 |
Sensitive High-resolution Ion Microprobe
The sensitive high-resolution ion microprobe (also sensitive high mass-resolution ion microprobe or SHRIMP) is a large-diameter, double-focusing secondary ion mass spectrometer (SIMS) sector instrument that was produced by Australian Scientific Instruments in Canberra, Australia and now has been taken over by Chinese company Dunyi Technology Development Co. (DTDC) in Beijing. Similar to the IMS 1270-1280-1300 large-geometry ion microprobes produced by CAMECA, Gennevilliers, France and like other SIMS instruments, the SHRIMP microprobe bombards a sample under vacuum with a beam of primary ions that sputters secondary ions that are focused, filtered, and measured according to their energy and mass. The SHRIMP is primarily used for geological and geochemical applications. It can measure the isotopic and elemental abundances in minerals at a 10 to 30 μm-diameter scale and with a depth resolution of 1–5 μm. Thus, SIMS method is well-suited for the analysis of complex mineral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
SHRIMP II
A shrimp (: shrimp (American English, US) or shrimps (British English, UK)) is a crustacean with an elongated body and a primarily Aquatic locomotion, swimming mode of locomotion – typically Decapods belonging to the Caridea or Dendrobranchiata, although some Shrimp#Non-decapods, crustaceans outside of this order are also referred to as "shrimp". Any small crustacean may also be referred to as "shrimp", regardless of resemblance. More narrow definitions may be restricted to Caridea, to smaller species of either of the aforementioned groups, or only the Marine life, marine species. Under a broader definition, ''shrimp'' may be synonymous with prawn, covering stalk-eyed swimming crustaceans with long, narrow muscular tails (Abdomen#Arthropoda, abdomens), long whiskers (Antenna (biology), antennae), and slender, Biramous, biramous legs. They swim forward by paddling the swimmerets on the underside of their abdomens, although their escape response is typically repeated flicks wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Hadean
The Hadean ( ) is the first and oldest of the four geologic eons of Earth's history, starting with the planet's formation about 4.6 billion years ago (estimated 4567.30 ± 0.16 million years ago set by the age of the oldest solid material in the Solar System—protoplanetary disk dust particles—found as chondrules and calcium–aluminium-rich inclusions in some meteorites about 4.567 billion years old), and ended 4.031 billion years ago, the age of the oldest known intact rock formations on Earth as recognized by the International Commission on Stratigraphy. The interplanetary collision that created the Moon occurred early in this eon. The Hadean eon was succeeded by the Archean eon, with the Late Heavy Bombardment hypothesized to have occurred at the Hadean-Archean boundary. Hadean rocks are very rare, largely consisting of granular zircons from one locality ( Jack Hills) in Western Australia. Hadean geophysical models remain controversial among geologis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Snowball Earth
The Snowball Earth is a historical geology, geohistorical hypothesis that proposes that during one or more of Earth's greenhouse and icehouse Earth, icehouse climates, the planet's planetary surface, surface became nearly entirely freezing, frozen with no liquid oceanic or surface water exposed to the atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere. The most academically mentioned period of such a global ice age is believed to have occurred some time before 650 myr#Usage, mya during the Cryogenian period, which included at least two large glacial periods, the Sturtian glaciation, Sturtian and Marinoan glaciations. Proponents of the hypothesis argue that it best explains sedimentary deposition (geology), deposits that are generally believed to be of glacial origin at tropical palaeolatitudes and other enigmatic features in the geological record. Opponents of the hypothesis contest the geological evidence for global glaciation and the Geophysics, geophysical feasibility of an ice- or slush-cover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
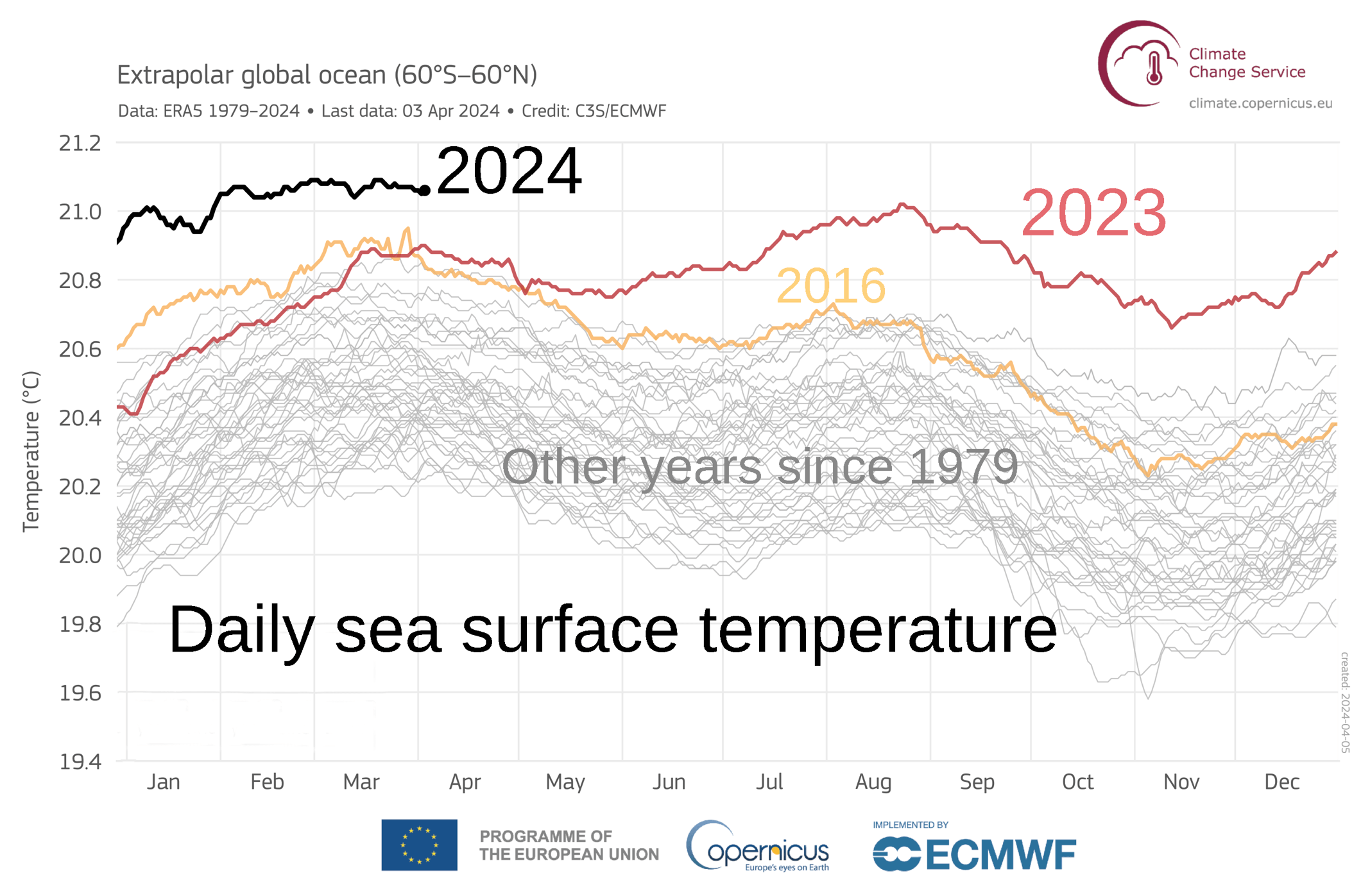 |
Sea Surface Temperature
Sea surface temperature (or ocean surface temperature) is the ocean temperature, temperature of ocean water close to the surface. The exact meaning of ''surface'' varies in the literature and in practice. It is usually between and below the sea surface. Sea surface temperatures greatly modify air masses in the Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere within a short distance of the shore. The thermohaline circulation has a major impact on average sea surface temperature throughout most of the world's oceans. Warm sea surface temperatures can develop and Tropical cyclogenesis, strengthen cyclones over the ocean. Tropical cyclones can also cause a cool wake. This is due to turbulent mixing of the upper of the ocean. Sea surface temperature changes during the day. This is like the air above it, but to a lesser degree. There is less variation in sea surface temperature on breezy days than on calm days. Coastal sea surface temperatures can cause offshore winds to generate upwelling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era, and the second of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon (geology), Eon. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period Megaannum, Ma (million years ago) to the start of the Silurian Period Ma. The Ordovician, named after the Celtic Britons, Welsh tribe of the Ordovices, was defined by Charles Lapworth in 1879 to resolve a dispute between followers of Adam Sedgwick and Roderick Murchison, who were placing the same Rock (geology), rock beds in North Wales in the Cambrian and Silurian systems, respectively. Lapworth recognized that the fossil fauna in the disputed Stratum, strata were different from those of either the Cambrian or the Silurian systems, and placed them in a system of their own. The Ordovician received international approval in 1960 (forty years after Lapworth's death), when it was adopted as an official per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Apatite
Apatite is a group of phosphate minerals, usually hydroxyapatite, fluorapatite and chlorapatite, with high concentrations of Hydroxide, OH−, Fluoride, F− and Chloride, Cl− ion, respectively, in the crystal. The formula of the admixture of the three most common Endmember (mineralogy), endmembers is written as Calcium, Ca10(Phosphate, PO4)6(OH,F,Cl)2, and the crystal unit cell formulae of the individual minerals are written as Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2, Ca10(PO4)6F2 and Ca10(PO4)6Cl2. The mineral was named apatite by the German geologist Abraham Gottlob Werner in 1786, although the specific mineral he had described was reclassified as fluorapatite in 1860 by the German mineralogist Karl Friedrich August Rammelsberg. Apatite is often mistaken for other minerals. This tendency is reflected in the mineral's name, which is derived from the Greek word ἀπατάω (apatáō), which means ''to deceive''. Geology Apatite is very common as an accessory mineral in igneous and metamorphic roc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Acasta Gneiss
The Acasta Gneiss Complex, also called the Acasta Gneiss, is a body of felsic to Ultramafic rock, ultramafic Archean Basement (geology), basement rocks, gneisses, that form the northwestern edge of the Slave craton, Slave Craton in the Northwest Territories, Canada, about north of Yellowknife, Canada. This geologic complex consists largely of tonalite, tonalitic and diorite, granodioritic gneisses and lesser amounts of mafic and ultramafic gneisses. It underlies and is largely concealed by thin, patchy cover of Quaternary glacial sediments over an area of about . The Acasta Gneiss Complex contains fragments of the oldest known Earth's crust, crust and record of more than a billion years (>4.0–2.9 Gigaannum, Ga) of magmatism and metamorphism.Reimink, J.R., Chacko, T., Carlson, R.W., Shirey, S.B., Liu, J., Stern, R.A., Bauer, A.M., Pearson, D.G. and Heaman, L.M., 2018. ''Petrogenesis and tectonics of the Acasta Gneiss Complex derived from integrated petrology and 142Nd and 182W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
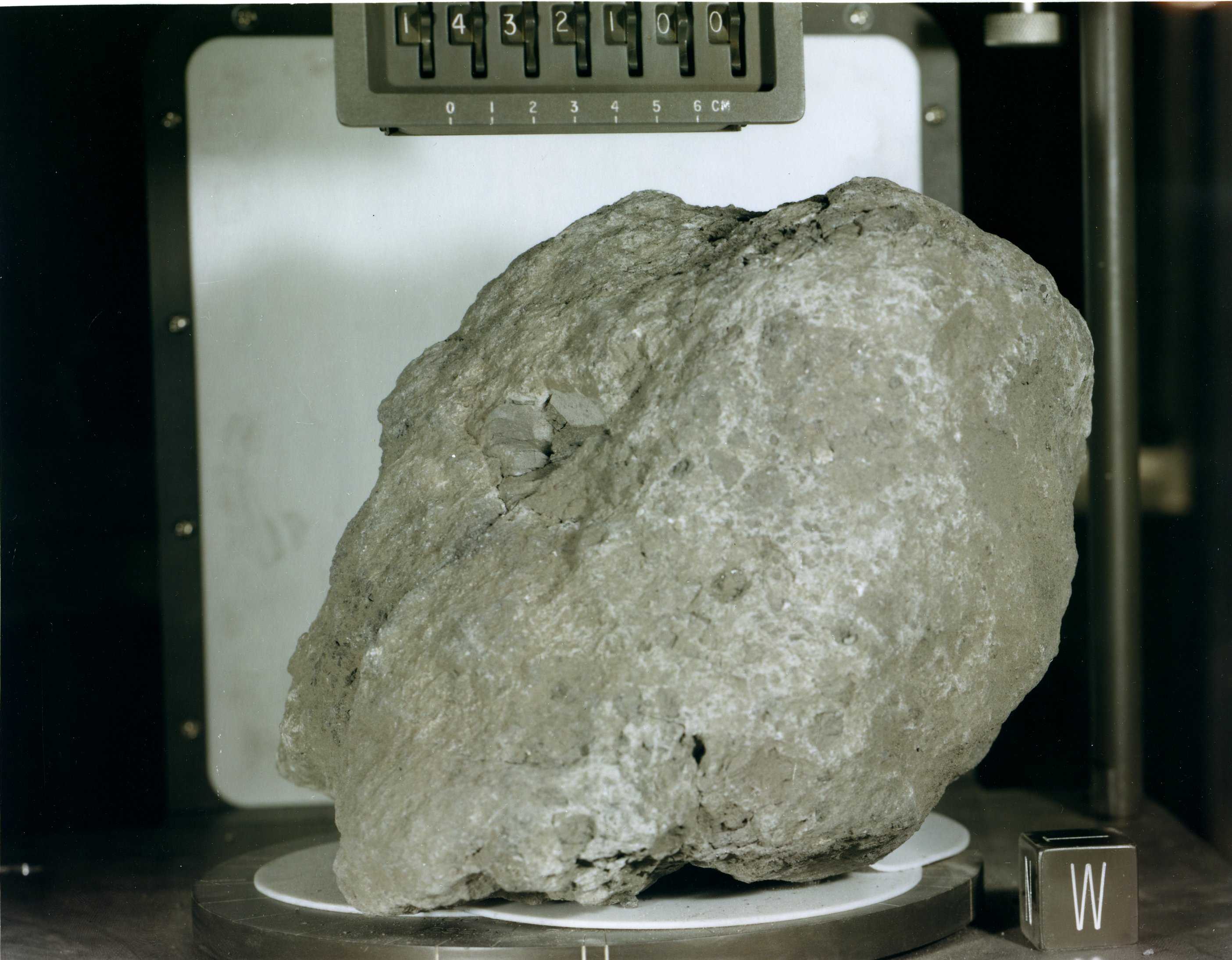 |
Oldest Dated Rocks
The oldest dated rocks formed on Earth, as an aggregate of minerals that have not been subsequently broken down by erosion or melted, are more than 4 billion years old, formed during the Hadean Eon of Earth's geological history, and mark the start of the Archean Eon, which is defined to start with the formation of the oldest intact rocks on Earth. Archean rocks are exposed on Earth's surface in very few places, such as in the geologic shields of Canada, Australia, and Africa. The ages of these felsic rocks are generally between 2.5 and 3.8 billion years. The approximate ages have a margin of error of millions of years. In 1999, the oldest known rock on Earth was dated to 4.031 ±0.003 billion years, and is part of the Acasta Gneiss of the Slave Craton in northwestern Canada. Researchers at McGill University found a rock with a very old model age for extraction from the mantle (3.8 to 4.28 billion years ago) in the Nuvvuagittuq greenstone belt on the coast of Hudson Bay, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Curtin University
Curtin University (previously Curtin University of Technology and Western Australian Institute of Technology) is an Australian public university, public research university based in Bentley, Western Australia, Bentley, Perth, Western Australia. It is named after John Curtin, Prime Minister of Australia from 1941 to 1945, and is Western Australia's largest university, with students in . WAIT was established in 1966. Curtin was conferred university status after the Parliament of Western Australia passed legislation in 1986. Since then, the university has expanded its presence and has campuses in Curtin Singapore, Singapore, Curtin University Malaysia, Malaysia, Dubai and Curtin Mauritius, Mauritius, and has ties with 90 exchange universities in 20 countries. The university comprises five main faculties with over 95 specialists centres. It had a campus in Sydney from 2005 to 2016. Curtin University is a member of the Australian Technology Network. Curtin is active in research in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
John Robert De Laeter
John Robert de Laeter, AO, FTSE, FAIP (3 May 193316 August 2010) was an Australian scientist with a distinguished career across several fields in nuclear physics, cosmochemistry, geochronology, isotope geochemistry. He was also a prominent administrator and promoter who oversaw the establishment of several scientific research and education centres in Western Australia. Early life and education John Robert de Laeter was born on 3 May 1933 in South Perth, Western Australia. He attended South Perth Primary School on Forrest Street and then won a scholarship to Perth Modern School in Subiaco. At the University of Western Australia he achieved first class honours in physics and education to start a career as a science teacher. Scientific career De Laeter began teaching in 1957 at the Perth Technical College. While teaching at Bunbury High School in the late 1950s, de Laeter attended a science teachers' conference in Sydney, where he described the following: :I heard two of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with the chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature. Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most common on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means "burning stone". Almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum.. Downloahere Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Hafnium
Hafnium is a chemical element; it has symbol Hf and atomic number 72. A lustrous, silvery gray, tetravalent transition metal, hafnium chemically resembles zirconium and is found in many zirconium minerals. Its existence was predicted by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, though it was not identified until 1922, by Dirk Coster and George de Hevesy. Hafnium is named after , the Latin name for Copenhagen, where it was discovered. Hafnium is used in filaments and electrodes. Some semiconductor fabrication processes use its oxide for integrated circuits at 45 nanometers and smaller feature lengths. Some superalloys used for special applications contain hafnium in combination with niobium, titanium, or tungsten. Hafnium's large neutron capture cross section makes it a good material for neutron absorption in control rods in nuclear power plants, but at the same time requires that it be removed from the neutron-transparent corrosion-resistant zirconium alloys used in nuclear r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |