|
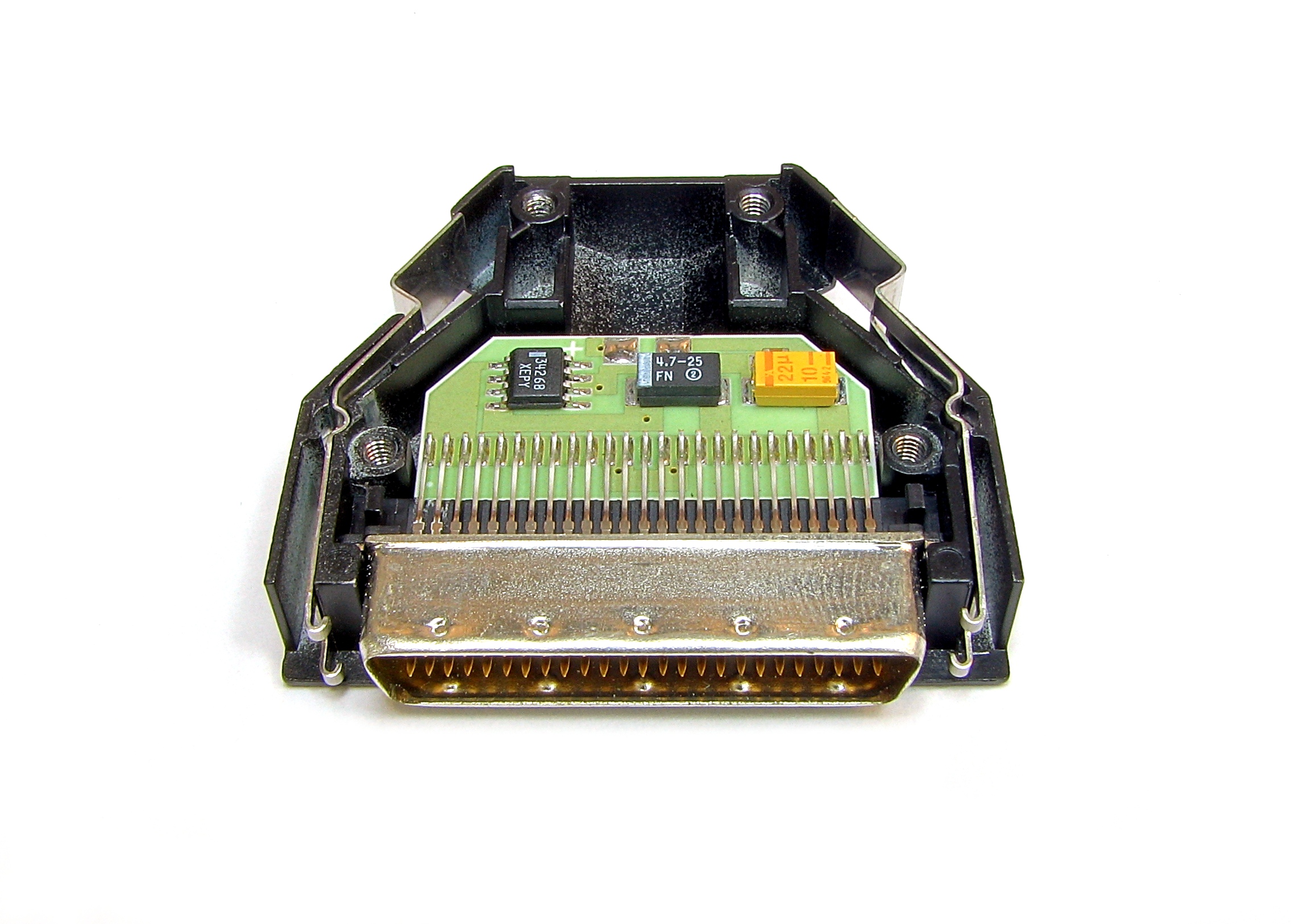
Serial Attached SCSI
In computing, Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) is a point-to-point serial Communications protocol, protocol that moves data to and from Computer storage, computer-storage devices such as hard disk drives, solid-state drives and tape drives. SAS replaces the older Parallel SCSI (Parallel Small Computer System Interface, usually pronounced "scuzzy" ) bus technology that first appeared in the mid-1980s. SAS, like its predecessor, uses the standard SCSI command, SCSI command set. SAS offers optional compatibility with Serial ATA (SATA), versions 2 and later. This allows the connection of SATA drives to most SAS backplanes or controllers. The reverse, connecting SAS drives to SATA backplanes, is not possible. The T10 technical committee of the International Committee for Information Technology Standards (INCITS) develops and maintains the SAS protocol; the SCSI Trade Association (SCSITA) promotes the technology. Introduction A typical Serial Attached SCSI system consists of the following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, hardware and software. Computing has scientific, engineering, mathematical, technological, and social aspects. Major computing disciplines include computer engineering, computer science, cybersecurity, data science, information systems, information technology, and software engineering. The term ''computing'' is also synonymous with counting and calculation, calculating. In earlier times, it was used in reference to the action performed by Mechanical computer, mechanical computing machines, and before that, to Computer (occupation), human computers. History The history of computing is longer than the history of computing hardware and includes the history of methods intended for pen and paper (or for chalk and slate) with or without the aid of tables. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Wide Name
A World Wide Name (WWN) or World Wide Identifier (WWID) is a unique identifier used in storage technologies including Fibre Channel, Parallel ATA, Serial ATA, SCSI and Serial Attached SCSI (SAS). A WWN may be employed in a variety of roles, such as a serial number or for addressability; for example, in Fibre Channel networks, a WWN may be used as a WWNN (World Wide Node Name) to identify an endpoint, or a WWPN (World Wide Port Name) to identify an individual port on a switch. Two WWNs which do not refer to the same thing should always be different even if the two are used in different roles, i.e. a role such as WWPN or WWNN does not define a separate WWN space. The use of burned-in addresses and specification compliance by vendors is relied upon to enforce uniqueness. Formats Each WWN is an 8- or 16-byte number, the length and format of which is determined by the most significant four bits, which are referred to as an NAA (Network Address Authority). The remainder of the valu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel ATA
Parallel ATA (PATA), originally , also known as Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE), is a standard interface designed for IBM PC-compatible computers. It was first developed by Western Digital and Compaq in 1986 for compatible hard drives and CD or DVD drives. The connection is used for storage devices such as hard disk drives, floppy disk drives, optical disc drives, and tape drives in computers. The standard is maintained by the X3/INCITS committee. It uses the underlying (ATA) and Packet Interface ( ATAPI) standards. The Parallel ATA standard is the result of a long history of incremental technical development, which began with the original AT Attachment interface, developed for use in early PC AT equipment. The ATA interface itself evolved in several stages from Western Digital's original Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) interface. As a result, many near-synonyms for ATA/ATAPI and its previous incarnations are still in common informal use, in particular Extended I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Command Queuing
In computing, Native Command Queuing (NCQ) is an extension of the Serial ATA protocol allowing hard disk drives to internally optimize the order in which received read and write commands are executed. This can reduce the amount of unnecessary drive head movement, resulting in increased performance (and slightly decreased wear of the drive) for workloads where multiple simultaneous read/write requests are outstanding, most often occurring in Server (computing), server-type applications. History Native Command Queuing was preceded by Parallel ATA's version of Tagged Command Queuing (TCQ). ATA's attempt at integrating TCQ was constrained by the requirement that ATA host bus adapters use Industry Standard Architecture, ISA bus device protocols to interact with the operating system. The resulting high CPU overhead and negligible performance gain contributed to a lack of market acceptance for ATA TCQ. NCQ differs from TCQ in that, with NCQ, each command is of equal importance, but NCQ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCSI
Small Computer System Interface (SCSI, ) is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices, best known for its use with storage devices such as hard disk drives. SCSI was introduced in the 1980s and has seen widespread use on servers and high-end workstations, with new SCSI standards being published as recently as SAS-4 in 2017. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, electrical, optical and logical interfaces. The SCSI standard defines command sets for specific peripheral device types; the presence of "unknown" as one of these types means that in theory it can be used as an interface to almost any device, but the standard is highly pragmatic and addressed toward commercial requirements. The initial Parallel SCSI was most commonly used for hard disk drives and tape drives, but it can connect a wide range of other devices, including scanners and optical disc drives, although not all controllers can handle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multipath I/O
In computer storage, multipath I/O is a fault-tolerance and performance-enhancement technique that defines more than one physical path between the Central processing unit, CPU in a computer system and its mass storage, mass-storage devices through the Computer bus, buses, controllers, switches, and bridge devices connecting them. As an example, a SCSI hard disk drive may connect to two SCSI Disk controller, controllers on the same computer, or a disk may connect to two Fibre Channel ports. Should one controller, port or switch fail, the operating system can route the Input/output, I/O through the remaining controller, port or switch transparently and with no changes visible to the applications, other than perhaps resulting in increased Latency (engineering), latency. Multipath software layers can leverage the redundant paths to provide performance-enhancing features, including dynamic load balancing (computing), load balancing, traffic shaping, automatic path management, and dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clock Skew
Clock skew (sometimes called timing skew) is a phenomenon in synchronous digital circuit systems (such as computer systems) in which the same sourced clock signal arrives at different components at different times due to gate or, in more advanced semiconductor technology, wire signal propagation delay. The instantaneous difference between the readings of any two clocks is called their skew. The operation of most digital circuits is synchronized by a periodic signal known as a " clock" that dictates the sequence and pacing of the devices on the circuit. This clock is distributed from a single source to all the memory elements of the circuit, which for example could be registers or flip-flops. In a circuit using edge-triggered registers, when the clock edge or tick arrives at a register, the register transfers the register input to the register output, and these new output values flow through combinational logic to provide the values at register inputs for the next clock tic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Termination
In electronics, electrical termination is the practice of ending a transmission line with a device that matches the characteristic impedance of the line. Termination prevents signals from Signal reflection, reflecting off the end of the transmission line. Reflections at the ends of unterminated transmission lines cause distortion, which can produce ambiguous digital signal levels and misoperation of digital systems. Reflections in analog signal systems cause such effects as ghosting (television), video ghosting, or Power margin, power loss in radio transmitter transmission lines. Transmission lines Signal termination often requires the installation of a terminator at the beginning and end of a wire or cable to prevent an RF signal from being reflected back from each end, causing Interference (communication), interference, or power loss. The terminator is usually placed at the end of a transmission line or Daisy chain (electrical engineering), daisy chain Bus (computing), bus (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bus Contention
Bus contention is an undesirable state in computer design where more than one device on a bus attempts to place values on it at the same time. Bus contention is the kind of telecommunication contention that occurs when all communicating devices communicate directly with each other through a single shared channel, and contrasted with "network contention" that occurs when communicating devices communicate indirectly with each other, through point-to-point connections through routers or bridges. Bus contention can lead to erroneous operation, excess power consumption, and, in unusual cases, permanent damage to the hardware—such as burning out a MOSFET. Ian Sinclair; John Dunton"Practical Electronics Handbook"2013. section "Three-state control". p. 208. Description Most bus architectures requires devices sharing a bus to follow an arbitration protocol carefully designed to make the likelihood of contention negligible.. However, when devices on the bus have logic errors, man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multidrop Bus
A multidrop bus (MDB) is a computer bus able to connect three or more devices. A process of arbitration determines which device sends information at any point. The other devices listen for the data they are intended to receive. Multidrop buses have the advantage of simplicity and extensibility, but their differing electrical characteristics make them relatively unsuitable for high frequency or high bandwidth applications. In computing Since 2000, multidrop standards such as PCI and Parallel ATA are increasingly being replaced by point-to-point systems such as PCI Express and SATA. Modern SDRAM chips exemplify the problem of electrical impedance discontinuity. Fully Buffered DIMM is an alternative approach to connecting multiple DRAM Dram, DRAM, or drams may refer to: Technology and engineering * Dram (unit), a unit of mass and volume, and an informal name for a small amount of liquor, especially whisky or whiskey * Dynamic random-access memory, a type of electronic semicondu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point-to-point (network Topology)
Network topology is the arrangement of the elements ( links, nodes, etc.) of a communication network. Network topology can be used to define or describe the arrangement of various types of telecommunication networks, including command and control radio networks, industrial fieldbusses and computer networks. Network topology is the topological structure of a network and may be depicted physically or logically. It is an application of graph theory wherein communicating devices are modeled as nodes and the connections between the devices are modeled as links or lines between the nodes. Physical topology is the placement of the various components of a network (e.g., device location and cable installation), while logical topology illustrates how data flows within a network. Distances between nodes, physical interconnections, transmission rates, or signal types may differ between two different networks, yet their logical topologies may be identical. A network's physical topology is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |