|
Seismic Risk In Malta
Seismic risk in Malta is considered to be low with little historic damage noted and no known victims. The archipelago is however in a potentially significant seismic zone and the risk to the population is probably undervalued. Tectonics The Maltese Archipelago rests on an underwater plateau, a relatively stable part of the African Plate. The islands are situated around 200 km to the south of the subduction fault between the African Plate and the Eurasian Plate. The pelagic plate forms a shallow platform separating the Ionian basin from the Western Mediterranean Basin, situated roughly under the Strait of Sicily. The plate is crossed by a rift zone formed of three grabens: the Pantelleria graben, that of Malta, and that of Linosa. These grabens are linked by a system of north–south orientation faults (sometimes west–east) with dextral cavities that are responsible for most of the earthquakes that can affect the archipelago. The islands themselves are made up of l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismic Zone
In seismology, a seismic zone or seismic belt is an area of seismicity potentially sharing a common cause. It can be referred to as an earthquake belt as well. It may also be a region on a map for which a common areal rate of seismicity is assumed for the purpose of calculating probabilistic ground motions. An obsolete definition is a region on a map in which a common level of seismic design is required. The major seismic zones A type of seismic zone is a Wadati–Benioff zone which corresponds with the down-going slab in a subduction zone. The world's greatest seismic belt, known as the Circum-Pacific seismic belt, is where a majority of the Earth's quakes occur. Approximately 81% of major earthquakes occur along this belt. The Circum-Pacific seismic belt has earned its own nickname and is often referred to as the Ring of Fire, a ring-like formation that encompasses a majority of the Pacific Ocean. The notorious San Andreas Fault, responsible for many major quakes in the West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
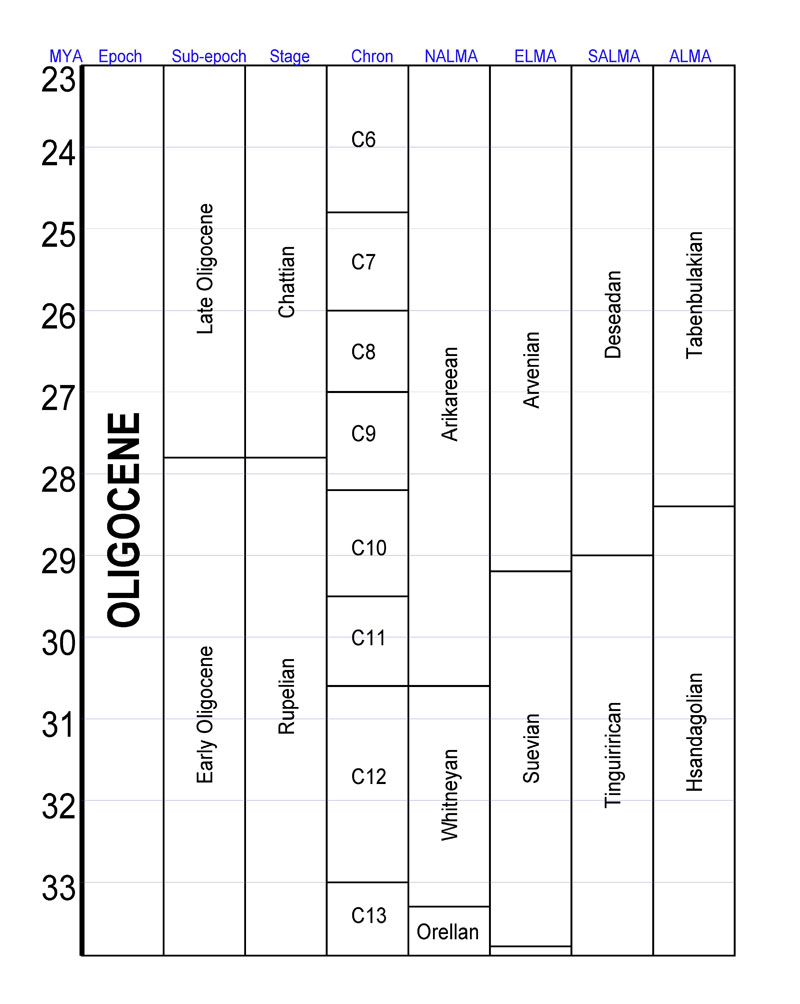
Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from Ancient Greek (''olígos'') 'few' and (''kainós'') 'new', and refers to the sparsity of Neontology, extant forms of Mollusca, molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and Corsica. Crete is located about south of the Peloponnese, and about southwest of Anatolia. Crete has an area of and a coastline of 1,046 km (650 mi). It bounds the southern border of the Aegean Sea, with the Sea of Crete (or North Cretan Sea) to the north and the Libyan Sea (or South Cretan Sea) to the south. Crete covers 260 km from west to east but is narrow from north to south, spanning three longitudes but only half a latitude. Crete and a number of islands and islets that surround it constitute the Region of Crete (), which is the southernmost of the 13 Modern regions of Greece, top-level administrative units of Greece, and the fifth most popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionian Sea
The Ionian Sea (, ; or , ; , ) is an elongated bay of the Mediterranean Sea. It is connected to the Adriatic Sea to the north, and is bounded by Southern Italy, including Basilicata, Calabria, Sicily, and the Salento peninsula to the west, southern Albania (and western Apulia, Italy) to the north, and the west coast of Greece, including the Peloponnese. All major islands in the sea, which are located in the east of the sea, belong to Greece. They are collectively named the Ionian Islands, the main ones being Corfu, Kefalonia, Zakynthos, Lefkada, and Ithaca. There are ferry routes between Patras and Igoumenitsa, Greece, and Brindisi and Ancona, Italy, that cross the east and north of the Ionian Sea, and from Piraeus westward. Calypso Deep, the deepest point in the Mediterranean at , is in the Ionian Sea, at . The sea is one of the most seismically active areas in the world. Etymology The name ''Ionian'' comes from the Greek word . Its etymology is unknown. Ancient G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4.7 million inhabitants, including 1.2 million in and around the capital city of Palermo, it is both the largest and most populous island in the Mediterranean Sea. Sicily is named after the Sicels, who inhabited the eastern part of the island during the Iron Age. Sicily has a rich and unique culture in #Art and architecture, arts, Music of Sicily, music, #Literature, literature, Sicilian cuisine, cuisine, and Sicilian Baroque, architecture. Its most prominent landmark is Mount Etna, the tallest active volcano in Europe, and one of the most active in the world, currently high. The island has a typical Mediterranean climate. It is separated from Calabria by the Strait of Messina. It is one of the five Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moment Magnitude Scale
The moment magnitude scale (MMS; denoted explicitly with or Mwg, and generally implied with use of a single M for magnitude) is a measure of an earthquake's magnitude ("size" or strength) based on its seismic moment. was defined in a 1979 paper by Thomas C. Hanks and Hiroo Kanamori. Similar to the local magnitude scale, local magnitude/Richter scale () defined by Charles Francis Richter in 1935, it uses a logarithmic scale; small earthquakes have approximately the same magnitudes on both scales. Despite the difference, news media often use the term "Richter scale" when referring to the moment magnitude scale. Moment magnitude () is considered the authoritative magnitude scale for ranking earthquakes by size. It is more directly related to the energy of an earthquake than other scales, and does not saturatethat is, it does not underestimate magnitudes as other scales do in certain conditions. It has become the standard scale used by seismological authorities like the United State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Macroseismic Scale
The European Macroseismic Scale (EMS) is the basis for evaluation of seismic intensity in European countries and is also used in a number of countries outside Europe. Issued in 1998 as an update of the test version from 1992, the scale is referred to as EMS-98. Overview The history of the EMS began in 1988 when the European Seismological Commission (ESC) decided to review and update the Medvedev–Sponheuer–Karnik scale (MSK-64), which was used in its basic form in Europe for almost a quarter of a century. After more than five years of intensive research and development and a four-year testing period, the new scale was officially released. In 1996, the XXV General Assembly of the ESC in Reykjavík passed a resolution recommending the adoption of the new scale by the member countries of the European Seismological Commission. The European macroseismic scale EMS-98 is the first seismic intensity scale designed to encourage co-operation between engineers and seismologists, rather t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicilian Channel
The Strait of Sicily (also known as Sicilian Strait, Sicilian Channel, Channel of Sicily, Sicilian Narrows and Pantelleria Channel; or the ; or , ' or ') is the strait between Sicily and Tunisia. The strait is about wide and divides the Tyrrhenian Sea and the western Mediterranean Sea, from the eastern Mediterranean Sea. The maximum depth is . The island of Pantelleria lies in the middle of the strait. There are regular ferries between Sicily and Tunis across the Strait of Sicily; a tunnel has been proposed to link the two regions. Flows Deep ocean current, currents in the strait flow from east to west, and the current nearer the surface travels from west to east. This unusual water flow is of interest to oceanographers. Within the Central Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean sea it is one of the topographically complex regions. With a length of 600 km it connects the Eastern and Western Mediterranean basins. The strait is delimited by two systems; at the eastern side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epicentre
The epicenter (), epicentre, or epicentrum in seismology is the point on the Earth's surface directly above a hypocenter or focus, the point where an earthquake or an underground explosion originates. Determination The primary purpose of a seismometer is to locate the initiating points of earthquake epicenters. The secondary purpose, of determining the 'size' or magnitude must be calculated after the precise location is known. The earliest seismographs were designed to give a sense of the direction of the first motions from an earthquake. The Chinese frog seismograph would have dropped its ball in the general compass direction of the earthquake, assuming a strong positive pulse. We now know that first motions can be in almost any direction depending on the type of initiating rupture (focal mechanism). The first refinement that allowed a more precise determination of the location was the use of a time scale. Instead of merely noting, or recording, the absolute motions of a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Malta
Malta has been inhabited since 6400 BC initially by Mesolithic hunter gatherers, who were replaced by Early European Farmers, Neolithic farmers from Sicily around 5400 BC. These farmers practiced mixed farming after clearing most of the existing conifer forest that dominated the islands, but their agricultural methods degraded the soil until the islands became uninhabitable. The islands were repopulated around 3850 BC by a civilization that at its peak built the Megalithic Temples of Malta, Megalithic Temples, which today are among the oldest surviving buildings in the world. Their civilization collapsed in around 2350 BC; the islands were repopulated by Bronze Age warriors soon afterwards. Malta's prehistory ends in around 700 BC, when the islands were colonized by the Phoenicians. They ruled the islands until they Capture of Malta (218 BC), fell in 218 BC to the Roman Republic. The island was acquired by the Eastern Romans or Byzantine Empire, Byzantines in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of St John Of Jerusalem
The Order of Knights of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem, commonly known as the Knights Hospitaller (), is a Catholic military order. It was founded in the crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem in the 12th century and had headquarters there until 1291, thereafter being based in Kolossi Castle in Cyprus (1302–1310), the island of Rhodes (1310–1522), Malta (1530–1798), and Saint Petersburg (1799–1801). The Hospitallers arose in the early 12th century at the height of the Cluniac movement, a reformist movement within the Benedictine monastic order that sought to strengthen religious devotion and charity for the poor. Earlier in the 11th century, merchants from Amalfi founded a hospital in Jerusalem dedicated to John the Baptist where Benedictine monks cared for sick, poor, or injured Christian pilgrims to the Holy Land. Blessed Gerard, a lay brother of the Benedictine order, became its head when it was established. After the Christian conquest of Jerusalem in 1099 dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologic Time Scale
The geologic time scale or geological time scale (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronology (a scientific branch of geology that aims to determine the age of rocks). It is used primarily by Earth scientists (including geologists, paleontologists, geophysicists, geochemists, and paleoclimatologists) to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. The time scale has been developed through the study of rock layers and the observation of their relationships and identifying features such as lithologies, paleomagnetic properties, and fossils. The definition of standardised international units of geological time is the responsibility of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), a constituent body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), whose primary objective is to preci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |