|
Self-organized Criticality Control
In applied physics, the concept of controlling self-organized criticality refers to the control of processes by which a self-organized system dissipates energy. The objective of the control is to reduce the probability of occurrence of and size of energy dissipation bursts, often called ''avalanches'', of self-organized systems. Dissipation of energy in a self-organized critical system into a lower energy state can be costly for society, since it depends on avalanches of all sizes usually following a kind of power law distribution and large avalanches can be damaging and disruptive. Schemes Several strategies have been proposed to deal with the issue of controlling self-organized criticality: #''The design of controlled avalanches.'' Daniel O. Cajueiro and Roberto F. S. Andrade show that if well-formulated small and medium avalanches are exogenously triggered in the system, the energy of the system is released in a way that large avalanches are rarer. #'' The modification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Applied Physics
Applied physics is the application of physics to solve scientific or engineering problems. It is usually considered a bridge or a connection between physics and engineering. "Applied" is distinguished from "pure" by a subtle combination of factors, such as the motivation and attitude of researchers and the nature of the relationship to the technology or science that may be affected by the work. Applied physics is rooted in the fundamental truths and basic concepts of the physical sciences but is concerned with the utilization of scientific principles in practical devices and systems and with the application of physics in other areas of science and high technology. Examples of research and development areas * Accelerator physics *Acoustics * Atmospheric physics *Biophysics * Brain–computer interfacing *Chemistry * Chemical physics * Differentiable programming **Artificial intelligence ** Scientific computing *Engineering physics **Chemical engineering **Electrical engineeri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ischemic Cascade
The ischemic (ischaemic) cascade is a series of biochemical reactions that are initiated in the brain and other aerobic tissues after seconds to minutes of ischemia (inadequate blood supply). This is typically secondary to stroke, injury, or cardiac arrest due to heart attack. Most ischemic neurons that die do so due to the activation of chemicals produced during and after ischemia.Stroke Center of the Washington University School of Medicine. The ischemic cascade usually goes on for two to three hours but can last for days, even after normal blood flow returns. __TOC__ Mechanism A is a series of events in which one event triggers the next, in a ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaos Theory
Chaos theory is an interdisciplinary area of Scientific method, scientific study and branch of mathematics. It focuses on underlying patterns and Deterministic system, deterministic Scientific law, laws of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions. These were once thought to have completely random states of disorder and irregularities. Chaos theory states that within the apparent randomness of chaotic complex systems, there are underlying patterns, interconnection, constant feedback loops, repetition, self-similarity, fractals and self-organization. The butterfly effect, an underlying principle of chaos, describes how a small change in one state of a deterministic nonlinear system can result in large differences in a later state (meaning there is sensitive dependence on initial conditions). A metaphor for this behavior is that a butterfly flapping its wings in Brazil can cause or prevent a tornado in Texas. Text was copied from this source, which is avai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Theory
Control theory is a field of control engineering and applied mathematics that deals with the control system, control of dynamical systems in engineered processes and machines. The objective is to develop a model or algorithm governing the application of system inputs to drive the system to a desired state, while minimizing any ''delay'', ''overshoot'', or ''steady-state error'' and ensuring a level of control Stability theory, stability; often with the aim to achieve a degree of Optimal control, optimality. To do this, a controller with the requisite corrective behavior is required. This controller monitors the controlled process variable (PV), and compares it with the reference or Setpoint (control system), set point (SP). The difference between actual and desired value of the process variable, called the ''error'' signal, or SP-PV error, is applied as feedback to generate a control action to bring the controlled process variable to the same value as the set point. Other aspects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-organized Criticality
Self-organized criticality (SOC) is a property of dynamical systems that have a critical point as an attractor. Their macroscopic behavior thus displays the spatial or temporal scale-invariance characteristic of the critical point of a phase transition, but without the need to tune control parameters to a precise value, because the system, effectively, tunes itself as it evolves towards criticality. The concept was put forward by Per Bak, Chao Tang and Kurt Wiesenfeld ("BTW") in a paper , following an earlier paper by Jonathan Katz published in 1987 in ''Physical Review Letters'', and is considered to be one of the mechanisms by which complexity arises in nature. Its concepts have been applied across fields as diverse as geophysics, physical cosmology, evolutionary biology and ecology, bio-inspired computing and optimization (mathematics), economics, quantum gravity, sociology, solar physics, plasma physics, neurobiology and others. SOC is typically observed in slowl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abelian Sandpile Model
The Abelian sandpile model (ASM) is the more popular name of the original Bak–Tang–Wiesenfeld model (BTW). The BTW model was the first discovered example of a dynamical system displaying self-organized criticality. It was introduced by Per Bak, Chao Tang and Kurt Wiesenfeld in a 1987 paper. Three years later Deepak Dhar discovered that the BTW sandpile model follows abelian dynamics, and therefore referred to this model as the Abelian sandpile model. The model is a cellular automaton. In its original formulation, each site on a finite grid has an associated value that corresponds to the slope of the pile. This slope builds up as "grains of sand" (or "chips") are randomly placed onto the pile, until the slope exceeds a specific threshold value at which time that site collapses transferring sand into the adjacent sites, increasing their slope. Bak, Tang, and Wiesenfeld considered process of successive random placement of sand grains on the grid; each such placement of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taleb Distribution
In economics and finance, a Taleb distribution is the statistical profile of an investment which normally provides a payoff of small positive returns, while carrying a small but significant risk of catastrophic losses. The term was coined by journalist Martin Wolf and economist John Kay to describe investments with a "high probability of a modest gain and a low probability of huge losses in any period." The concept is named after Nassim Nicholas Taleb, based on ideas outlined in his book '' Fooled by Randomness''. According to Taleb in ''Silent Risk'', the term should be called "payoff" to reflect the importance of the payoff function of the underlying probability distribution, rather than the distribution itself. The term is meant to refer to an investment returns profile in which there is a high probability of a small gain, and a small probability of a very large loss, which more than outweighs the gains. In these situations the expected value is very much less than zero, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
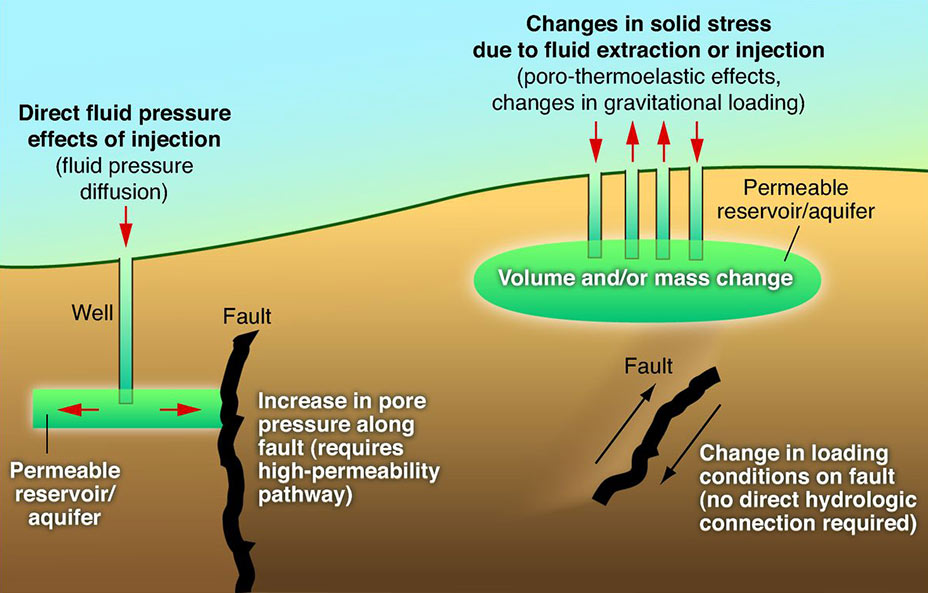
Induced Seismicity
Induced seismicity is typically earthquakes and tremors that are caused by human activity that alters the stresses and strains on Earth's crust. Most induced seismicity is of a low magnitude. A few sites regularly have larger quakes, such as The Geysers geothermal plant in California which averaged two M4 events and 15 M3 events every year from 2004 to 2009. The Human-Induced Earthquake Database (''HiQuake'') documents all reported cases of induced seismicity proposed on scientific grounds and is the most complete compilation of its kind. Results of ongoing multi-year research on induced earthquakes by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) published in 2015 suggested that most of the significant earthquakes in Oklahoma, such as the 1952 magnitude 5.7 El Reno earthquake may have been induced by deep injection of wastewater by the oil industry. A huge number of seismic events in oil and gas extraction states like Oklahoma is caused by increasing the volume of wastewater injec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. In its most general sense, the word ''earthquake'' is used to describe any seismic event that generates seismic waves. Earthquakes can occur naturally or be induced by human activities, such as mining, fracking, and nuclear weapons testing. The initial point of rupture is called the hypocenter or focus, while the ground level directly above it is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Criticality Accident
A criticality accident is an accidental uncontrolled nuclear fission chain reaction. It is sometimes referred to as a critical excursion, critical power excursion, divergent chain reaction, or simply critical. Any such event involves the unintended accumulation or arrangement of a critical mass of fissile material, for example enriched uranium or plutonium. Criticality accidents can release potentially fatal radiation doses if they occur in an unprotected environment. Under normal circumstances, a critical or supercritical fission reaction (one that is self-sustaining in power or increasing in power) should only occur inside a safely shielded location, such as a reactor core or a suitable test environment. A criticality accident occurs if the same reaction is achieved unintentionally, for example in an unsafe environment or during reactor maintenance. Though dangerous and frequently lethal to humans within the immediate area, the critical mass formed would not be capable of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |