|
Seismic Communication
Seismic or vibrational communication is a process of conveying information through mechanical (seismology, seismic) vibrations of the substrate. The substrate may be the earth, a plant stem or leaf, the surface of a body of water, a spider's web, a honeycomb, or any of the myriad types of soil substrates. Seismic cues are generally conveyed by surface Rayleigh waves, Rayleigh or bending waves generated through vibrations on the substrate, or acoustical waves that couple with the substrate. Vibrational communication is an ancient sensory modality and it is widespread in the animal kingdom where it has evolved several times independently. It has been reported in mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, insects, arachnids, crustaceans and nematode worms.Hill, P.S.M., (2008). ''Vibrational Communication in Animals.'' Harvard, Cambridge, London Vibrations and other communication channels are not necessarily mutually exclusive, but can be used in multi-modal communication. Functions Comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
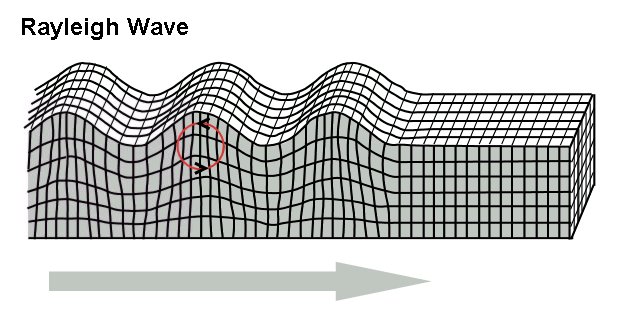
Rayleigh Wave
Rayleigh waves are a type of surface acoustic wave that travel along the surface of solids. They can be produced in materials in many ways, such as by a localized impact or by Piezoelectricity, piezo-electric Interdigital transducer, transduction, and are frequently used in non-destructive testing for detecting defects. Rayleigh waves are part of the seismic waves that are produced on the Earth by earthquakes. When guided in layers they are referred to as Lamb waves, Rayleigh–Lamb waves, or generalized Rayleigh waves. Characteristics Rayleigh waves are a type of surface wave that travel near the surface of solids. Rayleigh waves include both longitudinal and transverse motions that decrease exponentially in amplitude as distance from the surface increases. There is a phase difference between these component motions. The existence of Rayleigh waves was predicted in 1885 by Lord Rayleigh, after whom they were named. In isotropic solids these waves cause the surface particles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eavesdropping
Eavesdropping is the act of secretly or stealthily listening to the private conversation or communications of others without their consent in order to gather information. Etymology The verb ''eavesdrop'' is a back-formation from the noun ''eavesdropper'' ("a person who eavesdrops"), which was formed from the related noun ''eavesdrop'' ("the dripping of water from the eaves of a house; the ground on which such water falls"). An eavesdropper was someone who would hang from the eave of a building so as to hear what is said within. The PBS documentaries ''Inside the Court of Henry VIII'' (April 8, 2015) and ''Secrets of Henry VIII’s Palace'' (June 30, 2013) include segments that display and discuss "eavedrops", carved wooden figures Henry VIII had built into the eaves (overhanging edges of the beams in the ceiling) of Hampton Court to discourage unwanted gossip or dissension from the King's wishes and rule, to foment paranoia and fear, and demonstrate that everything said there wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gelotia
''Gelotia'' is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Tamerlan Thorell in 1890. Species It contains eleven species, found only in Asia and on New Britain: *'' Gelotia argenteolimbata'' ( Simon, 1900) – Singapore *'' Gelotia bimaculata'' Thorell, 1890 – Borneo *'' Gelotia bouchardi'' (Simon, 1903) – Indonesia (Sumatra) *'' Gelotia frenata'' Thorell, 1890 (type) – Indonesia (Sumatra) *'' Gelotia lanka'' Wijesinghe, 1991 – Sri Lanka *'' Gelotia liuae'' (Wang & Li, 2020) – China *'' Gelotia robusta'' Wanless, 1984 – Papua New Guinea (New Britain) *'' Gelotia salax'' (Thorell, 1877) – Indonesia (Sulawesi) *'' Gelotia syringopalpis'' Wanless, 1984 – China, Malaysia, Borneo *'' Gelotia zhengi'' Cao & Li, 2016 – China *'' Gelotia onoi'' Hoang, Phan & Vo, 2024 - Vietnam Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrba
''Cyrba'' is a genus of spiders in the family Salticidae (jumping spiders). The genus was erected by Hippolyte Lucas in 1846. Description ''Cyrba'' spiders are small to medium size spiders that are usually brightly colored. Their cephalothorax is long and moderately high. The eyes are lateral. The abdomen is long with bright colorful patterns. Their legs are thin and slender. The genus has been described as primitive because of their pervasive use of webs, large posterior median eyes, and the secretory organs on the femora of males. These characteristics were lost by advanced salticids. The genus are also almost wholly dependent on their vision. The primary mating season for the spider ''C. algerina'' is May. Juveniles emerge in July, grow to about half the adult size by winter, and then grow to adult size in the spring of the following year. The genus is commonly found on very rocky ground under rocks, or less often walking around on the ground or on the tops of rocks. Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brettus
''Brettus'' is a genus of jumping spiders. Its six described species are found in southern Asia from India to China and Sulawesi, with a single species endemic to Madagascar. Two species in this genus, ''B. celebensis'' and ''B. madagascarensis'', were originally described as members of the genus '' Macopaeus''. According to Thorell, the genus name is taken from Greek mythology. Brettos (Βρεττος) was a son of Heracles (appears at Stephanus of Byzantium). Diet and behaviour At least 2 species, '' Brettus cingulatus'' and '' Brettus adonis'', feed on other spiders. Taking advantage of their ability to not adhere to any kind of spider silk, they practise aggressive mimicry and pluck upon the webs of web-building spiders to lure them over to the ''Brettus'' at the edge of the web, where they capture/stab their victim. These two spider species also prefer web-building spiders to insects as prey. They are in these regards similar to the other Spartaeinae jumping spiders o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portia (genus)
''Portia'' is a genus of jumping spider that feeds on other spiders (i.e., they are Arachnophagy, arachnophagic). They are remarkable for their intelligent hunting behaviour, which suggests that they are capable of learning and problem solving, traits normally attributed to much larger animals. Taxonomy and evolution The genus was established in 1878 by German arachnologist Friedrich Karsch. The fringed jumping spider (''Portia fimbriata'') is the type species. Molecular phylogeny, a technique that compares the DNA of organisms to construct the Tree of life (biology), tree of life, indicates that ''Portia'' is a member of a basal clade (i.e. quite similar to the ancestors of all jumping spiders) and that the ''Spartaeus'', ''Phaeacius'', and ''Holcolaetis'' genera are its closest relatives. Fred Wanless, Wanless divided the genus ''Portia'' into two species groups: the ''schultzi'' group, in which males' palps have a fixed tibial tubercle, apophysis; and the ''kenti'' group, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pholcus
''Pholcus'' is a genus of spiders of long-bodied cellar spider and allies in the family Pholcidae, with 375 described species as of January 2023. It includes the cellar spider '' P. phalangioides'', often called the "daddy longlegs". This may cause confusion because the name "daddy longlegs" is also applied to two other unrelated arthropods: the harvestman and the crane fly. Description ''Pholcus'', like Pholcidae in general, have extremely long and thin legs. The genus can be distinguished from other pholcid genera by its large size (body length >4 mm), eight eyes, evenly domed prosoma (lacking a median furrow or pit) and cylindrical opisthosoma (longer than it is high). Habitat In the wild, ''Pholcus'' live in environments such as caves, under rocks, forest shrubs and deep limestone cracks. Synanthropic species such as ''P. phalangioides'' live in and around buildings and other disturbed habitats. Species * '' Pholcus abstrusus'' Yao & Li, 2012 — China * '' Pholcu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
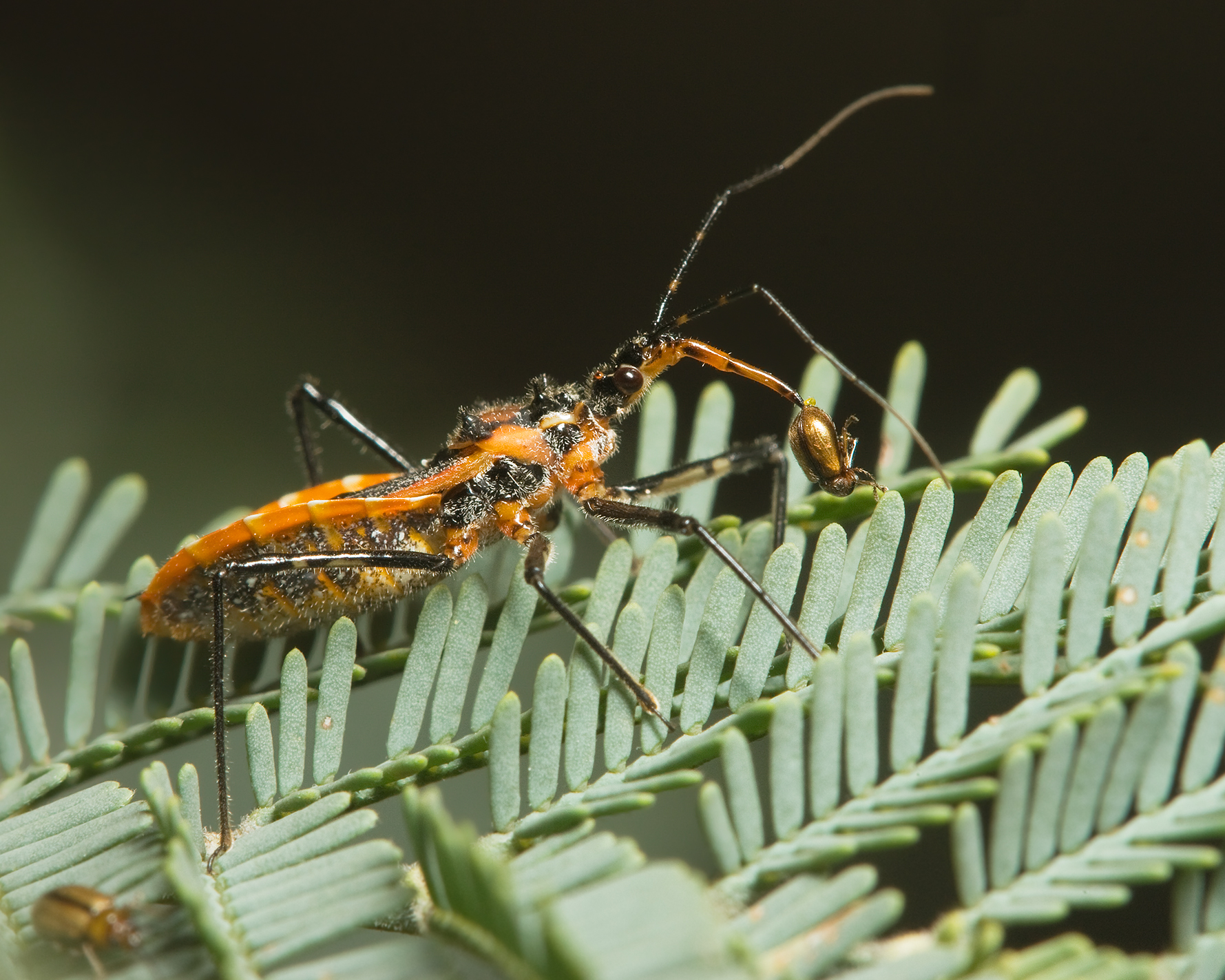
Assassin Bug
The Reduviidae is a large cosmopolitan family of the suborder Heteroptera of the order Hemiptera (true bugs). Among the Hemiptera and together with the Nabidae almost all species are terrestrial ambush predators; most other predatory Hemiptera are aquatic. The main examples of non-predatory Reduviidae are some blood-sucking ectoparasites in the subfamily Triatominae, with a few species from South America noted for their ability to transmit Chagas disease. Though spectacular exceptions are known, most members of the family are fairly easily recognizable: they have a relatively narrow neck, sturdy build, and formidable curved proboscis (sometimes called a rostrum). Large specimens should be handled with caution, if at all, because they sometimes defend themselves with a very painful stab from the proboscis. Taxonomy The family members are almost all predatory, except for a few blood-sucking species, some of which are important as disease vectors. About 7000 species have been des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing#Evolution of hairlessness, hairlessness, bipedality, bipedalism, and high Human intelligence, intelligence. Humans have large Human brain, brains, enabling more advanced cognitive skills that facilitate successful adaptation to varied environments, development of sophisticated tools, and formation of complex social structures and civilizations. Humans are Sociality, highly social, with individual humans tending to belong to a Level of analysis, multi-layered network of distinct social groups — from families and peer groups to corporations and State (polity), political states. As such, social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of Value theory, values, norm (sociology), social norms, languages, and traditions (co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Herring Gull
The European herring gull (''Larus argentatus'') is a large gull, up to long. It breeds throughout the northern and western coasts of Europe. Some European herring gulls, especially those resident in colder areas, bird migration, migrate further south in winter, but many are permanent residents, such as in Ireland, Great Britain, Britain, Iceland, or on the North Sea shores. They have a varied diet, including fish, crustaceans, as well as some plants, and are also scavengers, consuming carrion and food left by or stolen from humans. Taxonomy Their scientific name is from Latin. ''Larus'' appears to have referred to a gull or other large seabird and ''argentatus'' means decorated with silver. The taxonomy of the herring gull/lesser black-backed gull is contentious, with different authorities recognising between two and eight species. This group has a ring species, ring distribution around the Northern Hemisphere. Most adjacent populations interbreed; however, adjacent terminal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood Turtle
The wood turtle (''Glyptemys insculpta'') is a species of turtle in the family Emydidae. The species is native to northeastern North America. The genus '' Glyptemys'' contains only one other species of turtle: the bog turtle (''Glyptemys muhlenbergii)''. The wood turtle reaches a straight carapace length of , its defining characteristic being the pyramidal shape of the scutes on its upper shell. Morphologically, it is similar to the bog turtle, spotted turtle (''Clemmys guttata''), and Blanding's turtle (''Emydoidea blandingii)''. The wood turtle exists in a broad geographic range extending from Nova Scotia in the north (and east) to Minnesota in the west and Virginia in the south. In the past, it was forced south by encroaching glaciers: skeletal remains have been found as far south as Georgia. It spends a great deal of time in or near the water of wide rivers, preferring shallow, clear streams with compacted and sandy bottoms. The wood turtle can also be found in forests an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macaria Aemulataria
''Macaria aemulataria'', the common angle moth, is a moth in the family Geometridae. The species was first described by Francis Walker in 1861. It is found from Nova Scotia to Florida, west to Texas, north to Oregon and Alberta. The wingspan The wingspan (or just span) of a bird or an airplane is the distance from one wingtip to the opposite wingtip. For example, the Boeing 777–200 has a wingspan of , and a wandering albatross (''Diomedea exulans'') caught in 1965 had a wingsp ... is . Adults are on wing from mid-June to mid-July in Alberta and from May to September in Ohio. The larvae feed on '' Acer'' species. References Moths described in 1861 Macariini Moths of North America Lepidoptera of Canada Lepidoptera of the United States {{Macariini-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |