|
Session-based Testing
Session-based testing is a software test method that aims to combine accountability and exploratory testing to provide rapid defect discovery, creative on-the-fly test design, management control and metrics reporting. The method can also be used in conjunction with scenario testing. Session-based testing was developed in 2000 by Jonathan and James Marcus Bach. Session-based testing can be used to introduce measurement and control to an immature test process and can form a foundation for significant improvements in productivity and error detection. Session-based testing can offer benefits when formal requirements are not present, incomplete, or changing rapidly. Elements of session-based testing Mission The mission in Session Based Test Management identifies the purpose of the session, helping to focus the session while still allowing for exploration of the system under test. According to Jon Bach, one of the co-founders of the methodology, the mission explains "what we are te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Test
Software testing is the act of checking whether software satisfies expectations. Software testing can provide objective, independent information about the quality of software and the risk of its failure to a user or sponsor. Software testing can determine the correctness of software for specific scenarios but cannot determine correctness for all scenarios. It cannot find all bugs. Based on the criteria for measuring correctness from an oracle, software testing employs principles and mechanisms that might recognize a problem. Examples of oracles include specifications, contracts, comparable products, past versions of the same product, inferences about intended or expected purpose, user or customer expectations, relevant standards, and applicable laws. Software testing is often dynamic in nature; running the software to verify actual output matches expected. It can also be static in nature; reviewing code and its associated documentation. Software testing is often used to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Bug
A software bug is a design defect ( bug) in computer software. A computer program with many or serious bugs may be described as ''buggy''. The effects of a software bug range from minor (such as a misspelled word in the user interface) to severe (such as frequent crashing). In 2002, a study commissioned by the US Department of Commerce's National Institute of Standards and Technology concluded that "software bugs, or errors, are so prevalent and so detrimental that they cost the US economy an estimated $59 billion annually, or about 0.6 percent of the gross domestic product". Since the 1950s, some computer systems have been designed to detect or auto-correct various software errors during operations. History Terminology ''Mistake metamorphism'' (from Greek ''meta'' = "change", ''morph'' = "form") refers to the evolution of a defect in the final stage of software deployment. Transformation of a ''mistake'' committed by an analyst in the early stages of the softw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exploratory Testing
Exploratory testing is an approach to software testing that is concisely described as simultaneous learning, test design and test execution. Cem Kaner, who coined the term in 1984, defines exploratory testing as "a style of software testing that emphasizes the personal freedom and responsibility of the individual tester to continually optimize the quality of his/her work by treating test-related learning, test design, test execution, and test result interpretation as mutually supportive activities that run in parallel throughout the project." While the software is being tested, the tester learns things that together with experience and creativity generates new good tests to run. Exploratory testing is often thought of as a black box testing technique. Instead, those who have studied it consider it a test ''approach'' that can be applied to any test technique, at any stage in the development process. The key is not the test technique nor the item being tested or reviewed; the key i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Test Script
A test script in software testing is a set of instructions that will be performed on the system under test to test that the system functions as expected. Types of test scripts There are various means for executing test scripts. These last two types are also done in manual testing. * Manual testing. These are more commonly called test cases. * Automated testing. ** Short program written in a programming language used to test part of the functionality of a software system. Test scripts written as a short program can either be written using a special automated functional GUI test tool (such as HP QuickTest Professional, Borland SilkTest, IBM TPNS and Rational Robot) or in a well-known programming language (such as C++, C#, Tcl, Expect, Java, PHP, Perl, Powershell, Python, or Ruby). As documented in IEEE, ISO and IEC. ** Extensively parameterized short programs a.k.a. Data-driven testing ** Reusable steps created in a table a.k.a. keyword-driven or table-driven testing. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Test Case
In software engineering, a test case is a specification of the inputs, execution conditions, testing procedure, and expected results that define a single test to be executed to achieve a particular software testing objective, such as to exercise a particular program path or to verify compliance with a specific requirement. Test cases underlie testing that is methodical rather than haphazard. A battery of test cases can be built to produce the desired coverage of the software being tested. Formally defined test cases allow the same tests to be run repeatedly against successive versions of the software, allowing for effective and consistent regression testing. Formal test cases In order to fully test that all the requirements of an application are met, there must be at least two test cases for each requirement: one positive test and one negative test. If a requirement has sub-requirements, each sub-requirement must have at least two test cases. Keeping track of the link between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Testing
Software testing is the act of checking whether software satisfies expectations. Software testing can provide objective, independent information about the Quality (business), quality of software and the risk of its failure to a User (computing), user or sponsor. Software testing can determine the Correctness (computer science), correctness of software for specific Scenario (computing), scenarios but cannot determine correctness for all scenarios. It cannot find all software bug, bugs. Based on the criteria for measuring correctness from an test oracle, oracle, software testing employs principles and mechanisms that might recognize a problem. Examples of oracles include specifications, Design by Contract, contracts, comparable products, past versions of the same product, inferences about intended or expected purpose, user or customer expectations, relevant standards, and applicable laws. Software testing is often dynamic in nature; running the software to verify actual output ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
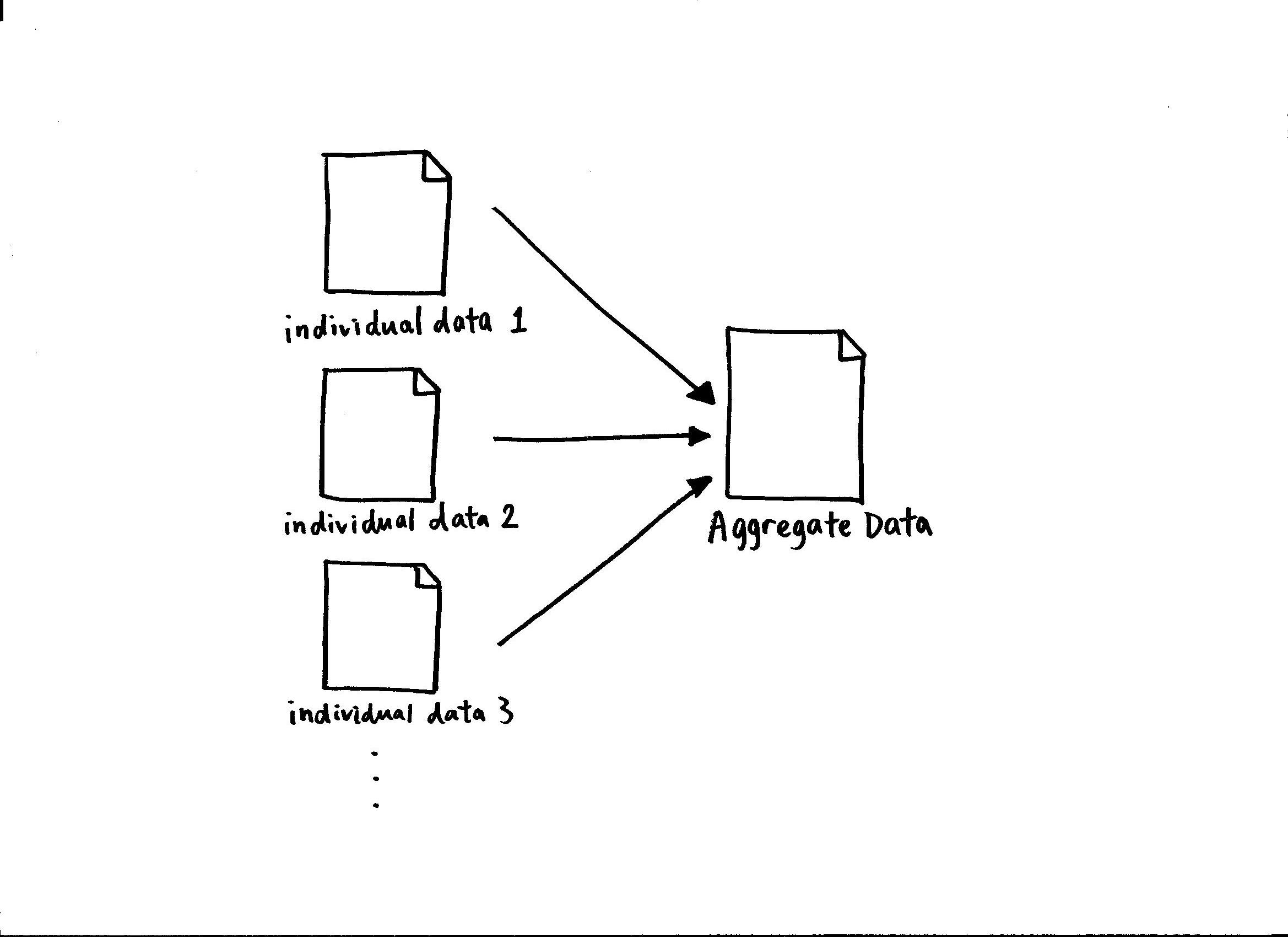
Aggregate Data
Aggregate data is high-level data which is acquired by combining individual-level data. For instance, the output of an industry is an aggregate of the firms’ individual outputs within that industry. Aggregate data are applied in statistics, data warehouses, and in economics. There is a distinction between aggregate data and individual data. Aggregate data refers to individual data that are averaged by geographic area, by year, by service agency, or by other means. Individual data are disaggregated individual results and are used to conduct analyses for estimation of subgroup differences. Aggregate data are mainly used by researchers and analysts, policymakers, banks and administrators for multiple reasons. They are used to evaluate policies, recognise trends and patterns of processes, gain relevant insights, and assess current measures for strategic planning. Aggregate data collected from various sources are used in different areas of studies such as comparative political ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parsing
Parsing, syntax analysis, or syntactic analysis is a process of analyzing a String (computer science), string of Symbol (formal), symbols, either in natural language, computer languages or data structures, conforming to the rules of a formal grammar by breaking it into parts. The term ''parsing'' comes from Latin ''pars'' (''orationis''), meaning Part of speech, part (of speech). The term has slightly different meanings in different branches of linguistics and computer science. Traditional Sentence (linguistics), sentence parsing is often performed as a method of understanding the exact meaning of a sentence or word, sometimes with the aid of devices such as sentence diagrams. It usually emphasizes the importance of grammatical divisions such as subject (grammar), subject and predicate (grammar), predicate. Within computational linguistics the term is used to refer to the formal analysis by a computer of a sentence or other string of words into its constituents, resulting in a par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Test Plan
A test plan is a document detailing the objectives, resources, and processes for a specific test session for a software or hardware product. The plan typically contains a detailed understanding of the eventual workflow. Test plans A test plan documents the strategy that will be used to verify and ensure that a product or system meets its design specifications and other requirements. A test plan is usually prepared by or with significant input from test engineers. Depending on the product and the responsibility of the organization to which the test plan applies, a test plan may include a strategy for one or more of the following: * Design verification or compliance test – to be performed during the development or approval stages of the product, typically on a small sample of units. * Manufacturing test or production test – to be performed during preparation or assembly of the product in an ongoing manner for purposes of performance verification and quality control. * Acceptanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accountability
In ethics and governance, accountability is equated with answerability, culpability, liability, and the expectation of account-giving. As in an aspect of governance, it has been central to discussions related to problems in the public sector, nonprofit, private (corporate), and individual contexts. In leadership roles, accountability is the acknowledgment of and assumption of responsibility for actions, products, decisions, and policies such as administration, governance, and implementation, including the obligation to report, justify, and be answerable for resulting consequences. In governance, accountability has expanded beyond the basic definition of "being called to account for one's actions". It is frequently described as an account-giving relationship between individuals, e.g. "A is accountable to B when A is obliged to inform B about A's (past or future) actions and decisions, to justify them, and to suffer punishment in the case of eventual misconduct." Accountabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specification
A specification often refers to a set of documented requirements to be satisfied by a material, design, product, or service. A specification is often a type of technical standard. There are different types of technical or engineering specifications (specs), and the term is used differently in different technical contexts. They often refer to particular documents, and/or particular information within them. The word ''specification'' is broadly defined as "to state explicitly or in detail" or "to be specific". A requirement specification is a documented requirement, or set of documented requirements, to be satisfied by a given material, design, product, service, etc. It is a common early part of engineering design and product development processes in many fields. A functional specification is a kind of requirement specification, and may show functional block diagrams. A design or product specification describes the features of the ''solutions'' for the Requirement Specification, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Requirement
In engineering, a requirement is a condition that must be satisfied for the output of a work effort to be acceptable. It is an explicit, objective, clear and often quantitative description of a condition to be satisfied by a material, design, product, or service. A specification or spec is a set of requirements that is typically used by developers in the design stage of new product development, product development and by testers in their verification process. With iterative and incremental development such as agile software development, requirements are developed in parallel with design and implementation. With the waterfall model, requirements are completed before design or implementation start. Requirements are used in many engineering fields including engineering design, system engineering, software engineering, enterprise engineering, New product development, product development, and process optimization. Requirement is a relatively broad concept that can describe any nec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |