|
Sea Ice Refreezing
Sea ice refreezing refers to various climate engineering techniques aimed at directly facilitating the formation or restoration of ice in Polar regions of Earth, polar regions, particularly in the Arctic Ocean. These approaches are being investigated as potential interventions to counter the accelerating loss of sea ice due to climate change, especially to avert a potential Arctic sea ice decline, blue ocean event and its potential runaway climate impacts. Background Sea ice, especially in the Arctic region, has declined in recent decades in area and volume due to climate change. It has been melting more in summer than it refreezes in winter. Global warming, caused by Radiative forcing#Forcing due to changes in atmospheric gases, greenhouse gas forcing is responsible for the decline in Arctic sea ice. The decline of sea ice has been accelerating during the early twenty-first century, with a decline rate of 4.7% per decade (it has declined over 50% since the first satellite reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Engineering
Geoengineering (also known as climate engineering or climate intervention) is the deliberate large-scale interventions in the Earth’s climate system intended to counteract human-caused climate change. The term commonly encompasses two broad categories: large-scale carbon dioxide removal (CDR) and solar radiation modification (SRM). CDR involves techniques to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and is generally considered a form of climate change mitigation. SRM aims to reduce global warming by reflecting a small portion of sunlight (solar radiation) away from Earth and back into space. Although historically grouped together, these approaches differ substantially in mechanisms, timelines, and risk profiles, and are now typically discussed separately.IPCC (2022Chapter 1: Introduction and FramingiClimate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Cambridge Unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Habitat
A marine habitat is a habitat that supports marine life. Marine life depends in some way on the seawater, saltwater that is in the sea (the term ''marine'' comes from the Latin ''mare'', meaning sea or ocean). A habitat is an ecological or Natural environment, environmental area inhabited by one or more living species.Abercrombie, M., Hickman, C.J. and Johnson, M.L. 1966.''A Dictionary of Biology.'' Penguin Reference Books, London The marine environment supports many kinds of these habitats. Marine habitats can be divided into coastal and open ocean habitats. Coastal habitats are found in the area that extends from as far as the tide comes in on the shoreline out to the edge of the continental shelf. Most marine life is found in coastal habitats, even though the shelf area occupies only seven percent of the total ocean area. Open ocean habitats are found in the deep ocean beyond the edge of the continental shelf. Alternatively, marine habitats can be divided into Pelagic zon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment (Freshwater ecosystem, freshwater or Marine ecosystem, marine), but may also be caught from Fish stocking, stocked Body of water, bodies of water such as Fish pond, ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. Fishing techniques include trawling, Longline fishing, longlining, jigging, Fishing techniques#Hand-gathering, hand-gathering, Spearfishing, spearing, Fishing net, netting, angling, Bowfishing, shooting and Fish trap, trapping, as well as Destructive fishing practices, more destructive and often Illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing, illegal techniques such as Electrofishing, electrocution, Blast fishing, blasting and Cyanide fishing, poisoning. The term fishing broadly includes catching aquatic animals other than fish, such as crustaceans (shrimp/lobsters/crabs), shellfish, cephalopods (octopus/squid) and echinoderms (starfish/sea urchins). The term is n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territory, and an experience of subjugation and discrimination under a dominant cultural model. Estimates of the population of Indigenous peoples range from 250 million to 600 million. There are some 5,000 distinct Indigenous peoples spread across every inhabited climate zone and inhabited continent of the world. Most Indigenous peoples are in a minority in the state or traditional territory they inhabit and have experienced domination by other groups, especially non-Indigenous peoples. Although many Indigenous peoples have experienced colonization by settlers from European nations, Indigenous identity is not determined by Western colonization. The rights of Indigenous peoples are outlined in national legislation, treaties and international law ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Temperature
Atmospheric temperature is a measure of temperature at different levels of the Earth's atmosphere. It is governed by many factors, including insolation, incoming solar radiation, humidity, and altitude. The abbreviation MAAT is often used for Mean Annual Air Temperature of a geographical location. Near-surface air temperature The temperature of the air near the surface of the Earth is measured at meteorological observatories and weather stations, usually using thermometers placed in a shelter such as a Stevenson screen—a standardized, well-ventilated, white-painted instrument shelter. The thermometers should be positioned 1.25–2 m above the ground. Details of this setup are defined by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO). A true daily mean could be obtained from a continuously recording thermograph. Commonly, it is approximated by the mean of discrete readings (e.g. 24 hourly readings, four 6-hourly readings, etc.) or by the mean of the daily minimum and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freezing
Freezing is a phase transition in which a liquid turns into a solid when its temperature is lowered below its freezing point. For most substances, the melting and freezing points are the same temperature; however, certain substances possess differing solid-liquid transition temperatures. For example, agar displays a Hysteresis#Liquid–solid-phase transitions, hysteresis in its melting point and freezing point. It melts at and solidifies from . Crystallization Most liquids freeze by crystallization, formation of crystal, crystalline solid from the uniform liquid. This is a first-order thermodynamic phase transition, which means that as long as solid and liquid coexist, the temperature of the whole system remains very nearly equal to the melting point due to the slow removal of heat when in contact with air, which is a poor heat conductor. Because of the latent heat of fusion, the freezing is greatly slowed and the temperature will not drop anymore once the freezing starts but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensation
Condensation is the change of the state of matter from the gas phase into the liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. The word most often refers to the water cycle. It can also be defined as the change in the state of water vapor to liquid water when in contact with a liquid or solid surface or cloud condensation nuclei within the atmosphere. When the transition happens from the gaseous phase into the solid phase directly, the change is called deposition. Condensation is usually associated with water. Initiation Condensation is initiated by the formation of atomic/molecular clusters of that species within its gaseous volume—like rain drop or snow flake formation within clouds—or at the contact between such gaseous phase and a liquid or solid surface. In clouds, this can be catalyzed by water-nucleating proteins, produced by atmospheric microbes, which are capable of binding gaseous or liquid water molecules. Reversibility scenarios A few distinct rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunlight
Sunlight is the portion of the electromagnetic radiation which is emitted by the Sun (i.e. solar radiation) and received by the Earth, in particular the visible spectrum, visible light perceptible to the human eye as well as invisible infrared (typically perceived by humans as warmth) and ultraviolet (which can have physiological effects such as sunburn) lights. However, according to the American Meteorological Society, there are "conflicting conventions as to whether all three [...] are referred to as light, or whether that term should only be applied to the visible portion of the spectrum." Upon reaching the Earth, sunlight is light scattering by particles, scattered and attenuation, filtered through the atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere as daylight when the Sun is above the horizon. When direct solar radiation is not blocked by clouds, it is experienced as sunshine, a combination of bright light and radiant heat (atmospheric). When cloud cover, blocked by clouds or dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capillary Action
Capillary action (sometimes called capillarity, capillary motion, capillary rise, capillary effect, or wicking) is the process of a liquid flowing in a narrow space without the assistance of external forces like Gravitation, gravity. The effect can be seen in the drawing up of liquids between the hairs of a paint-brush, in a thin tube such as a Drinking straw, straw, in porous materials such as paper and plaster, in some non-porous materials such as clay and liquefied carbon fiber, or in a biological cell. It occurs because of intermolecular forces between the liquid and surrounding solid surfaces. If the diameter of the tube is sufficiently small, then the combination of surface tension (which is caused by Cohesion (chemistry), cohesion within the liquid) and Adhesion, adhesive forces between the liquid and container wall act to propel the liquid. Etymology Capillary comes from the Latin word capillaris, meaning "of or resembling hair". The meaning stems from the tiny, hairl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microchannel (microtechnology)
Microchannel in microtechnology is a channel with a hydraulic diameter below 1 mm, usually 1–99 μm. Microchannels are used in fluid control (see Microfluidics), heat transfer (see Micro heat exchanger) and cell migration observation. They are more efficient than their 'macro' counterparts, because of a high surface-area to volume ratio yet pose a multitude of challenges due to their small size. Materials Different types of materials are required for the different uses of microchannels. These are the three main categories. Polymeric and glass substrates Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is used as a solution to a wide range of microfluidic devices due to its low cost and easier fabricating methods. Silicon elastomers can be used for situations in which elasticity and deformation is necessary. Metallic substrates Metallic substrates are often chosen for their advantageous metallic properties, such as withstanding high temperatures and transferring heat faster. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
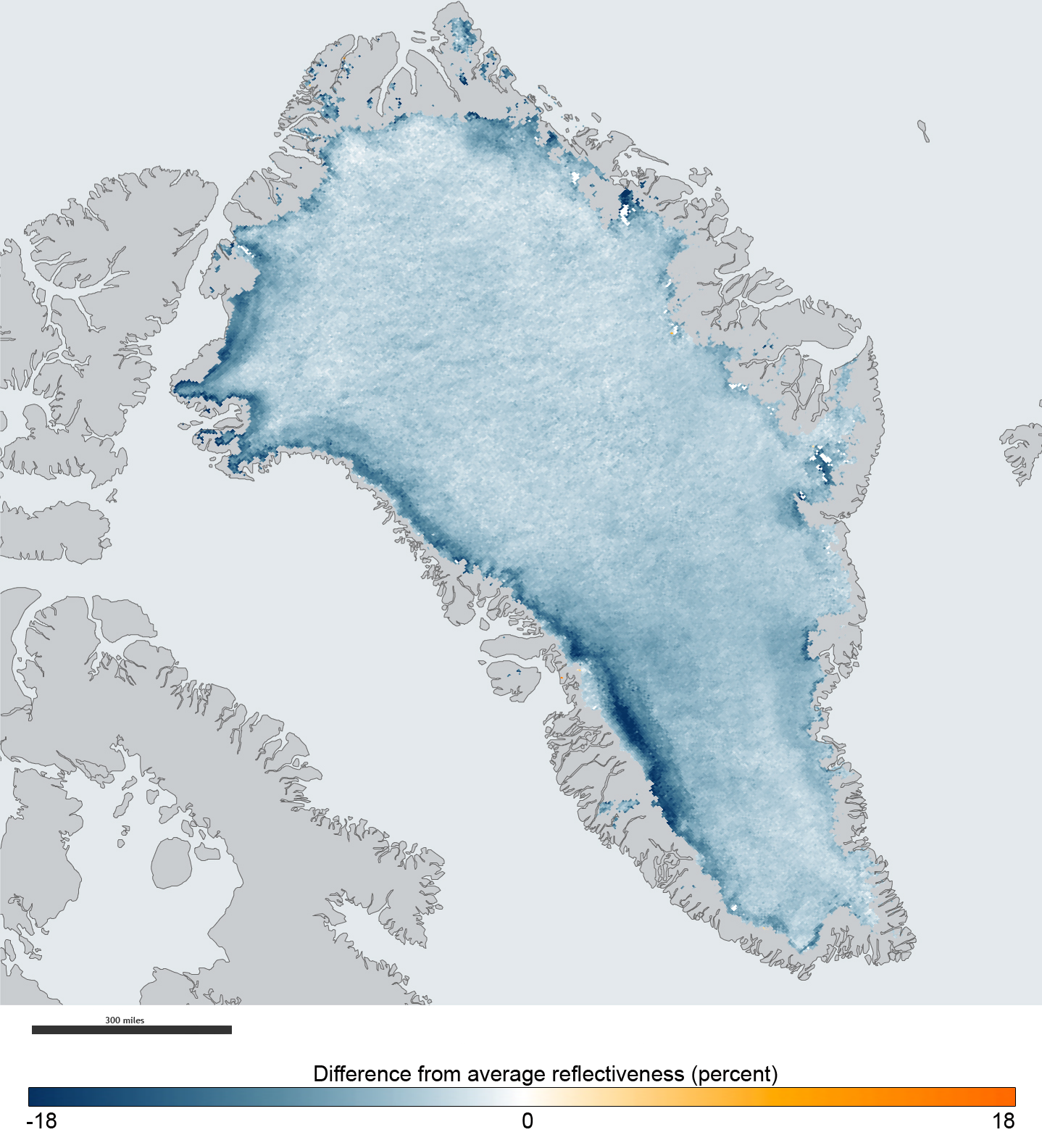
Albedo
Albedo ( ; ) is the fraction of sunlight that is Diffuse reflection, diffusely reflected by a body. It is measured on a scale from 0 (corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation) to 1 (corresponding to a body that reflects all incident radiation). ''Surface albedo'' is defined as the ratio of Radiosity (radiometry), radiosity ''J''e to the irradiance ''E''e (flux per unit area) received by a surface. The proportion reflected is not only determined by properties of the surface itself, but also by the spectral and angular distribution of solar radiation reaching the Earth's surface. These factors vary with atmospheric composition, geographic location, and time (see position of the Sun). While directional-hemispherical reflectance factor is calculated for a single angle of incidence (i.e., for a given position of the Sun), albedo is the directional integration of reflectance over all solar angles in a given period. The temporal resolution may range from seconds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidity and do not rot easily. Chemically, lignins are polymers made by cross-linking phenolic precursors. History Lignin was first mentioned in 1813 by the Swiss botanist A. P. de Candolle, who described it as a fibrous, tasteless material, insoluble in water and alcohol but soluble in weak alkaline solutions, and which can be precipitated from solution using acid. He named the substance "lignine", which is derived from the Latin word '' lignum'', meaning wood. It is one of the most abundant organic polymers on Earth, exceeded only by cellulose and chitin. Lignin constitutes 30% of terrestrial non-fossil organic carbon on Earth, and 20 to 35% of the dry mass of wood. Lignin is present in red algae, which suggest that the common ancestor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |