|
Sex Chromosomes
Sex chromosomes (also referred to as allosomes, heterotypical chromosome, gonosomes, heterochromosomes, or idiochromosomes) are chromosomes that carry the genes that determine the sex of an individual. The human sex chromosomes are a typical pair of mammal allosomes. They differ from autosomes in form, size, and behavior. Whereas autosomes occur in homologous pairs whose members have the same form in a diploid cell, members of an allosome pair may differ from one another. Nettie Stevens and Edmund Beecher Wilson both independently discovered sex chromosomes in 1905. However, Stevens is credited for discovering them earlier than Wilson. Differentiation In humans, each cell nucleus contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, a total of 46 chromosomes. The first 22 pairs are called autosomes. Autosomes are homologous chromosomes i.e. chromosomes which contain the same genes (regions of DNA) in the same order along their chromosomal arms. The 23rd pair of chromosomes are called allosomes. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most important of these proteins are the histones. Aided by chaperone proteins, the histones bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity. These eukaryotic chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure that has a significant role in transcriptional regulation. Normally, chromosomes are visible under a light microscope only during the metaphase of cell division, where all chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell in their condensed form. Before this stage occurs, each chromosome is duplicated ( S phase), and the two copies are joined by a centromere—resulting in either an X-shaped structure if the centromere is located equatorially, or a two-armed structure if the centromere is located distally; the jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
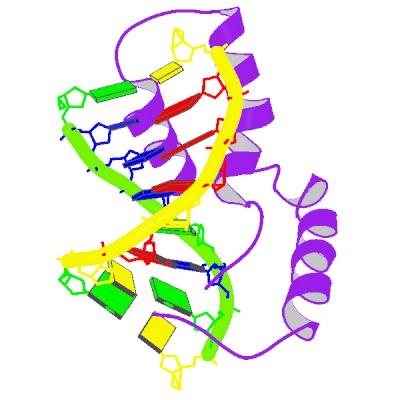
PRC2
PRC2 (polycomb repressive complex 2) is one of the two classes of polycomb-group proteins or (PcG). The other component of this group of proteins is PRC1 ( Polycomb Repressive Complex 1). This complex has histone methyltransferase activity and primarily methylates histone H3 on lysine 27 (i.e. H3K27me3), a mark of transcriptionally silent chromatin. PRC2 is required for initial targeting of genomic region (PRC Response Elements or PRE) to be silenced, while PRC1 is required for stabilizing this silencing and underlies cellular memory of silenced region after cellular differentiation. PRC1 also mono-ubiquitinates histone H2A on lysine 119 (H2AK119Ub1). These proteins are required for long term epigenetic silencing of chromatin and have an important role in stem cell differentiation and early embryonic development. PRC2 are present in most multicellular organisms. The mouse PRC2 has four subunits: Suz12 (zinc finger), Eed, Ezh1 or Ezh2 ( SET domain with histone methyltrans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flowering Plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (). The term angiosperm is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek words (; 'container, vessel') and (; 'seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed within a fruit. The group was formerly called Magnoliophyta. Angiosperms are by far the most diverse group of Embryophyte, land plants with 64 Order (biology), orders, 416 Family (biology), families, approximately 13,000 known Genus, genera and 300,000 known species. They include all forbs (flowering plants without a woody Plant stem, stem), grasses and grass-like plants, a vast majority of broad-leaved trees, shrubs and vines, and most aquatic plants. Angiosperms are distinguished from the other major seed plant clade, the gymnosperms, by having flowers, xylem consisting of vessel elements instead of tracheids, endosperm within their seeds, and fruits that completely envelop the seeds. The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from the commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature-dependent Sex Determination
Temperature-dependent sex determination (TSD) is a type of environmental sex determination in which the temperatures experienced during embryonic/larval development determine the sex of the offspring. It is observed in reptiles and teleost fish, with some reports of it occurring in species of shrimp. TSD differs from the chromosomal sex-determination systems common among vertebrates. It is the most studied type of environmental sex determination (ESD). Some other conditions, e.g. density, pH, and environmental background color, are also observed to alter sex ratio, which could be classified either as temperature-dependent sex determination or temperature-dependent sex differentiation, depending on the involved mechanisms. As sex-determining mechanisms, TSD and genetic sex determination (GSD) should be considered in an equivalent manner, which can lead to reconsidering the status of fish species that are claimed to have TSD when submitted to extreme temperatures instead of the temp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Turtle
Sea turtles (superfamily Chelonioidea), sometimes called marine turtles, are reptiles of the order Testudines and of the suborder Cryptodira. The seven existing species of sea turtles are the flatback, green, hawksbill, leatherback, loggerhead, Kemp's ridley, and olive ridley. Six of the seven sea turtle species, all but the flatback, are present in U.S. waters, and are listed as endangered and/or threatened under the Endangered Species Act. They are listed as threatened with extinction globally on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. The flatback turtle is found only in the waters of Australia, Papua New Guinea, and Indonesia. Sea turtles can be categorized as hard-shelled ( cheloniid) or leathery-shelled ( dermochelyid).Wyneken, J. 2001. The Anatomy of Sea Turtles. U.S Department of Commerce NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS-SEFSC-470, 1-172 pp. The only dermochelyid species of sea turtle is the leatherback. Description For each of the seven species of sea turtles, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scitable
Nature Portfolio (formerly known as Nature Publishing Group and Nature Research) is a division of the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature that publishes academic journals, magazines, online databases, and services in science and medicine. Nature Research's flagship publication is ''Nature'', a weekly multidisciplinary journal first published in 1869. It also publishes the ''Nature-''titled research journals, ''Nature Reviews'' journals (since 2000), society-owned academic journals, and a range of open access journals, including ''Scientific Reports'' and ''Nature Communications''. Springer Nature also publishes ''Scientific American'' in 16 languages, a magazine intended for the general public. In 2013, prior to the merger with Springer and the creation of Springer Nature, Nature Publishing Group's owner, Holtzbrinck Publishing Group, bought a controlling stake in Frontiers. Before Springer Nature was formed in 2015, Nature Research (as the Nature Publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one copy of each chromosome (haploid). Additionally, prior to the division, genetic material from the paternal and maternal copies of each chromosome is crossed over, creating new combinations of code on each chromosome. Later on, during fertilisation, the haploid cells produced by meiosis from a male and a female will fuse to create a zygote, a cell with two copies of each chromosome. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes) are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosomal Translocation
In genetics, chromosome translocation is a phenomenon that results in unusual rearrangement of chromosomes. This includes "balanced" and "unbalanced" translocation, with three main types: "reciprocal", "nonreciprocal" and "Robertsonian" translocation. Reciprocal translocation is a chromosome abnormality caused by exchange of parts between non-homologous chromosomes. Two detached fragments of two different chromosomes are switched. Robertsonian translocation occurs when two non-homologous chromosomes get attached, meaning that given two healthy pairs of chromosomes, one of each pair "sticks" and blends together homogeneously. Each type of chromosomal translocation can result in disorders for growth, function and the development of an individuals body, often resulting from a change in their genome. A gene fusion may be created when the translocation joins two otherwise-separated genes. It is detected on cytogenetics or a karyotype of affected cells. Translocations can be bala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XX Male Syndrome
XX male syndrome, also known as de la Chapelle syndrome or 46,XX testicular disorder of sex development (or 46,XX DSD) is a rare intersex condition in which an individual with a 46,XX karyotype develops a male phenotype.updated 2015 In 90 percent of these individuals, the syndrome is caused by the Y chromosome's '' SRY'' gene, which triggers male reproductive development, being atypically included in the crossing over of genetic information that takes place between the pseudoautosomal regions of the X and Y chromosomes during meiosis in the father. When the X with the ''SRY'' gene combines with a normal X from the mother during fertilization, the result is an XX genetic male. Less common are ''SRY''-negative individuals, who appear to be XX genetic females, which is caused by a mutation in an autosomal or X chromosomal gene. Masculinization in those with the condition is variable, and those with the condition are sterile. This syndrome is diagnosed and occurs in appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SRY Gene
Sex-determining region Y protein (SRY), or testis-determining factor (TDF), is a DNA-binding protein (also known as gene-regulatory protein/transcription factor) encoded by the ''SRY'' gene that is responsible for the initiation of male sex determination in therian mammals ( placentals and marsupials). ''SRY'' is an intronless sex-determining gene on the Y chromosome. Mutations in this gene lead to a range of disorders of sex development with varying effects on an individual's phenotype and genotype. SRY is a member of the SOX (SRY-like box) gene family of DNA-binding proteins. When complexed with the steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1) protein, SRY acts as a transcription factor that causes upregulation of other transcription factors, most importantly SOX9. Its expression causes the development of primary sex cords, which later develop into seminiferous tubules. These cords form in the central part of the yet-undifferentiated gonad, turning it into a testis. The now-induced L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intersex
Intersex people are those born with any of several sex characteristics, including chromosome patterns, gonads, or genitals that, according to the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights, "do not fit typical binary notions of male or female bodies". Sex assignment at birth usually aligns with a child's external genitalia. The number of births with ambiguous genitals is in the range of 1:4,500–1:2,000 (0.02%–0.05%). Other conditions involve the development of atypical chromosomes, gonads, or hormones. The portion of the population that is intersex has been reported differently depending on which definition of intersex is used and which conditions are included. Estimates range from 0.018% (one in 5,500 births) to 1.7%. The difference centers on whether conditions in which chromosomal sex matches a phenotypic sex which is clearly identifiable as male or female, such as late onset congenital adrenal hyperplasia (1.5 percentage points) and Kline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chimera (genetics)
A genetic chimerism or chimera ( or ) is a single organism composed of cells of different genotype, genotypes. Animal chimeras can be produced by the fusion of two (or more) embryos. In plants and some animal chimeras, Mosaic (genetics), mosaicism involves distinct types of tissue that originated from the same zygote but differ due to mutation during ordinary cell division. Normally, genetic chimerism is not visible on casual inspection; however, it has been detected in the course of proving parentage. More practically, in agronomy, "chimera" indicates a plant or portion of a plant whose tissues are made up of two or more types of cells with different genetic makeup; it can derive from a bud mutation or, more rarely, at the grafting point, from the concrescence of cells of the two bionts; in this case it is commonly referred to as a "graft hybrid", although it is not a hybrid in the genetic sense of "hybrid". In contrast, an individual where each cell contains genetic materi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |