|
Service Level
Service level measures the performance of a system, service or supply. Certain goals are defined and the service level gives the percentage to which those goals should be achieved. Examples of service level: * Percentage of calls answered in a call center * Percentage of customers waiting less than a given fixed time * Percentage of customers that do not experience a stockout * Percentage of all parts of an order being fulfilled completely *Use of a safety stock to ensure that a target percentage of orders can be met in full and on time.Aberdeen GroupAre Your Inventory Management Practices Outdated? published on 1 March 2005, accessed on 14 July 2024 The term "service level" is used in supply-chain management and in inventory management to measure the performance of inventory replenishment policies. Under consideration, from the optimal solution of such a model also the optimal size of back orders can be derived. A back order is an order placed for an item which is out-of-stock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Service (economics)
A service is an act or use for which a consumer, company, or government is willing to payment, pay. Examples include work done by barbers, doctors, lawyers, mechanics, banks, insurance companies, and so on. Public services are those that society (nation state, fiscal union or region) as a whole pays for. Using resources, skill, ingenuity, and experience, service providers benefit service consumers. Services may be defined as intangible acts or performances whereby the service provider provides value to the customer. Key characteristics Services have three key characteristics: Intangibility Services are by definition intangible. They are not manufactured, transported or stocked. One cannot store services for future use. They are produced and consumed simultaneously. Perishability Services are perishable in two regards: * Service-relevant resources, processes, and systems are assigned for service delivery during a specific period in time. If the service consumer does not request ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Service Level Indicator
In information technology, a service level indicator (SLI) is a measure of the service level provided by a service provider to a customer. SLIs form the basis of service level objectives (SLOs), which in turn form the basis of service level agreements (SLAs); an SLI can be called an SLA metric (also ''customer service metric'', or simply ''service metric''). Though every system is different in the services provided, often common SLIs are used. Common SLIs include latency, throughput, availability, and error rate; others include durability Durability is the ability of a physical product to remain functional, without requiring excessive maintenance or repair, when faced with the challenges of normal operation over its design lifetime. There are several measures of durability in us ... (in storage systems), end-to-end latency (for complex data processing systems, especially pipelines), and correctness. References IT service management Outsourcing {{management-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Service Level Requirement
Service may refer to: Activities * Administrative service, a required part of the workload of university faculty * Civil service, the body of employees of a government * Community service, volunteer service for the benefit of a community or a punishment that may be imposed by a court * Fan service, a Japanese term referring to something which is specifically designed to entertain fans * Feudal service, see Feudal land tenure in England * Funeral or memorial service * Military service, serving in a country's armed forces * Public service, services carried out with the aim of providing a public good * Selfless service, a service which is performed without any expectation of result or award Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Service'' (album), a 1983 album by Yellow Magic Orchestra * ''Service'' (film), a 2008 film * ''Service'' (play), a 1932 play by British writer Dodie Smith * Service (record label), a Swedish record label * "Service" (''The Walking Dead''), a 2016 tele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Service Level Objective
A service-level objective (SLO), as per the O'Reilly Site Reliability Engineering book, is a "target value or range of values for a service level that is measured by an SLI." An SLO is a key element of a service-level agreement (SLA) between a service provider and a customer. SLOs are agreed upon as a means of measuring the performance of the service provider and are outlined as a way of avoiding disputes between the two parties based on misunderstanding. Overview There is often confusion in the use of SLAs and SLOs. The SLA is the entire agreement that specifies what service is to be provided, how it is supported, times, locations, costs, performance, and responsibilities of the parties involved. SLOs are specific measurable characteristics of the SLA such as availability, throughput, frequency, response time, or quality. These SLOs together are meant to define the expected service between the provider and the customer and vary depending on the service's urgency, resources, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Service Level Indicator
In information technology, a service level indicator (SLI) is a measure of the service level provided by a service provider to a customer. SLIs form the basis of service level objectives (SLOs), which in turn form the basis of service level agreements (SLAs); an SLI can be called an SLA metric (also ''customer service metric'', or simply ''service metric''). Though every system is different in the services provided, often common SLIs are used. Common SLIs include latency, throughput, availability, and error rate; others include durability Durability is the ability of a physical product to remain functional, without requiring excessive maintenance or repair, when faced with the challenges of normal operation over its design lifetime. There are several measures of durability in us ... (in storage systems), end-to-end latency (for complex data processing systems, especially pipelines), and correctness. References IT service management Outsourcing {{management-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Service Level Agreement
A service-level agreement (SLA) is an agreement between a service provider and a customer. Particular aspects of the service – quality, availability, responsibilities – are agreed between the service provider and the service user. The most common component of an SLA is that the services should be provided to the customer as agreed upon in the contract. As an example, Internet service providers and telcos will commonly include service level agreements within the terms of their contracts with customers to define the level(s) of service being sold in plain language terms. In this case, the SLA will typically have a technical definition of '' mean time between failures'' (MTBF), '' mean time to repair'' or '' mean time to recovery'' (MTTR); identifying which party is responsible for reporting faults or paying fees; responsibility for various data rates; throughput; jitter; or similar measurable details. Overview A service-level agreement is an agreement between two or m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Inventory Optimization
Inventory optimization refers to the techniques used by businesses to improve their oversight, control and management of inventory size and location across their extended supply network.Scheuffele, G. and Kulshreshtha, A.Inventory Optimization: A Necessity Turning to Urgency ''SETLabs Briefings'', Volume 5, No. 3, July–September 2007, accessed 3 December 2023 It has been observed within operations research that "every company has the challenge of matching its supply volume to customer demand. How well the company manages this challenge has a major impact on its profitability." Inventory management challenges In contrast to the traditional "binge and purge" inventory cycle in which companies over-purchase product to prepare for possible demand spikes and then discard extra product, inventory optimization seeks to more efficiently match supply to expected customer demand. American Productivity and Quality Center (APQC) Open Standards data shows that the median company carries an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Inventory
Inventory (British English) or stock (American English) is a quantity of the goods and materials that a business holds for the ultimate goal of resale, production or utilisation. Inventory management is a discipline primarily about specifying the shape and placement of stocked goods. It is required at different locations within a facility or within many locations of a supply network to precede the regular and planned course of production and stock of materials. The concept of inventory, stock or work in process (or work in progress) has been extended from manufacturing systems to service businesses and projects, by generalizing the definition to be "all work within the process of production—all work that is or has occurred prior to the completion of production". In the context of a manufacturing production system, inventory refers to all work that has occurred—raw materials, partially finished products, finished products prior to sale and departure from the manufacturing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Service Level Agreement
A service-level agreement (SLA) is an agreement between a service provider and a customer. Particular aspects of the service – quality, availability, responsibilities – are agreed between the service provider and the service user. The most common component of an SLA is that the services should be provided to the customer as agreed upon in the contract. As an example, Internet service providers and telcos will commonly include service level agreements within the terms of their contracts with customers to define the level(s) of service being sold in plain language terms. In this case, the SLA will typically have a technical definition of '' mean time between failures'' (MTBF), '' mean time to repair'' or '' mean time to recovery'' (MTTR); identifying which party is responsible for reporting faults or paying fees; responsibility for various data rates; throughput; jitter; or similar measurable details. Overview A service-level agreement is an agreement between two or m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Service Level Objective
A service-level objective (SLO), as per the O'Reilly Site Reliability Engineering book, is a "target value or range of values for a service level that is measured by an SLI." An SLO is a key element of a service-level agreement (SLA) between a service provider and a customer. SLOs are agreed upon as a means of measuring the performance of the service provider and are outlined as a way of avoiding disputes between the two parties based on misunderstanding. Overview There is often confusion in the use of SLAs and SLOs. The SLA is the entire agreement that specifies what service is to be provided, how it is supported, times, locations, costs, performance, and responsibilities of the parties involved. SLOs are specific measurable characteristics of the SLA such as availability, throughput, frequency, response time, or quality. These SLOs together are meant to define the expected service between the provider and the customer and vary depending on the service's urgency, resources, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Availability
In reliability engineering, the term availability has the following meanings: * The degree to which a system, subsystem or equipment is in a specified operable and committable state at the start of a mission, when the mission is called for at an unknown, ''i.e.'' a random, time. * The probability that an item will operate satisfactorily at a given point in time when used under stated conditions in an ideal support environment. Normally high availability systems might be specified as 99.98%, 99.999% or 99.9996%. The converse, unavailability, is 1 minus the availability. Representation The simplest representation of availability (''A'') is a ratio of the expected value of the uptime of a system to the aggregate of the expected values of up and down time (that results in the "total amount of time" ''C'' of the observation window) : A = \frac = \frac Another equation for availability (''A'') is a ratio of the Mean Time To Failure (MTTF) and Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF), or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
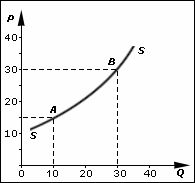 |
Supply (economics)
In economics, supply is the amount of a resource that firms, producers, labourers, providers of financial assets, or other economic agents are willing and able to provide to the marketplace or to an individual. Supply can be in produced goods, labour time, raw materials, or any other scarce or valuable object. Supply is often plotted graphically as a supply curve, with the price per unit on the vertical axis and quantity supplied as a function of price on the horizontal axis. This reversal of the usual position of the dependent variable and the independent variable is an unfortunate but standard convention. The supply curve can be either for an individual seller or for the market as a whole, adding up the quantity supplied by all sellers. The quantity supplied is for a particular time period (e.g., the tons of steel a firm would supply in a year), but the units and time are often omitted in theoretical presentations. In the goods market, supply is the amount of a product ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |