|
Sensory Gating
Sensory gating describes neural processes of filtering out redundant or irrelevant stimuli from all possible environmental stimuli reaching the brain. Also referred to as gating or filtering, sensory gating prevents an overload of information in the higher cortical centers of the brain. Sensory gating can also occur in different forms through changes in both perception and sensation, affected by various factors such as "arousal, recent stimulus exposure, and selective attention. Although sensory gating is largely automatic, it also occurs within the context of attention processing as the brain selectively seeks for goal-relevant information. Previous studies have shown a correlation between sensory gating and different cognitive functions, but there is not yet a solid evidence implying that the relationship between sensory gating and cognitive functions are modality-independent. Cocktail party effect The cocktail party effect illustrates how the brain inhibits input from environme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain
The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head ( cephalization), usually near organs for special senses such as vision, hearing and olfaction. Being the most specialized organ, it is responsible for receiving information from the sensory nervous system, processing those information (thought, cognition, and intelligence) and the coordination of motor control (muscle activity and endocrine system). While invertebrate brains arise from paired segmental ganglia (each of which is only responsible for the respective body segment) of the ventral nerve cord, vertebrate brains develop axially from the midline dorsal nerve cord as a vesicular enlargement at the rostral end of the neural tube, with centralized control over all body segments. All vertebrate brains can be embryonically divided into three parts: the forebrain (prosencep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social withdrawal, decreased emotional expression, and apathy. Symptoms typically develop gradually, begin during young adulthood, and in many cases never become resolved. There is no objective diagnostic test; diagnosis is based on observed behavior, a history that includes the person's reported experiences, and reports of others familiar with the person. To be diagnosed with schizophrenia, symptoms and functional impairment need to be present for six months (DSM-5) or one month ( ICD-11). Many people with schizophrenia have other mental disorders, especially substance use disorders, depressive disorders, anxiety disorders, and obsessive–compulsive disorder. About 0.3% to 0.7% of people are diagnosed with schizophrenia during their lifet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
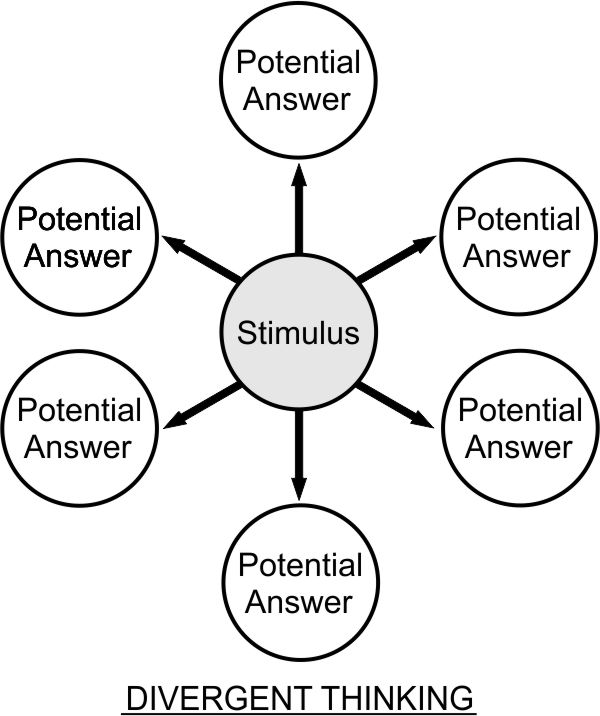
Divergent Thinking
Divergent thinking is a thought process or method used to generate creative ideas by exploring many possible solutions. It typically occurs in a spontaneous, free-flowing, "non-linear" manner, such that many ideas are generated in an emergent cognitive fashion. Many possible solutions are explored in a short amount of time, and unexpected connections are drawn. Following divergent thinking, ideas and information are organized and structured using convergent thinking, which follows a particular set of logical steps to arrive at one solution, which in some cases is a "correct" solution. The psychologist J.P. Guilford first coined the terms convergent thinking and divergent thinking in 1956. Activities Activities which promote divergent thinking include creating lists of questions, setting aside time for thinking and meditation, brainstorming, subject mapping, bubble mapping, keeping a journal, playing tabletop role-playing games, creating artwork, and free writing. In free wri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicotine
Nicotine is a naturally produced alkaloid in the nightshade family of plants (most predominantly in tobacco and '' Duboisia hopwoodii'') and is widely used recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As a pharmaceutical drug, it is used for smoking cessation to relieve withdrawal symptoms. Nicotine acts as a receptor agonist at most nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs), except at two nicotinic receptor subunits ( nAChRα9 and nAChRα10) where it acts as a receptor antagonist. Nicotine constitutes approximately 0.6–3.0% of the dry weight of tobacco. Nicotine is also present at ppb-concentrations in edible plants in the family Solanaceae, including potatoes, tomatoes, and eggplants, though sources disagree on whether this has any biological significance to human consumers. It functions as an antiherbivore toxin; consequently, nicotine was widely used as an insecticide in the past, and neonicotinoids (structurally similar to nicotine), such as imidaclopri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-traumatic Stress Disorder
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental and behavioral disorder that can develop because of exposure to a traumatic event, such as sexual assault, warfare, traffic collisions, child abuse, domestic violence, or other threats on a person's life. Symptoms may include disturbing thoughts, feelings, or dreams related to the events, mental or physical distress to trauma-related cues, attempts to avoid trauma-related cues, alterations in the way a person thinks and feels, and an increase in the fight-or-flight response. These symptoms last for more than a month after the event. Young children are less likely to show distress but instead may express their memories through play. A person with PTSD is at a higher risk of suicide and intentional self-harm. Most people who experience traumatic events do not develop PTSD. People who experience interpersonal violence such as rape, other sexual assaults, being kidnapped, stalking, physical abuse by an intimate partner, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensory Overload
Sensory overload occurs when one or more of the body's senses experiences over-stimulation from the environment. There are many environmental elements that affect an individual. Examples of these elements are urbanization, crowding, noise, mass media, and technology. Symptoms There are a wide variety of symptoms that have been found to be associated with sensory overload. These symptoms can occur in both children and adults. Some of these symptoms are: * Irritability * "Shutting down", or refusing to participate in activities and interact with others * Avoiding touching or being touched * Complaining about noises that do not affect others * Getting overexcited * Covering eyes around bright lights * Making poor eye contact * Covering ears to close out sounds or voices * Constantly changing activities without completing any tasks * Irritation caused by shoes, socks, tags, or different textures * Over-sensitivity to touch, movement, sights, or sounds * Having trouble with socia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P50 (neuroscience)
In electroencephalography, the P50 is an event related potential occurring approximately 50 ms after the presentation of a stimulus, usually an auditory click. The P50 response is used to measure sensory gating, or the reduced neurophysiological response to redundant stimuli. Research has found an abnormal P50 suppression in people with schizophrenia, making it an example of a biological marker for the disorder. Besides schizophrenia, abnormal P50 suppression has been found in patients with traumatic brain injury, recreational drug use, and post-traumatic stress disorder. Paired click test In a paired click test, one auditory click sound will be presented, followed by a second click approximately 500 ms after the first one. The second sound is considered redundant, and so a typical control showing normal sensory gating will produce a reduced response (in wave amplitude) to the second click. The suppression is measured as the percentage of amplitude decrease in response to the secon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Event-related Potential
An event-related potential (ERP) is the measured brain response that is the direct result of a specific sensory, cognitive, or motor event. More formally, it is any stereotyped electrophysiological response to a stimulus. The study of the brain in this way provides a noninvasive means of evaluating brain functioning. ERPs are measured by means of electroencephalography (EEG). The magnetoencephalography (MEG) equivalent of ERP is the ERF, or event-related field. Evoked potentials and induced potentials are subtypes of ERPs. History With the discovery of the electroencephalogram (EEG) in 1924, Hans Berger revealed that one could measure the electrical activity of the human brain by placing electrodes on the scalp and amplifying the signal. Changes in voltage can then be plotted over a period of time. He observed that the voltages could be influenced by external events that stimulated the senses. The EEG proved to be a useful source in recording brain activity over the en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positron Emission Tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. Different tracers are used for various imaging purposes, depending on the target process within the body. For example: * Fluorodeoxyglucose ( 18F">sup>18FDG or FDG) is commonly used to detect cancer; * 18Fodium fluoride">sup>18Fodium fluoride (Na18F) is widely used for detecting bone formation; * Oxygen-15 (15O) is sometimes used to measure blood flow. PET is a common imaging technique, a medical scintillography technique used in nuclear medicine. A radiopharmaceutical – a radioisotope attached to a drug – is injected into the body as a radioactive tracer, tracer. When the radiopharmaceutical undergoes beta plus decay, a positron is emitted, and when the positron interacts with an or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetoencephalography
Magnetoencephalography (MEG) is a functional neuroimaging technique for mapping brain activity by recording magnetic fields produced by electrical currents occurring naturally in the brain, using very sensitive magnetometers. Arrays of SQUIDs (superconducting quantum interference devices) are currently the most common magnetometer, while the SERF (spin exchange relaxation-free) magnetometer is being investigated for future machines. Applications of MEG include basic research into perceptual and cognitive brain processes, localizing regions affected by pathology before surgical removal, determining the function of various parts of the brain, and neurofeedback. This can be applied in a clinical setting to find locations of abnormalities as well as in an experimental setting to simply measure brain activity. History MEG signals were first measured by University of Illinois physicist David Cohen in 1968, before the availability of the SQUID, using a copper induction coil as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electroencephalography
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex and allocortex. It is typically non-invasive, with the EEG electrodes placed along the scalp (commonly called "scalp EEG") using the International 10-20 system, or variations of it. Electrocorticography, involving surgical placement of electrodes, is sometimes called "intracranial EEG". Clinical interpretation of EEG recordings is most often performed by visual inspection of the tracing or quantitative EEG analysis. Voltage fluctuations measured by the EEG bioamplifier and electrodes allow the evaluation of normal brain activity. As the electrical activity monitored by EEG originates in neurons in the underlying brain tissue, the recordings made by the electrodes on the surface of the scalp vary in accordance with their orienta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electroencephalography (EEG) - FET09 Prague
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex and allocortex. It is typically non-invasive, with the EEG electrodes placed along the scalp (commonly called "scalp EEG") using the International 10–20 system, or variations of it. Electrocorticography, involving surgical placement of electrodes, is sometimes called "intracranial EEG". Clinical interpretation of EEG recordings is most often performed by visual inspection of the tracing or quantitative EEG analysis. Voltage fluctuations measured by the EEG bioamplifier and electrodes allow the evaluation of normal brain activity. As the electrical activity monitored by EEG originates in neurons in the underlying brain tissue, the recordings made by the electrodes on the surface of the scalp vary in accordance with their orientatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_-_FET09_Prague.jpg)



.jpg)



