuza
KwaDukuza, previously known as Stanger, is a town in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. In 2006, the municipal name was changed to KwaDukuza (which incorporates towns such as Stanger, Ballito and Shakaskraal), but the Zulu people in the area called it "Dukuza" well before then. The city has undergone minor economic construction since 2015, having built a multi-million rand regional shopping mall in 2018. KwaDukuza also has a college called North Coast Agricultural College located in Shakaskraal. History The town was founded in about 1820 by King Shaka and was named KwaDukuza () because of the capital's labyrinth of huts. After Shaka was assassinated on 22 September 1828 during a coup by two of his half-brothers, Dingane and Umthlangana (Mhlangane), the city was burnt to the ground. In 1873, European settlers built a town on the site, naming it Stanger after William Stanger, the surveyor-general of Natal. Stanger became a municipality in 1949 and is the commercial, magisteria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zulu Kingdom
The Zulu Kingdom ( ; ), sometimes referred to as the Zulu Empire, was a monarchy in Southern Africa. During the 1810s, Shaka established a standing army that consolidated rival clans and built a large following which ruled a wide expanse of Southern Africa that extended along the coast of the Indian Ocean from the Tugela River in the south to the Pongola River in the north. A bitter civil war in the mid-19th century erupted which culminated in the 1856 Battle of Ndondakusuka between the brothers Cetshwayo and Mbuyazi. In 1879, a British force invaded Zululand, beginning the Anglo-Zulu War. After an initial Zulu victory at the Battle of Isandlwana in January, the British regrouped and defeated the Zulus in July during the Battle of Ulundi, ending the war. The area was absorbed into the Colony of Natal and later became part of the Union of South Africa. The current Zulu king is Misuzulu Sinqobile, who serves as the monarch of South Africa's KwaZulu-Natal province. States a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mfecane
The Mfecane, also known by the Sesotho names Difaqane or Lifaqane (all meaning "crushing," "scattering," "forced dispersal," or "forced migration"), was a historical period of heightened military conflict and migration associated with state formation and expansion in Southern Africa. The exact range of dates that comprise the Mfecane varies between sources. At its broadest, the period lasted from the late eighteenth century to the mid-nineteenth century, but scholars often focus on an intensive period from the 1810s to the 1840s. Traditional estimates for the death toll range from 1 million to 2 million; however, these numbers are controversial, and some recent scholars revise the mortality figure significantly downwards and attribute the root causes to complex political, economic, and environmental developments. The Mfecane is significant in that it saw the formation of new states, institutions, and ethnic identities in southeastern Africa. The Mfecane's historiography itsel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of The Zulu Nation
The King of the Zulu Nation (IsiZulu: ''Isilo Samabandla Onke'' or ''Ingonyama yamaZulu'') or simply the Zulu King, is the paramount Monarchy#Non-sovereign monarchies, subnational Tribal chief, traditional leader of the Zulu people, amaZulu ethnolinguistic group, the Monarch of the KwaZulu-Natal Provinces of South Africa, province of South Africa (i.e., the ceremonial figurehead of the Government of KwaZulu-Natal) and the Lord of the Usuthu. The Zulu Kings trace their lineage to Mnguni. Having been a minor but independent polity, they fell under the suzerainty of the Mthethwa Paramountcy, Mthethwa when Shaka Zulu ascended to the throne with the support of his suzerain, King Dingiswayo. During the Mfecane, the Zulu Kingdom expanded significantly until the cession of territory by King Dingane to the Natalia Republic following the Battle of Blood River. Zulu territory was annexed into the Natal Colony and the South African Republic following the Anglo-Zulu War during the reign of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dingane
Dingane ka Senzangakhona Zulu (–29 January 1840), commonly referred to as Dingane, Dingarn or Dingaan, was a Zulu prince who became king of the Zulu Kingdom in 1828, after assassinating his half-brother Shaka Zulu. He set up his royal capital, uMgungundlovu, translated to "Place of the Elephant" or "elephant swallower". He also constructed one of numerous military encampments, or kraals, in the eMakhosini Valley just south of the White Umfolozi River, on the slope of Lion Hill (''Singonyama''). Rise to power Dingane came to power in 1828 after assassinating his half-brother Shaka with the help of another brother, Umhlangana, as well as Mbopa, Shaka's bodyguard. Following the death of Nandi, Shaka's behavior became increasingly erratic and many of his relatives accused Shaka of killing his mother. The true mastermind behind the murder of Shaka was his paternal aunt Mkabayi kaJama, who saw Dingane as the best of the choices for next King of the Zulu Nation. The assassin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dingane KaSenzangakhona
Dingane ka Senzangakhona Zulu (–29 January 1840), commonly referred to as Dingane, Dingarn or Dingaan, was a Zulu people, Zulu prince who became king of the Zulu Kingdom in 1828, after assassinating his half-brother Shaka Zulu. He set up his royal capital, uMgungundlovu, translated to "Place of the Elephant" or "elephant swallower". He also constructed one of numerous military encampments, or kraals, in the eMakhosini Valley just south of the White Umfolozi River, on the slope of Lion Hill (''Singonyama''). Rise to power Dingane came to power in 1828 after assassinating his half-brother Shaka with the help of another brother, Umhlangana, as well as Mbopa, Shaka's bodyguard. Following the death of Nandi (mother of Shaka), Nandi, Shaka's behavior became increasingly erratic and many of his relatives accused Shaka of killing his mother. The true mastermind behind the murder of Shaka was his paternal aunt Mkabayi kaJama, who saw Dingane as the best of the choices for next King of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Zulu Kings
This is a list of the monarchs of the Zulu nation, including chieftains and kings of the Zulu royal family from their earliest known history up to the present time. Pre-Zulu The Zulu King lineage stretches to as far as Luzumana, who is believed to have lived as long ago as the 16th century. Luzumana is the child of Mnguni, but details about him are unknown. * NkosinKulu * Mnguni kaNkosinKulu * Luzumana kaMnguni * Malandela kaLuzumana Chieftains of the Zulus ( 1600–1818) When Malandela died, he divided the kingdom into two clans, the Qwabe and the Zulu. * Zulu I kaMalandela ( 1627 – 1709), founder of the clan * Nkosinkulu kaZulu I * Ntombela kaNkosinkulu * Zulu II kaNtombela * Gumede kaZulu * Phunga kaGumede ( 1657 – 1727) * Mageba kaGumede ( 1667 – 1745), son of Gumede, chief 1727 to 1745 * Ndaba kaMageba, son of Mageba, chief 1745 to 1763 * Jama kaNdaba ( 1727–1781), son of Ndaba, chief 1763 to 1781 ** Mkabayi kaJama ( 1750 – 1843), daughter of Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |