|
Schweizer's Reagent
Schweizer's reagent is a metal ammine complex with the formula salt consists of tetraamminediaquacopper(II) cations () and hydroxide anions (). It is prepared by dissolving copper(II) hydroxide in an aqueous solution of ammonia. It forms an azure solution. Evaporation of these solutions leaves light blue residue of copper hydroxide, reflecting the lability of the copper-ammonia bonding. If conducted under a stream of ammonia, then deep blue needle-like crystals of the tetrammine form. In presence of oxygen, concentrated solutions give rise to nitrites . The nitrite results from oxidation of the ammonia. Reactions with cellulose Schweizer's reagent was once used in production of cellulose products such as rayon and cellophane (see cupro). Cellulose, which is quite insoluble in water (hence its utility as clothing), dissolves in the presence of Schweizer's reagent. Using the reagent, cellulose can be extracted from wood pulp, cotton fiber, and other natural cellulose sources. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable, unalloyed metallic form. This means that copper is a native metal. This led to very early human use in several regions, from . Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, ; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, ; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create bronze, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
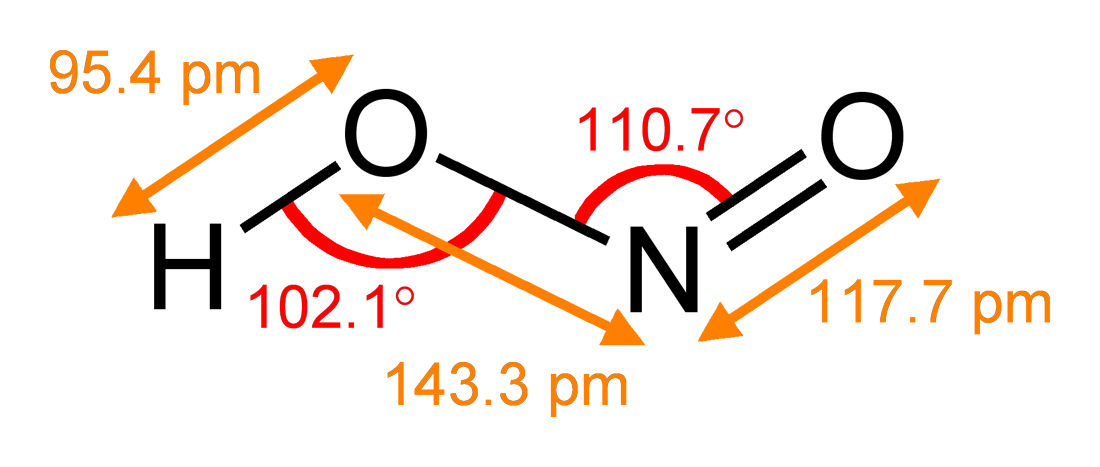
Nitrite
The nitrite polyatomic ion, ion has the chemical formula . Nitrite (mostly sodium nitrite) is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name nitrite also refers to organic compounds having the –ONO group, which are esters of nitrous acid. Production Sodium nitrite is made industrially by passing a mixture of nitrogen oxides into aqueous sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate solution: : : The product is purified by recrystallization. Alkali metal nitrites are thermally stable up to and beyond their melting point (441 °C for KNO2). Ammonium nitrite can be made from dinitrogen trioxide, N2O3, which is formally the anhydride of nitrous acid: :2 NH3 + H2O + N2O3 → 2 NH4NO2 Structure The nitrite ion has a symmetrical structure (C2v molecular point group, symmetry), with both N–O bonds having equal length and a bond angle of about 115°. In valence bond theory, it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxides
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a single covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It functions as a base, a ligand, a nucleophile, and a catalyst. The hydroxide ion forms salts, some of which dissociate in aqueous solution, liberating solvated hydroxide ions. Sodium hydroxide is a multi-million-ton per annum commodity chemical. The corresponding electrically neutral compound HO• is the hydroxyl radical. The corresponding covalently bound group of atoms is the hydroxy group. Both the hydroxide ion and hydroxy group are nucleophiles and can act as catalysts in organic chemistry. Many inorganic substances which bear the word ''hydroxide'' in their names are not ionic compounds of the hydroxide ion, but covalent compounds which contain hydroxy groups. Hydroxide ion The hydroxide ion is naturally produced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper Complexes
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable, unalloyed metallic form. This means that copper is a native metal. This led to very early human use in several regions, from . Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, ; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, ; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create bronze, . Common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetraamminecopper(II) Sulfate
Tetraamminecopper(II) sulfate monohydrate, or more precisely tetraammineaquacopper(II) sulfate, is the salt with the formula , or more precisely metal complex (tetraammineaquacopper(II) cation). It is closely related to Schweizer's reagent, which is used for the production of cellulose fibers in the production of rayon. Synthesis This compound can be prepared by adding concentrated aqueous solution of ammonia to a saturated aqueous solution of copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate followed by precipitation of the product with ethanol or isopropanol.Editor G.Brauer "Tetraamminecopper (II) Sulfate" Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed., Academic Press, 1965, New York. Vol. 2. p. 1021. : Chemical reaction and solubility The deep blue crystalline solid tends to hydrolyse and evolve (release) ammonia upon standing in air. It is fairly soluble in water. The brilliant dark blue-violet color of tetraamminecopper(II) sulfate solution is due to presence of (tetraamminecop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matthias Eduard Schweizer
Matthias Eduard Schweizer (8 August 1818 – 23 October 1860) was a Swiss people, Swiss chemist who in 1857 invented Schweizer's reagent, in which cellulose can be dissolved to produce artificial silk or rayon. He was one of the pioneers of the synthetic textile industry. Life Matthias Eduard Schweizer was born on 8 August 1818 in Wila, Switzerland, Wila, Zurich canton. He was awarded his doctorate in at the University of Zurich, then worked as an assistant at the Zurich Polytechnic. He was a student and assistant of Carl Jacob Löwig, and was mainly involved in analysis of different minerals. He lectured at the university, and was an associate professor at the university from 1852. From 1855 he taught chemistry at the Higher Industrial School (''Oberen Industrieschule'') in Zurich. Schweizer published a paper in 1857 (''Das Kupferoxid-Ammoniak, ein Auflösungsmittel für die Pflanzenfaser'') in which he reported that cotton, linen cellulose and silk could be dissolved in a cupramm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Weight
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, e.g. water (molecule), water (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diol
A diol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups ( groups). An aliphatic diol may also be called a glycol. This pairing of functional groups is pervasive, and many subcategories have been identified. They are used as protecting groups of carbonyl groups, making them essential in synthesis of organic chemistry. The most common industrial diol is ethylene glycol. Examples of diols in which the hydroxyl functional groups are more widely separated include 1,4-butanediol and propylene-1,3-diol, or beta propylene glycol, . Synthesis of classes of diols Geminal diols A geminal diol has two hydroxyl groups bonded to the same atom. These species arise by hydration of the carbonyl compounds. The hydration is usually unfavorable, but a notable exception is formaldehyde which, in water, exists in equilibrium with methanediol H2C(OH)2. Another example is (F3C)2C(OH)2, the hydrated form of hexafluoroacetone. Many gem-diols undergo further condensation to give dimer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cupro
Cuprammonium rayon is a rayon fiber made from cellulose dissolved in a cuprammonium solution, Schweizer's reagent. It is produced by making cellulose a soluble compound by combining it with copper and ammonia with caustic soda. The solution is passed through a spinneret and the cellulose is regenerated in hardening baths that remove the copper and ammonia and neutralize the caustic soda. Cuprammonium rayon is usually made in fine filaments that are used in suit jacket linings as well as lightweight summer dresses and blouses, sometimes in combination with cotton to make textured fabrics with slubbed, uneven surfaces. The fabric is commonly known by the trade name "Bemberg", owned by the J.P. Bemberg company. The fabric may also be known as "cupro" or "cupra". It is also known as "ammonia silk" on Chinese fashion retail websites. History Cuprammonium rayon was invented in 1890. Swiss chemist Matthias Eduard Schweizer (1818–1860) discovered that cellulose dissolves in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellophane
Cellophane is a thin, transparent sheet made of regenerated cellulose. Its low permeability to air, oils, greases, bacteria, and liquid water makes it useful for food packaging. Cellophane is highly permeable to water vapour, but may be coated with nitrocellulose lacquer to prevent this. Cellophane is also used in transparent pressure-sensitive tape, tubing, and many other similar applications. Cellophane is compostable and biodegradable, and can be obtained from biomaterials. The original production process uses carbon disulfide (CS2), which has been found to be highly toxic to workers. The newer lyocell process can be used to produce cellulose film without involving carbon disulfide. "Cellophane" is a generic term in some countries, while in other countries it is a registered trademark owned by DuPont. Production Cellulose is produced from wood, cotton, hemp, and other organic fibres, dissolved in alkali and carbon disulfide to make a solution of liquid viscose. The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rayon
Rayon, also called viscose and commercialised in some countries as sabra silk or cactus silk, is a semi-synthetic fiber made from natural sources of regenerated cellulose fiber, cellulose, such as wood and related agricultural products. It has the same molecular structure as cellulose. Many types and grades of viscose fibers and films exist. Some imitate the feel and texture of natural fibers such as silk, wool, cotton, and linen. The types that resemble silk are often called artificial silk. It can be woven or knit to make textiles for clothing and other purposes. Rayon production involves solubilizing cellulose to allow turning the fibers into required form. Three common solubilization methods are: * The Cuprammonium rayon, cuprammonium process (not in use today), using ammoniacal solutions of copper salts * The viscose process, the most common today, using alkali and carbon disulfide * The Lyocell process, using amine oxide, avoids producing neurotoxic carbon disulfide but is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of glycosidic bond, β(1→4) linked glucose, D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall of green plants, many forms of algae and the oomycetes. Some species of bacteria secrete it to form biofilms. Cellulose is the most abundant biopolymer, organic polymer on Earth. The cellulose content of cotton fibre is 90%, that of wood is 40–50%, and that of dried hemp is approximately 57%. Cellulose is mainly used to produce paperboard and paper. Smaller quantities are converted into a wide variety of derivative products such as cellophane and rayon. Conversion of cellulose from energy crops into biofuels such as cellulosic ethanol is under development as a renewable fuel source. Cellulose for industrial use is mainly obtained from wood pulp and cotton. Cellulose is also greatly affected by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |