|
Serial Number Arithmetic
Many protocols and algorithms require the serialization or enumeration of related entities. For example, a communication protocol must know whether some packet comes "before" or "after" some other packet. The IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) attempts to define "serial number arithmetic" for the purposes of manipulating and comparing these sequence numbers. In short, when the absolute serial number value decreases by more than half of the maximum value (e.g. 128 in an 8-bit value), it is considered to be "after" the former, whereas other decreases are considered to be "before". This task is rather more complex than it might first appear, because most algorithms use fixed-size (binary) representations for sequence numbers. It is often important for the algorithm not to "break down" when the numbers become so large that they are incremented one last time and "wrap" around their maximum numeric ranges (go instantly from a large positive number to 0 or a large negative number). Som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protocol (computing)
A communication protocol is a system of rules that allows two or more entities of a communications system to transmit information via any variation of a physical quantity. The protocol defines the rules, syntax, semantics, and synchronization of communication and possible error recovery methods. Protocols may be implemented by hardware, software, or a combination of both. Communicating systems use well-defined formats for exchanging various messages. Each message has an exact meaning intended to elicit a response from a range of possible responses predetermined for that particular situation. The specified behavior is typically independent of how it is to be implemented. Communication protocols have to be agreed upon by the parties involved. To reach an agreement, a protocol may be developed into a technical standard. A programming language describes the same for computations, so there is a close analogy between protocols and programming languages: ''protocols are to communica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission Control Protocol
The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is one of the main communications protocol, protocols of the Internet protocol suite. It originated in the initial network implementation in which it complemented the Internet Protocol (IP). Therefore, the entire suite is commonly referred to as TCP/IP. TCP provides reliability (computer networking), reliable, ordered, and error detection and correction, error-checked delivery of a reliable byte stream, stream of octet (computing), octets (bytes) between applications running on hosts communicating via an IP network. Major internet applications such as the World Wide Web, email, remote administration, and file transfer rely on TCP, which is part of the transport layer of the TCP/IP suite. Transport Layer Security, SSL/TLS often runs on top of TCP. TCP is Connection-oriented communication, connection-oriented, meaning that sender and receiver firstly need to establish a connection based on agreed parameters; they do this through three-way Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modular Arithmetic
In mathematics, modular arithmetic is a system of arithmetic operations for integers, other than the usual ones from elementary arithmetic, where numbers "wrap around" when reaching a certain value, called the modulus. The modern approach to modular arithmetic was developed by Carl Friedrich Gauss in his book '' Disquisitiones Arithmeticae'', published in 1801. A familiar example of modular arithmetic is the hour hand on a 12-hour clock. If the hour hand points to 7 now, then 8 hours later it will point to 3. Ordinary addition would result in , but 15 reads as 3 on the clock face. This is because the hour hand makes one rotation every 12 hours and the hour number starts over when the hour hand passes 12. We say that 15 is ''congruent'' to 3 modulo 12, written 15 ≡ 3 (mod 12), so that 7 + 8 ≡ 3 (mod 12). Similarly, if one starts at 12 and waits 8 hours, the hour hand will be at 8. If one instead waited twice as long, 16 hours, the hour hand would be on 4. This ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lollipop Sequence Numbering
Lollipop sequence numbering is a numbering scheme used in routing protocols A routing protocol specifies how routers communicate with each other to distribute information that enables them to select paths between nodes on a computer network. Routers perform the traffic directing functions on the Internet; data packets .... In this numbering scheme, sequence numbers start at a negative value, increase until they reach zero, then cycle through a finite set of positive numbers indefinitely. When a system is rebooted, the sequence is restarted from a negative number again. This allows recently rebooted systems to be distinguished from systems which have simply looped around their numbering space. This path can be visualized as a line with a circle at the end; hence a lollipop. Lollipop sequence numbering was originally believed to resolve the ambiguity problem in cyclic sequence numbering schemes, and was used in OSPF version 1 for this reason. Later work showed that this was no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
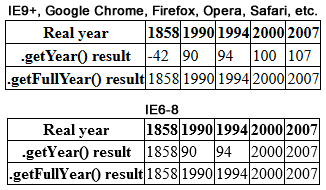
Date Windowing
Date windowing is a method by which dates with two-digit years are converted to and from dates with four-digit years. The year at which the century changes is called the pivot year of the date window. Date windowing was one of several techniques used to resolve the year 2000 problem in legacy computer systems. Reasoning For organizations and institutions with data that is only decades old, a "date windowing" solution was considered easier and more economical than the massive conversions and testing required when converting two-digit years into four-digit years. Windowing methods There are three primary methods used to determine the date window: * Fixed pivot year: simplest to code, works for most business dates. * Sliding pivot year: determined by subtracting some constant from the current year, typically used for birth dates. * Closest date: Three different interpretations (last century, this century, and next century) are compared to the current date, and the closest date is ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two's Complement
Two's complement is the most common method of representing signed (positive, negative, and zero) integers on computers, and more generally, fixed point binary values. Two's complement uses the binary digit with the ''greatest'' value as the ''sign'' to indicate whether the binary number is positive or negative; when the most significant bit is ''1'' the number is signed as negative and when the most significant bit is ''0'' the number is signed as positive. As a result, non-negative numbers are represented as themselves: 6 is 0110, zero is 0000, and −6 is 1010 (the result of applying the bitwise NOT operator to 6 and adding 1). However, while the number of binary bits is fixed throughout a computation it is otherwise arbitrary. Unlike the ones' complement scheme, the two's complement scheme has only one representation for zero. Furthermore, arithmetic implementations can be used on signed as well as unsigned integers and differ only in the integer overflow situations. Proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modulo Operation
In computing and mathematics, the modulo operation returns the remainder or signed remainder of a Division (mathematics), division, after one number is divided by another, the latter being called the ''modular arithmetic, modulus'' of the operation. Given two positive numbers and , modulo (often abbreviated as ) is the remainder of the Euclidean division of by , where is the Division (mathematics), dividend and is the divisor. For example, the expression "5 mod 2" evaluates to 1, because 5 divided by 2 has a quotient of 2 and a remainder of 1, while "9 mod 3" would evaluate to 0, because 9 divided by 3 has a quotient of 3 and a remainder of 0. Although typically performed with and both being integers, many computing systems now allow other types of numeric operands. The range of values for an integer modulo operation of is 0 to . mod 1 is always 0. When exactly one of or is negative, the basic definition breaks down, and programming languages differ in how these valu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integer
An integer is the number zero (0), a positive natural number (1, 2, 3, ...), or the negation of a positive natural number (−1, −2, −3, ...). The negations or additive inverses of the positive natural numbers are referred to as negative integers. The set (mathematics), set of all integers is often denoted by the boldface or blackboard bold The set of natural numbers \mathbb is a subset of \mathbb, which in turn is a subset of the set of all rational numbers \mathbb, itself a subset of the real numbers \mathbb. Like the set of natural numbers, the set of integers \mathbb is Countable set, countably infinite. An integer may be regarded as a real number that can be written without a fraction, fractional component. For example, 21, 4, 0, and −2048 are integers, while 9.75, , 5/4, and Square root of 2, are not. The integers form the smallest Group (mathematics), group and the smallest ring (mathematics), ring containing the natural numbers. In algebraic number theory, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sliding Window Protocol
A sliding window protocol is a feature of packet-based data transmission protocols. Sliding window protocols are used where reliable in-order delivery of packets is required, such as in the data link layer (OSI layer 2) as well as in the Transmission Control Protocol (i.e., TCP windowing). They are also used to improve efficiency when the channel may include high latency. Packet-based systems are based on the idea of sending a batch of data, the ''packet'', along with additional data that allows the receiver to ensure it was received correctly, perhaps a checksum. The paradigm is similar to a window sliding sideways to allow entry of fresh packets and reject the ones that have already been acknowledged. When the receiver verifies the data, it sends an acknowledgment signal, or ACK, back to the sender to indicate it can send the next packet. In a simple automatic repeat request protocol (ARQ), the sender stops after every packet and waits for the receiver to ACK. This ensures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algorithms
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing calculations and data processing. More advanced algorithms can use conditionals to divert the code execution through various routes (referred to as automated decision-making) and deduce valid inferences (referred to as automated reasoning). In contrast, a heuristic is an approach to solving problems without well-defined correct or optimal results.David A. Grossman, Ophir Frieder, ''Information Retrieval: Algorithms and Heuristics'', 2nd edition, 2004, For example, although social media recommender systems are commonly called "algorithms", they actually rely on heuristics as there is no truly "correct" recommendation. As an effective method, an algorithm can be expressed within a finite amount of space and time"Any classic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year 2000 Problem
The term year 2000 problem, or simply Y2K, refers to potential computer errors related to the Time formatting and storage bugs, formatting and storage of calendar data for dates in and after the year 2000. Many Computer program, programs represented four-digit years with only the final two digits, making the year 2000 indistinguishable from 1900. Computer systems' inability to distinguish dates correctly had the potential to bring down worldwide infrastructures for computer-reliant industries. In the years leading up to the turn of the millennium, the public gradually became aware of the "Y2K scare", and individual companies predicted the global damage caused by the bug would require anything between $400 million and $600 billion to rectify. A lack of clarity regarding the potential dangers of the bug led some to stock up on food, water, and firearms, purchase backup generators, and withdraw large sums of money in anticipation of a computer-induced Global catastrophic risk, ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Numeral System
A binary number is a number expressed in the base-2 numeral system or binary numeral system, a method for representing numbers that uses only two symbols for the natural numbers: typically "0" ( zero) and "1" ( one). A ''binary number'' may also refer to a rational number that has a finite representation in the binary numeral system, that is, the quotient of an integer by a power of two. The base-2 numeral system is a positional notation with a radix of 2. Each digit is referred to as a bit, or binary digit. Because of its straightforward implementation in digital electronic circuitry using logic gates, the binary system is used by almost all modern computers and computer-based devices, as a preferred system of use, over various other human techniques of communication, because of the simplicity of the language and the noise immunity in physical implementation. History The modern binary number system was studied in Europe in the 16th and 17th centuries by Thomas Harrio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |