|
Seibu 6000 Series
The is an electric multiple unit (EMU) train type operated by the private railway operator Seibu Railway on commuter services in the Tokyo area of Japan. Twenty-five 10-car sets were manufactured by Tokyu Car Corporation and Hitachi between 1992 and 1998. Featuring several advances in design, accessibility, and technology over older Seibu Railway sets, the 6000 series was developed for use on through services to the TRTA (now Tokyo Metro) Tokyo Metro Yūrakuchō Line, Yurakucho Line and to serve as the basis for future Seibu train types. The type first entered service on 1 June 1992 on the Seibu Ikebukuro Line and has since been introduced onto other lines, including the Seibu Seibu Yurakucho Line, Yurakucho and Seibu Shinjuku Line, Shinjuku lines, the Tokyo Metro Fukutoshin Line, and the Tokyu Toyoko Line. Design The 6000 series was developed for use on through services to the Tokyo Metro Yūrakuchō Line, Yurakucho Subway Line, as well as to be the basis for future Seibu R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyu Car Corporation
is a manufacturer of heavy rail cars in Japan, formerly known as . The company is based in Kanazawa-ku, Yokohama, and a member of East Japan Railway Company (JR East) group. J-TREC manufactures rail vehicles not only for JR East and Tokyu Corporation but for other Japanese operators, including various Japan Railways Group companies and international operators as well. Tokyu Car Corporation, the predecessor of J-TREC, was founded on 23 August 1948. Tokyu Car was a licensee of early-generation (early-1960s) stainless-steel commuter EMU train body and related bogie technology from the Budd Company of the United States. Since then, Tokyu Car has specialised in stainless-steel body car technology. On 27 October 2011, Tokyu Car Corporation announced that its rolling stock manufacturing division would be acquired by East Japan Railway Company (JR East), and the company cease operations with effect from 1 April 2012. It is to be subsequently split into two companies, Tokyu Car Engineer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regenerative Braking
Regenerative braking is an energy recovery mechanism that slows down a moving vehicle or object by converting its kinetic energy or potential energy into a form that can be either used immediately or stored until needed. Typically, regenerative brakes work by driving an electric motor in reverse to recapture energy that would otherwise be lost as heat during braking, effectively turning the traction motor into a generator. Feeding power backwards through the system like this allows the energy harvested from deceleration to resupply an energy storage solution such as a battery or a capacitor. Once stored, this power can then be later used to aid forward propulsion. Because of the electrified vehicle architecture required for such a braking system, automotive regenerative brakes are most commonly found on hybrid and electric vehicles. This method contrasts with conventional braking systems, where excess kinetic energy is converted to unwanted and wasted heat due to friction i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
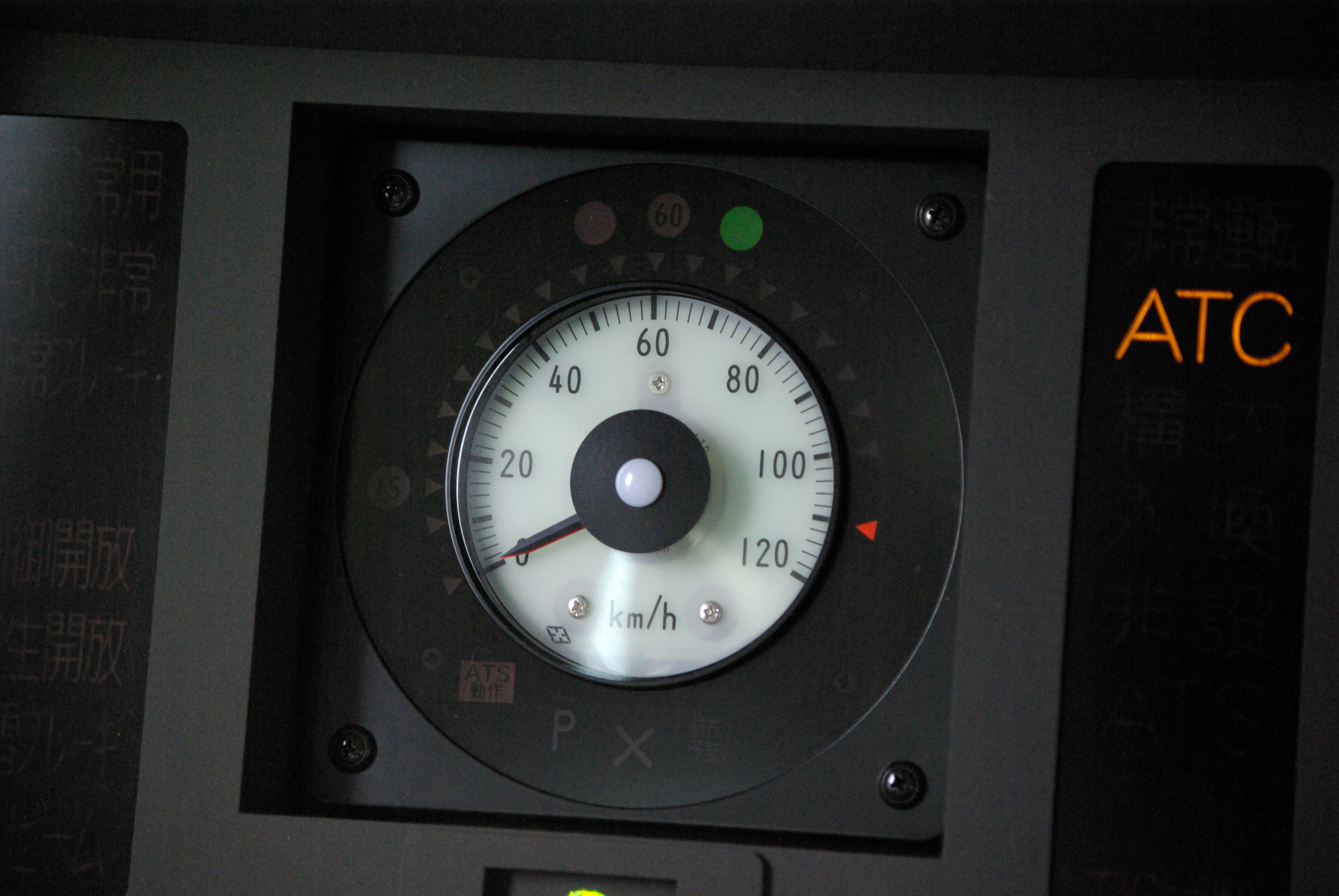
Automatic Train Control
Automatic train control (ATC) is a general class of train protection systems for railways that involves a speed control mechanism in response to external inputs. For example, a system could effect an emergency brake application if the driver does not react to a signal at danger. ATC systems tend to integrate various cab signalling technologies and they use more granular deceleration patterns in lieu of the rigid stops encountered with the older automatic train stop (ATS) technology. ATC can also be used with automatic train operation (ATO) and is usually considered to be the safety-critical part of a railway system. There have been numerous different safety systems referred to as "automatic train control" over time. The first experimental apparatus was installed on the Henley branch line in January 1906 by the Great Western Railway, although it would now be referred to as an automatic warning system (AWS) because the driver retained full command of braking. The term is especi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerima Station
is a railway station in Nerima, Tokyo, Japan, operated by the private railway operator Seibu Railway and the Tokyo subway operator Toei Subway. Lines Nerima Station is served by the Seibu Ikebukuro Line, Seibu Yurakucho Line, and Seibu Toshima Line, and also by the Toei Ōedo Line subway. It is located from the terminus of the Ikebukuro Line at . Station layout Nerima is an elevated station with two island platforms serving four tracks, with an additional outer track on either side used by passing trains. Elevators and escalators connect the platforms to the ticket entrances, and the station contains a waiting room as well. The Toei station consists of an underground island platform serving two tracks. Nerima Station in western Tokyo is a busy commuter station on the Toei Oedo Line, the Seibu Ikebukuro Line and the Seibu Toshima Line. Platforms Seibu File:Seibu Nerima-STA Central-Gate.jpg, Ticket gates, 2023 File:Seibu Nerima-STA Platform1-2.jpg, Platforms, 2023 Toe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seibu 101 Series
The and are electric multiple unit (EMU) train types operated by the private railway operator Seibu Railway in Japan. Original 101 series The 101 series began service in 1969, in conjunction with the opening of the Seibu Chichibu Line. New 101 series and 301 series The New 101 series features changes in design. The 301 series is based on the New 101 series, and were formed as eight-car sets. File:Seibu-Series-New101_Inside.jpg, Interior view File:Seibu-Series-New101_Inside_Priority-seat.jpg, Priority seating File:Seibu-Series-New101_Inside_Free-space.jpg, Wheelchair space Resale The Chichibu Railway 6000 series trains were rebuilt from former Seibu New 101 series trains. Sangi Railway operates former New 101 series trains as Sangi Railway 751 series. Former Seibu New 101 series trains were also transferred to Ryutetsu, becoming Ryutetsu 5000 series trains. File:Chichibu Railway 6000.jpg, Chichibu Railway 6000 series File:0903150740 hobo sangi S751.jpg, Sangi Railway 751 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
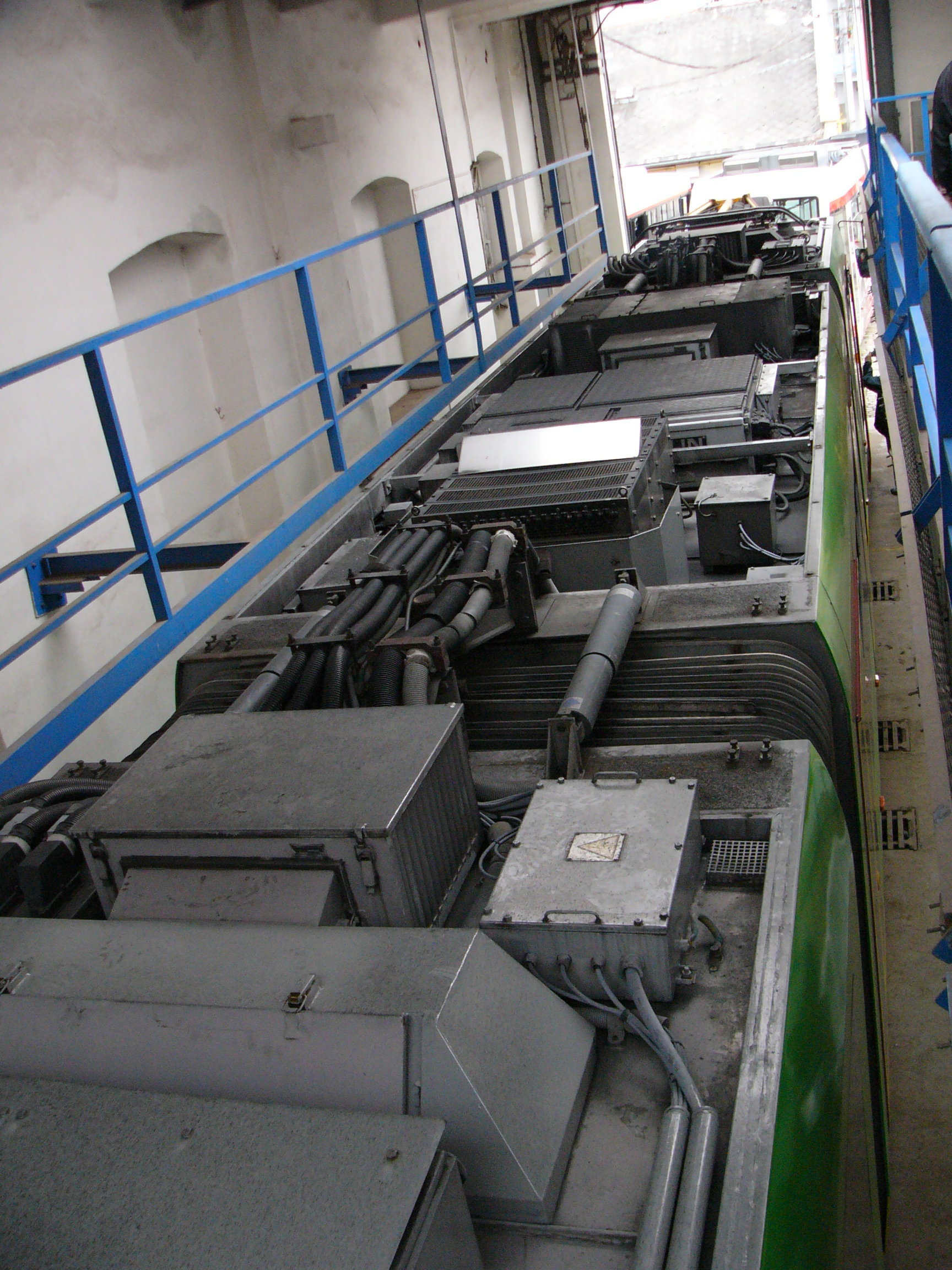
Variable-frequency Drive
A variable-frequency drive (VFD, or adjustable-frequency drive, adjustable-speed drive, variable-speed drive, AC drive, micro drive, inverter drive, variable voltage variable frequency drive, or drive) is a type of AC motor, AC motor drive (system incorporating a motor) that controls speed and torque by varying the frequency of the input electricity. Depending on its Topology (electrical circuits), topology, it controls the associated voltage or electric current, current variation., quote is per definition on p. 4 of NEMA Standards Publication ICS 7.2-2021. VFDs are used in applications ranging from small appliances to large compressors. Systems using VFDs can be more efficient than hydraulics, hydraulic systems, such as in systems with pumps and damper control for fans. Since the 1980s, power electronics technology has reduced VFD cost and size and has improved performance through advances in semiconductor switching devices, drive topologies, simulation and control techniques ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Railfan Magazine
is a Japanese-language monthly magazine for railfans covering the mainly Japanese railways published by Koyusha. It has been published in Japan since 1961. Issues go on sale on the 21st of each month, two months before the cover month (e.g. the March issue is on sale on 21 January). Each copy sells for between ¥1,100 and ¥1,200, depending on the number of pages. The magazine reports on railway prototypes, complete with technical plans, photos, maps, graphs, and tables. See also * List of railroad-related periodicals A list is a set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but ... References External links * 1961 establishments in Japan Magazines published in Japan Monthly magazines published in Japan Magazines established in 1961 Railway culture in Japan Rail transport magaz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
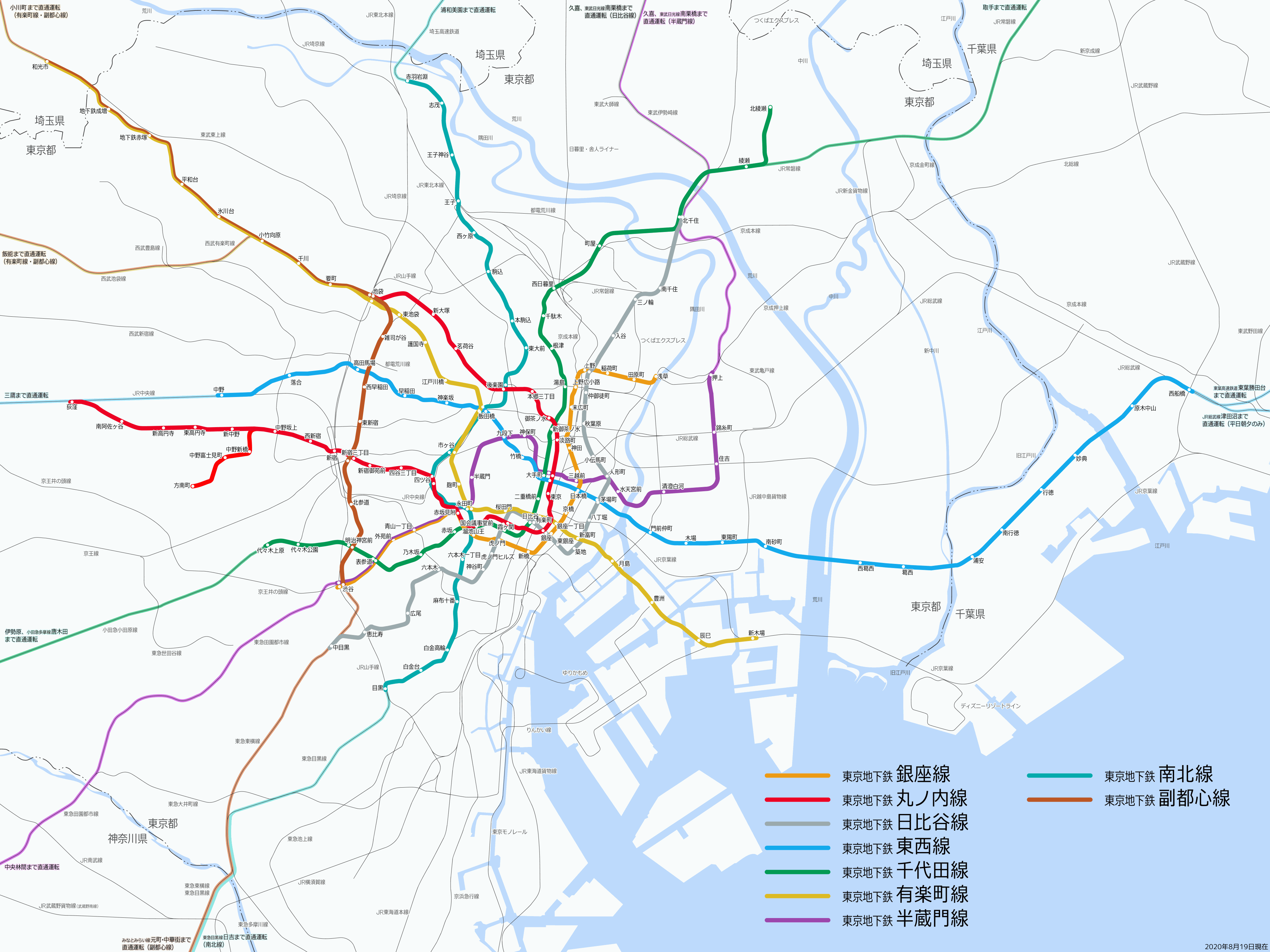
Tokyo Metro Yūrakuchō Line
The is a rapid transit, subway line in Japan owned and operated by Tokyo Metro. The line connects Wakōshi Station in Wakō, Saitama and Shin-Kiba Station in Kōtō, Tokyo. On maps, diagrams and signboards, the line is shown using the color "gold", and its stations are given numbers using the letter "Y". The line was named after the Yūrakuchō business district in Chiyoda, Tokyo. The proper name as given in an annual report of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport (Japan), Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport is . According to the Tokyo urban transportation plan, however, it is more complicated. The line number assigned to the section south from Kotake-Mukaihara to Shin-Kiba is Line 8, but that north of Kotake-Mukaihara to Wakōshi is Line 13, which indicates the section is a portion of Tokyo Metro Fukutoshin Line, Fukutoshin Line which shares the same number. Services The Yurakucho Line runs generally northwest to southeast between Wakōshi Station in S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo Metro
The Tokyo Metro () is a major rapid transit system in Tokyo, Japan, operated by the #Organization, Tokyo Metro Co. With an average daily ridership of 6.52 million passengers (as of 2023), the Tokyo Metro is the larger of the Tokyo subway, two subway operators in the city, the other being the Toei Subway, with 2.85 million average daily rides. Organization Tokyo Metro is operated by , a joint-stock company jointly owned by the Government of Japan and the Tokyo Metropolitan Government. The company, founded as a part of then-Prime Minister Junichiro Koizumi's policy of converting statutory corporations into Joint-stock company, joint-stock companies, replaced the , commonly known as Eidan or TRTA, on April 1, 2004. TRTA was administered by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport (Japan), Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport, and jointly funded by the national and metropolitan governments. It was formed in 1941 as a part-nationalization of the Tokyo Undergrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seibu Railway
is a conglomerate based in Tokorozawa, Saitama, Japan, with principal business areas in railways, tourism, and real estate. Seibu Railway's operations are concentrated in northwest Tokyo and Saitama Prefecture; the name "Seibu" is an abbreviation of "west Musashi", referring to the historic name for this area. It and its holding company hold shares of numerous bus, hotel and tourism operations nationwide. History "Seibu Railway" was originally the name of a tram service between Shinjuku and Ogikubo, which was transferred to the Tokyo metropolitan government in 1951 and eventually closed in 1962. The Seibu Railway was acquired in 1921 by the Kawagoe Railway, which had operated a train service between Kokubunji and Kawagoe since 1894; the merged company kept the "Seibu" name and expanded its main line to Takadanobaba, forming what is now known as the Seibu Shinjuku Line. The current Seibu Railway is a product of a 1945 merger between the former Seibu Railway and the Musashi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Private Railway
A private railway is a railroad run by a private business entity (usually a corporation but not need be), as opposed to a railroad run by a public sector. Japan In Japan, , commonly simply ''private railway'', refers to a public transit railway owned and operated by private sector, almost always organized as a joint-stock company, or in Japanese: kabushiki gaisha (), but may be any type of private business entity. Although the Japan Railways Group (JR Group) companies are also kabushiki gaishas, they are not classified as private railways because of their unique status as the primary successors of the Japanese National Railways (JNR). Voluntary sector railways (semi-public) are additionally not classified as ''shitetsu'' due to their origins as rural, money-losing JNR lines that have since been transferred to local possession, in spite of their organizational structures being corporatized. Among ''private railways'' in Japan, the categorizes 16 companies as "major" operators. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |