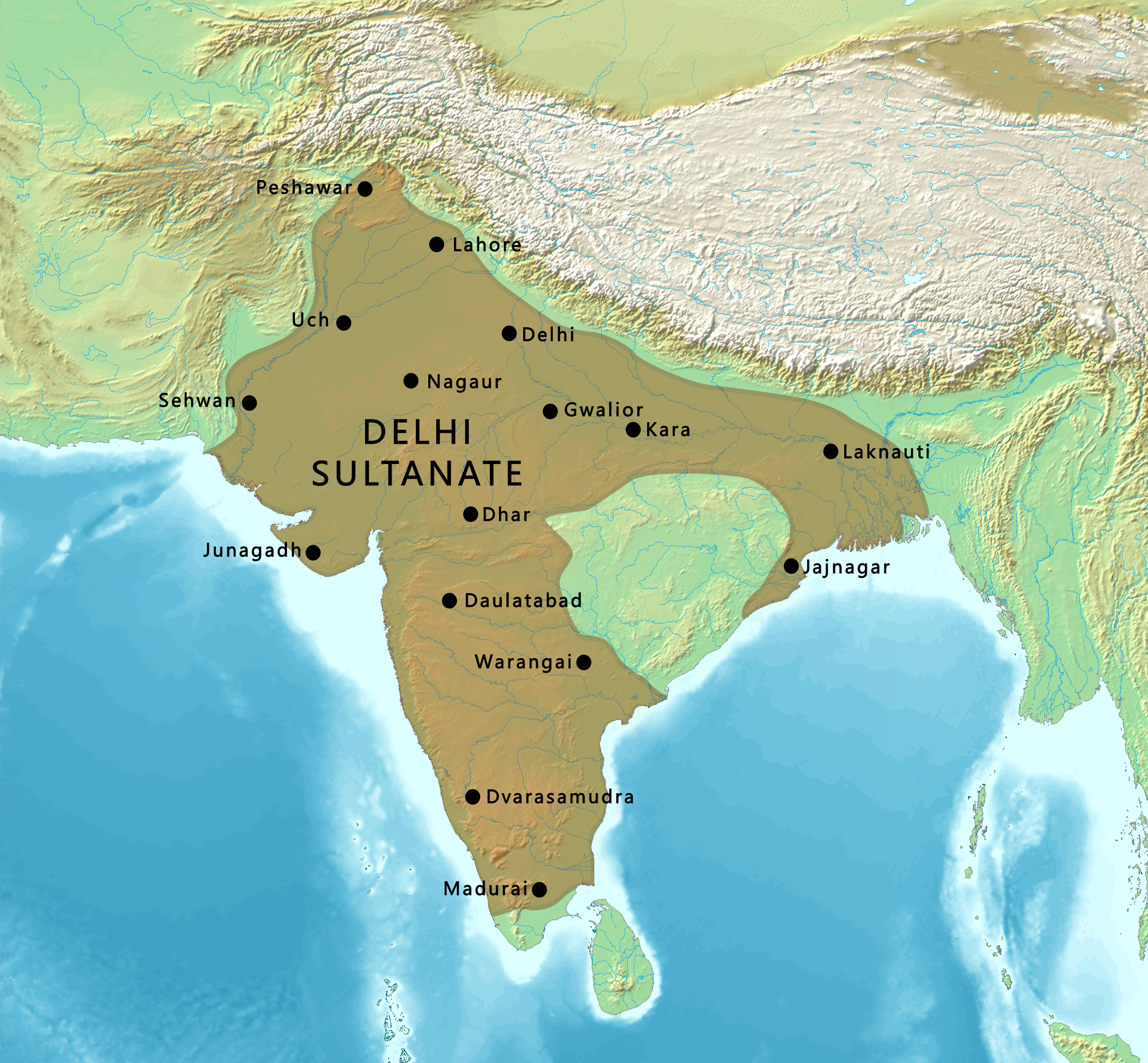
|
Second Battle Of Laghman
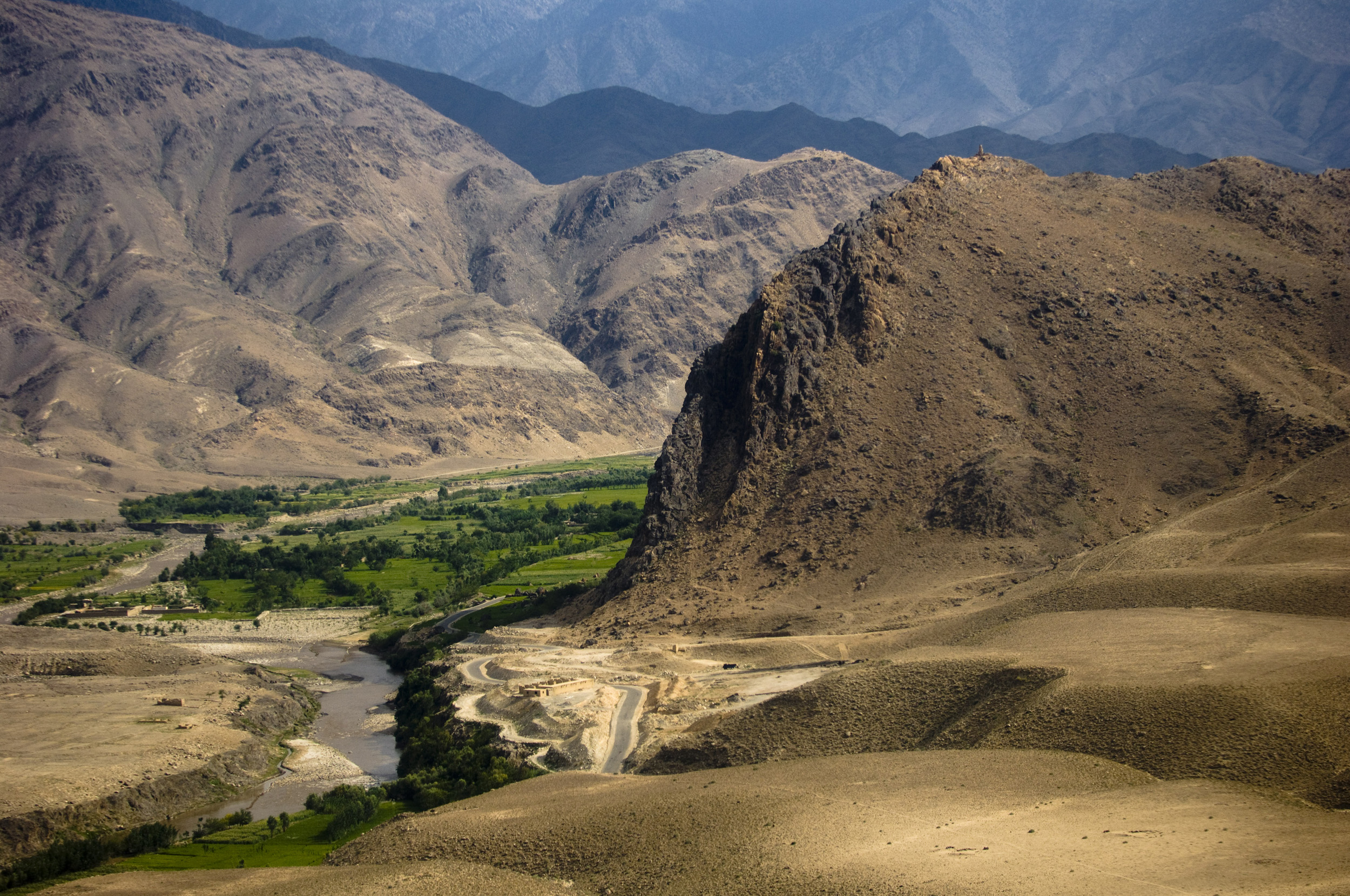
The Second Battle of Laghman was fought between the Ghaznavid forces under Sabuktigin and the Hindu Shahi under Jayapala near Laghman in 991 AD. It took place near Laghman, present day Afghanistan. The Ghaznavids defeated the Hindu Shahis and emerged victorious in the battle. This battle laid the foundation for the Ghaznavids to establish their dominance over parts of present-day Afghanistan and northern India. Background Ghaznavids had defeated the Hindu Shahis at the first battle of Laghman in 988. The Hindu Shahi King Jayapala, who was forced to sign a treaty after the battle, returned to his capital Multan, and made preparations to avenge his defeat. Jayapala orchestrated the formation of a confederacy comprising Hindu chiefs from the Tomara dynasty, Gurjara-Pratihara dynasty, Chahamanas, and Chandelas The Chandelas of Jejakabhukti was an Indian dynasty in Central India. The Chandelas ruled much of the Bundelkhand region (then called ''Jejakabhukti'') between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghaznavid Campaigns In India
The Ghaznavid campaigns in India refer to a series of military expeditions lasting 54 years (973–1027) launched by the Ghaznavid Empire, a prominent empire of the 10th and 11th centuries. They went to the Indian subcontinent, led primarily by Sultan Mahmud of Ghazni (), leaving a profound impact on the region's history and culture. Beginning in the late 10th century, these incursions marked a significant chapter in the history of South Asia, with Ghaznavid forces penetrating deep into the Indian subcontinent, including the Punjab region and northern India. The primary objectives of these campaigns included the acquisition of wealth, the propagation of Islam, and the establishment of Ghaznavid rule in the region. By the end of the 10th century, the Ghaznavid ruler Sabuktigin captured the region between Laghman and Peshawar from the Hindu Shahi ruler Jayapala. This laid the foundation for the Ghaznavids to establish their dominance over parts of present-day Afghanistan and I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Battle Of Laghman
The First Battle of Laghman was fought near Laghman in present-day Afghanistan, between the Ghaznavid empire under Sabuktigin and the Hindu Shahis under Jayapala in 988 CE. The Ghaznavids defeated the Hindu Shahis and Jayapala signed a treaty in which the Hindu Shahis paid tribute to Ghaznavids. Background Jayapala controlled the Laghman area. He heard traveler reports that Sabuktigin was encroaching on his dominions. Battle Jayapala advanced towards Ghazni and met the enemy near a place called Ghuzak between Ghazni and Lamghan. The battle continued for days without either side giving way. A thunderstorm broke out and Jayapala was forced to sign a humiliating treaty making him pay tribute to Sabuktigin. Aftermath Jayapala arranged a confederacy of army with the support of Kingdoms of Kannauj, Ajmer and Chandela to fight against Ghaznavids. But they were again defeated by Sabuktigin at Laghman. See also * Second Battle of Laghman The Second Battle of Laghman was fought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wars Involving The Pratihara Empire
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or between such organized groups. It is generally characterized by widespread violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular or irregular military forces. ''Warfare'' refers to the common activities and characteristics of types of war, or of wars in general. Total war is warfare that is not restricted to purely legitimate military targets, and can result in massive civilian or other non-combatant suffering and casualties. Etymology The English word ''war'' derives from the 11th-century Old English words and , from Old French ( as in modern French), in turn from the Frankish , ultimately deriving from the Proto-Germanic language">Proto-Germanic . The word is related to the Old Saxon , Old High German , and the modern German , meaning . History Anthr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Involving The Indian Kingdoms
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas batt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Involving The Ghaznavid Empire
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas batt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th Century In India
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural number, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslim Period In The Indian Subcontinent
The Muslim period in the Indian subcontinent or Indo-Muslim period is conventionally said to have started in 712, after the conquest of Sindh and Multan by the Umayyad Caliphate under the military command of Muhammad ibn al-Qasim. It began in the Indian subcontinent in the course of a Muslim conquest in the Indian subcontinent, gradual conquest. The perfunctory rule by the Ghaznavids in Punjab was followed by Ghurids, and Muhammad of Ghor, Sultan Muhammad of Ghor (r. 1173–1206) is generally credited with laying the foundation of Muslim rule in Northern India. From the late 12th century onwards, Muslim empires dominated the subcontinent, most notably the Delhi Sultanate and Mughal Empire. Various other Muslim kingdoms ruled most of South Asia from the mid-14th to late 18th centuries, including the Bahmani Sultanate, Bahmani, Bengal Sultanate, Bengal, Gujarat Sultanate, Gujarat, Malwa Sultanate, Malwa, Kashmir Sultanate, Kashmir, Sultanate of Multan, Multan, Mysore Sultanate, My ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military History Of Afghanistan
The Military history of Afghanistan () began before 1709 when the Hotaki dynasty was established in Kandahar followed by the Durrani Empire. The Afghan military was re-organized with assistance from the British Raj, British in 1880, when the country was ruled by Emir, Amir Abdur Rahman Khan. It was modernized during King Amanullah Khan's rule in the early 20th century, and then during King Mohammed Zahir Shah, Zahir Shah's forty-year rule; the Soviet Union supplied almost all weapons, training and military needs between the 1950s and 1970s. From 1978 to 1992, the Soviet-backed Afghan Armed Forces engaged in heavy fighting with the multi-national Afghan mujahideen, mujahideen groups who were then backed by the United States, Pakistan and others. After President of Afghanistan, President Mohammad Najibullah, Najibullah's resignation in 1992 and the end of Soviet support, the Afghan military dissolved into portions controlled by different factions. This era was followed by the Islamic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Involving The Rajputs
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas batt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firishta
Firishta or Ferešte (), full name Muhammad Qasim Hindu Shah Astarabadi (), was a Persian historian, who later settled in India and served the Deccan Sultans as their court historian. He was born in 1570 and died between 1611 and 1623. Life Firishta was born at Astarabad on the shores of the Caspian Sea to Gholam Ali Hindu Shah. While Firishta was still a child, his father was summoned away from his native country to Ahmednagar, India, to teach Persian to the young prince Miran Husain Nizam Shah, with whom Firishta studied. In 1587 Firishta was serving as the captain of guards of King Murtaza Nizam Shah I when Prince Miran overthrew his father and claimed the throne of Ahmednagar. At this time, the Sunni Deccani Muslims committed a general massacre of the foreign population, especially Shias of Iranian origin, of which Firishta was one of. However, Prince Miran spared the life of his former friend, who then left for Bijapur to enter the service of King Ibrahim Adil II i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandelas Of Jejakabhukti
The Chandelas of Jejakabhukti was an Indian dynasty in Central India. The Chandelas ruled much of the Bundelkhand region (then called ''Jejakabhukti'') between the 9th and the 13th centuries. They belonged to the Chandel (Rajput clan), Chandel clan of the Rajputs. The Chandelas initially ruled as feudatories of the Gurjara-Pratiharas of Kanyakubja (Kannauj). The 10th century Chandela ruler Yashovarman (Chandela dynasty), Yashovarman became practically independent, although he continued to acknowledge the Pratihara suzerainty. By the time of his successor Dhanga, the Chandelas had become a sovereign power. Their power rose and declined as they fought battles with the neighbouring dynasties, especially the Paramara dynasty, Paramaras of Malwa and the Kalachuris of Tripuri. From the 11th century onwards, the Chandelas faced raids by the northern Muslim dynasties, including the Ghaznavids and the Ghurids. The Chandela power effectively ended around the beginning of the 13th century, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |