|
Scotland During The Roman Empire
Scotland during the Roman Empire refers to the protohistory, protohistorical period during which the Roman Empire interacted within the area of modern Scotland. Despite sporadic attempts at conquest and government between the first and fourth centuries AD, most of modern Scotland, inhabited by the Caledonians and the Maeatae, was not incorporated into the Roman Empire with Roman control over the area fluctuating. In the Roman imperial period (chronology), Roman imperial period, the area of Caledonia lay north of the River Forth, while the area now called England was known as ''Britannia'', the name also given to the Roman province roughly consisting of modern England and Wales and which replaced the earlier Ancient Greek designation as ''Albion''. Roman legions arrived in the territory of modern Scotland around AD 71, having conquered the Celtic Britons of southern Britannia over the preceding three decades. Aiming to complete the Roman conquest of Britannia, the Roman a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Britain
Britain most often refers to: * Great Britain, a large island comprising the countries of England, Scotland and Wales * The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, a sovereign state in Europe comprising Great Britain and the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland. * The realm of the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, comprising the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies, and British Overseas Territories. Britain may also refer to: Places * British Isles, an archipelago comprising Great Britain, Ireland and many other smaller islands * British Islands, the UK, Channel Islands and Isle of Man collectively * Roman Britain, a Roman province corresponding roughly to modern-day England and Wales * Historical predecessors to the present-day United Kingdom: ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707 to 1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801 to 1922) * Britain (place name) * Britain, Virginia, an unincorporated community in the United States People * Calvin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Army
The Roman army () served ancient Rome and the Roman people, enduring through the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), the Roman Republic (509–27 BC), and the Roman Empire (27 BC–AD 1453), including the Western Roman Empire (collapsed Fall of the Western Roman Empire, AD 476/480) and the Byzantine Empire, Eastern Roman Empire (collapsed Fall of Constantinople, AD 1453). It is thus a term that broadly spans approximately 2,206 years, during which the force underwent numerous permutations in Size of the Roman army, size, Military of ancient Rome, composition, Structural history of the Roman military, organization, Roman military equipment, equipment and Strategy of the Roman military, tactics, while conserving a core of lasting traditions. Early Roman army (c. 550 – c. 300 BC) Until , there was no "national" Roman army, but a series of clan-based war-bands which only coalesced into a united force in periods of serious external threat. Around 550 BC, during the period conventiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanegate
The Stanegate (meaning "stone road" in Northumbrian dialect) was an important Roman road and early frontier built in what is now northern England. It linked many forts including two that guarded important river crossings: Corstopitum (Corbridge) on the River Tyne in the east (situated on Dere Street) and Luguvalium (Carlisle) (on the River Eden) in the west. The Stanegate ran through the natural gap formed by the valleys of the River Tyne in Northumberland and the River Irthing in Cumbria. It predated the Hadrian's Wall frontier by several decades; the Wall would later follow a similar route, albeit slightly to the north. The Stanegate should not be confused with the two Roman roads called Stane Street in the south of England, namely Stane Street (Chichester) and Stane Street (Colchester). In both these cases the meaning is the same as for the northern version, indicating a stone or paved road. The Stanegate differed from most other Roman roads in that it often followed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Tyne
The River Tyne is a river in North East England. Its length (excluding tributaries) is . It is formed by the North Tyne and the South Tyne, which converge at Warden, Northumberland, Warden near Hexham in Northumberland at a place dubbed 'The Meeting of the Waters'. The Tyne Rivers Trust measure the whole Tyne Drainage basin, catchment as , containing of waterways. Course North Tyne The Ordnance Survey records 'the source of the North Tyne river' at grid reference NY 605974 at Deadwater, a few tens of metres short of the Scottish border. It flows southeast through the village of Kielder before entering first Bakethin Reservoir and then Kielder Water, both set within Kielder Forest. It then passes by the village of Bellingham, Northumberland, Bellingham before the River Rede enters as a left-bank tributary at Redesmouth. It passes Hadrian's Wall near Chollerford before joining the South Tyne near Warden to the northwest of Hexham. South Tyne The South Tyne rises at Tyne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solway Firth
The Solway Firth is an inlet on the west coast of Great Britain, forming part of the border between England and Scotland. The firth (a Scottish term for an inlet of the sea) divides Cumbria (including the Solway Plain) from Dumfries and Galloway. The Isle of Man is also very near to the firth. The firth comprises part of the Irish Sea. The firth's coastline is characterised by lowland hills and small mountains. It is a mainly rural area, with mostly small villages and settlements (such as Powfoot). Fishing, hill farming, and some arable farming play a large part in the local economy, although tourism is increasing. The northern part of the English coast of the Solway Firth was designated as an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, known as the Solway Coast, in 1964. Construction of the Robin Rigg Wind Farm in the firth began in 2007. Within the firth, there are some Salt marsh, salt marshes and mud flats that can be dangerous, due to their frequently shifting patches of quicksa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
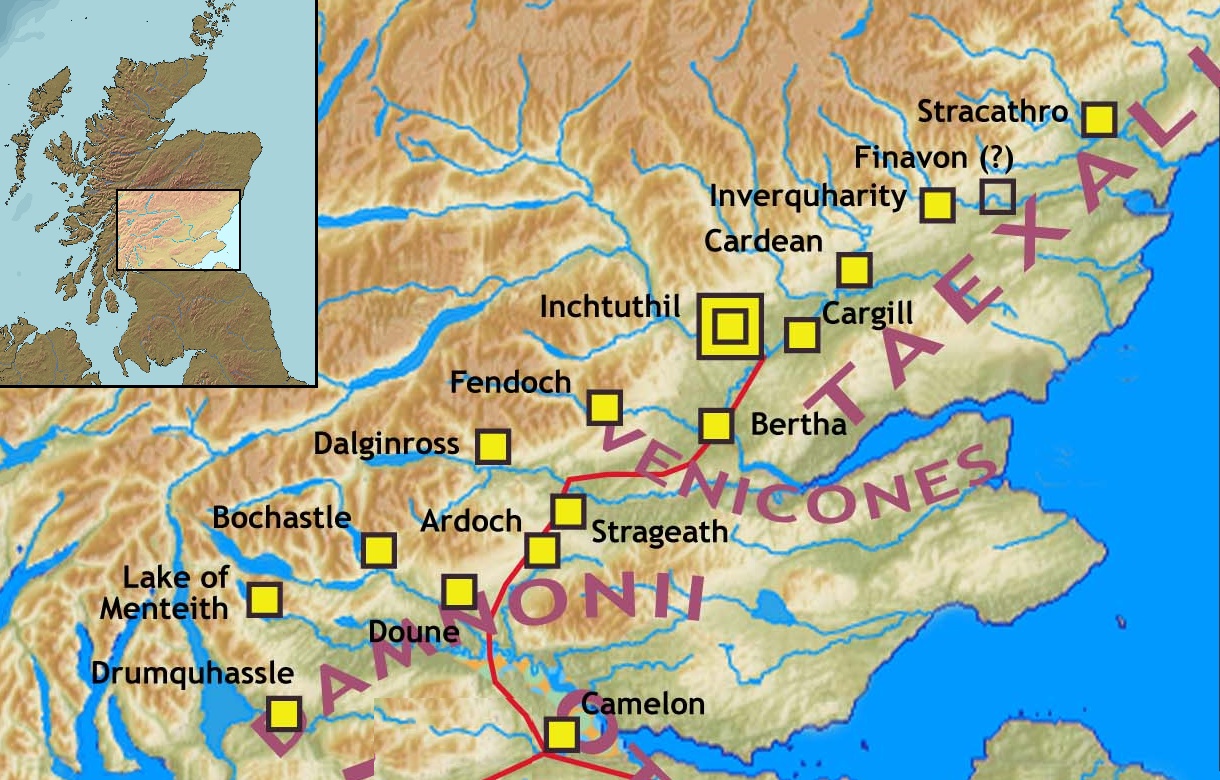
Gask Ridge
The Gask Ridge is the modern name given to an early series of Castra, fortifications, built by the Roman Empire, Romans in Scotland, close to the Highland Boundary Fault, Highland Line. Modern excavation and interpretation has been pioneered by the Roman Gask Project, with Birgitta Hoffmann and David Woolliscroft. The ridge fortifications: forts, fortlets and watchtowers were only in operation for a few years, probably fewer than ten. Name The name "Gask Ridge" refers to the ridge of land to the north of the River Earn in Perthshire. In Scottish Gaelic, a ''gasg'' is a projecting tail or strip of land. In the early 20th century, a line of Roman signal-towers (or watch-towers) was discovered along this ridge between the Roman forts of Strageath and Bertha (Perth), Bertha. History The Gask Ridge system was constructed sometime between 70 and 80 AD. Construction on Hadrian's Wall was started 42 years after completion of the Gask Ridge (from 122 to 130 AD), and the Antonine Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limes (Roman Empire)
(Latin; , : ) is a term used primarily for the Germanic border defence or delimiting system of ancient Rome marking the borders of the Roman Empire. The term has been extended in modern times to refer to the Roman military frontiers and fortifications, frontier defences in other parts of the empire, such as in the east and in Africa. Overview The Roman frontier stretched for more than from the Atlantic coast of northern Roman Britain, Britain, through Europe to the Black Sea, and from there to the Red Sea and across North Africa to the Atlantic coast. The positions of the borders changed especially during the main periods of Roman expansion and contraction, and first became more stable during the early Roman Empire, Empire period under Augustus, but the borders continued to change with time in different provinces. The borders had different constituents depending on local needs; often they consisted of natural boundaries (e.g. rivers) with roads behind for easier movement o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pytheas
Pytheas of Massalia (; Ancient Greek: Πυθέας ὁ Μασσαλιώτης ''Pythéās ho Massaliōtēs''; Latin: ''Pytheas Massiliensis''; born 350 BC, 320–306 BC) was a Greeks, Greek List of Graeco-Roman geographers, geographer, explorer and astronomer from the Greek colonies, Greek colony of Massalia (modern-day Marseille, France). He made a voyage of exploration to Northern Europe in about 325 BC, but his account of it, known widely in Ancient history, antiquity, has not survived and is now known only through the writings of others. On this voyage, he circumnavigated and visited a considerable part of the British Isles. He was the first known Greek scientific visitor to see and describe the Arctic, polar ice, and the Celtic peoples, Celtic and Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes. He is also the first person on record to describe the midnight sun. The theoretical existence of some Northern phenomena that he described, such as a frigid zone, and temperate zones wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grampian Mountains
The Grampian Mountains () is one of the three major mountain ranges in Scotland, that together occupy about half of Scotland. The other two ranges are the Northwest Highlands and the Southern Uplands. The Grampian range extends northeast to southwest between the Highland Boundary Fault and the Great Glen. The range includes many of the highest mountains in the British Isles, including Ben Nevis (whose peak contains the highest point in the British Isles at above sea level) and Ben Macdhui (Scotland), Ben Macdui (whose peak contains second-highest at ). A number of rivers and streams rise in the Grampians, including the River Tay, Tay, River Spey, Spey, Cowie Water, Burn of Muchalls, Burn of Pheppie, Burn of Elsick, Cairnie Burn, River Don, Aberdeenshire, Don, River Dee, Aberdeenshire, Dee and River South Esk, Esk. The area is generally sparsely populated. There is some ambiguity about the extent of the range, and until the nineteenth century, they were generally considered to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
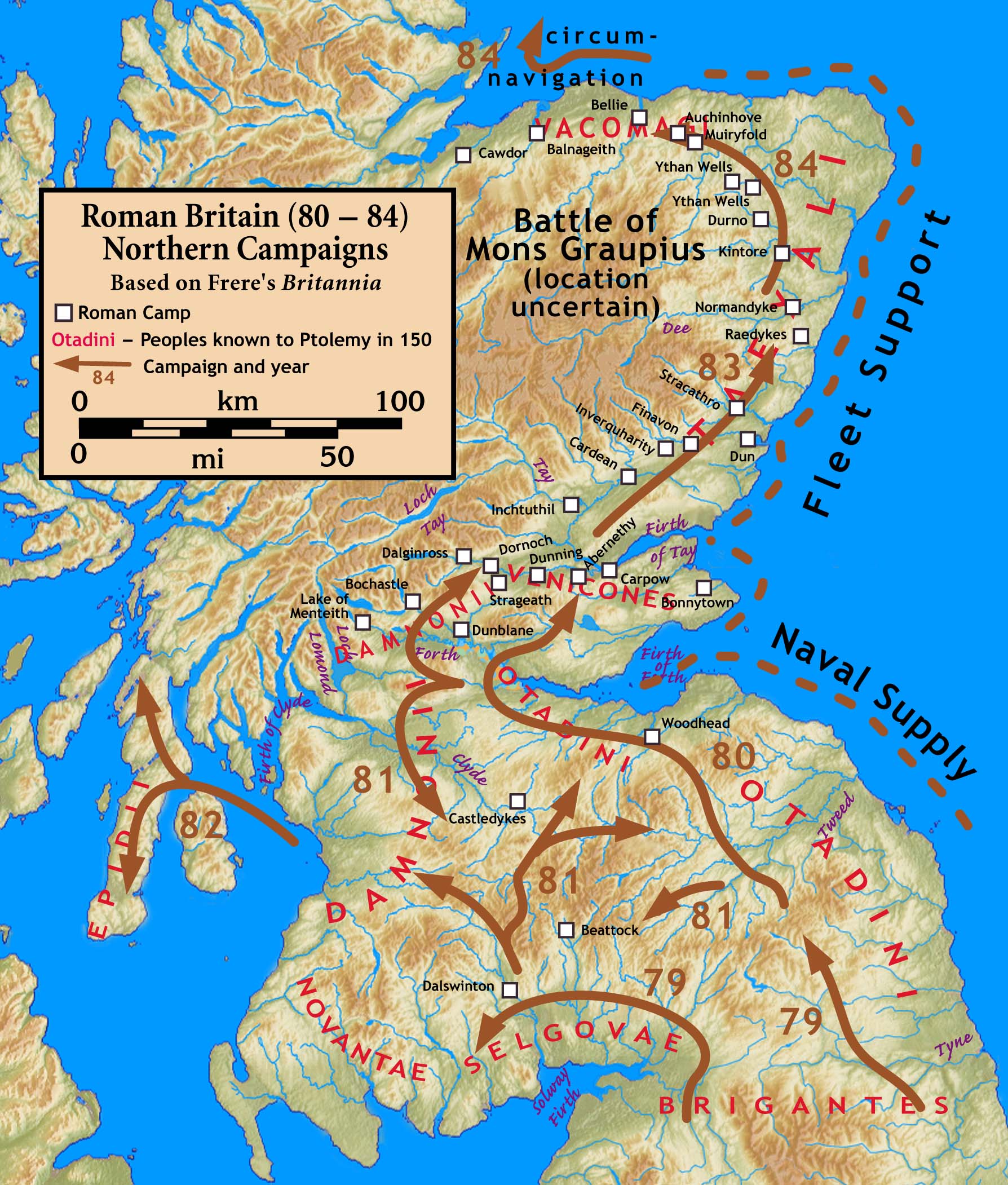
Mons Graupius
The Battle of Mons Graupius was, according to Tacitus, a Roman military victory in what is now Scotland, taking place in AD 83 or, less probably, 84. The exact location of the battle is a matter of debate. Historians have long questioned some details of Tacitus's account of the fight, suggesting that he exaggerated Roman success. Background Tacitus states that Gnaeus Julius Agricola, who was the Roman governor and Tacitus's father-in-law, had sent his fleet ahead to panic the Caledonians, and, with light infantry reinforced with British auxiliaries, reached the site, which he found occupied by the enemy. Even though the Romans were outnumbered in their campaign against the tribes of Britain, they often had difficulty getting their foes to face them in open battle. The Caledonii were the last unconquered British tribe (and were never entirely subdued). After many years of avoiding the fight, the Caledonians were forced to join battle when the Romans marched on the main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars. Tacitus’ two major historical works, ''Annals'' (Latin: ) and the ''Histories'' (Latin: ), originally formed a continuous narrative of the Roman Empire from the death of Augustus (14 AD) to the end of Domitian’s reign (96 AD). The surviving portions of the Annals focus on the reigns of Tiberius, Claudius, Nero, and those who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors (69 AD). Tacitus's other writings discuss oratory (in dialogue format, see ), Germania (in ''De origine et situ Germanorum''), and the life of his father-in-law, Agricola (the general responsible for much of the Roman conquest of Britain), mainly focusing on his campaign in Britannia ('' De vita et moribus Iulii Agricolae''). Tacitus's ''Histories'' offers insights into Roman attitudes towards Jews, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Governor
A Roman governor was an official either elected or appointed to be the chief administrator of Roman law throughout one or more of the many Roman province, provinces constituting the Roman Empire. The generic term in Roman legal language was ''rector provinciae,'' regardless of the specific titles, which also reflects the province's intrinsic and strategic status, and corresponding differences in authority. By the time of the early Roman Empire, Empire, two types of provinces existed—Senatorial province, senatorial and Imperial province, imperial—and several types of governor would emerge. Only ''proconsuls'' and ''propraetors'' fell under the classification of promagistrate. Duties of the governor The governor was the province's chief judge. He had the sole right to impose capital punishment, and capital cases were normally tried before him. To appeal a governor's decision necessitated travelling to Rome and presenting one's case before either the ''Praetor#Praetor urbanus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |