|
Schur Polynomial
In mathematics, Schur polynomials, named after Issai Schur, are certain symmetric polynomials in ''n'' variables, indexed by partitions, that generalize the elementary symmetric polynomials and the complete homogeneous symmetric polynomials. In representation theory they are the characters of polynomial irreducible representations of the general linear groups. The Schur polynomials form a linear basis for the space of all symmetric polynomials. Any product of Schur polynomials can be written as a linear combination of Schur polynomials with non-negative integral coefficients; the values of these coefficients is given combinatorially by the Littlewood–Richardson rule. More generally, skew Schur polynomials are associated with pairs of partitions and have similar properties to Schur polynomials. Definition (Jacobi's bialternant formula) Schur polynomials are indexed by integer partitions. Given a partition , where , and each is a non-negative integer, the functions a_ (x ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Young Tableau
In mathematics, a Young tableau (; plural: tableaux) is a combinatorial object useful in representation theory and Schubert calculus. It provides a convenient way to describe the group representations of the symmetric and general linear groups and to study their properties. Young tableaux were introduced by Alfred Young, a mathematician at Cambridge University, in 1900. They were then applied to the study of the symmetric group by Georg Frobenius in 1903. Their theory was further developed by many mathematicians, including Percy MacMahon, W. V. D. Hodge, G. de B. Robinson, Gian-Carlo Rota, Alain Lascoux, Marcel-Paul Schützenberger and Richard P. Stanley. Definitions ''Note: this article uses the English convention for displaying Young diagrams and tableaux''. Diagrams A Young diagram (also called a Ferrers diagram, particularly when represented using dots) is a finite collection of boxes, or cells, arranged in left-justified rows, with the row lengths in non-incre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unitary Group
*
*
{{disambiguation ...
Unitary may refer to: Mathematics * Unitary divisor * Unitary element * Unitary group * Unitary matrix * Unitary morphism * Unitary operator * Unitary transformation * Unitary representation * Unitarity (physics) * ''E''-unitary inverse semigroup Politics * Unitary authority * Unitary state See also * Unital (other) * Unitarianism Unitarianism () is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian sect of Christianity. Unitarian Christians affirm the wikt:unitary, unitary God in Christianity, nature of God as the singular and unique Creator deity, creator of the universe, believe that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Representation Theory Of The Symmetric Group
In mathematics, the representation theory of the symmetric group is a particular case of the representation theory of finite groups, for which a concrete and detailed theory can be obtained. This has a large area of potential applications, from symmetric function theory to quantum chemistry studies of atoms, molecules and solids. The symmetric group S''n'' has order ''n''!. Its conjugacy classes are labeled by partitions of ''n''. Therefore according to the representation theory of a finite group, the number of inequivalent irreducible representations, over the complex numbers, is equal to the number of partitions of ''n''. Unlike the general situation for finite groups, there is in fact a natural way to parametrize irreducible representations by the same set that parametrizes conjugacy classes, namely by partitions of ''n'' or equivalently Young diagrams of size ''n''. Each such irreducible representation can in fact be realized over the integers (every permutation acting by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gröbner Basis
In mathematics, and more specifically in computer algebra, computational algebraic geometry, and computational commutative algebra, a Gröbner basis is a particular kind of generating set of an ideal in a polynomial ring K _1,\ldots,x_n/math> over a field K. A Gröbner basis allows many important properties of the ideal and the associated algebraic variety to be deduced easily, such as the dimension and the number of zeros when it is finite. Gröbner basis computation is one of the main practical tools for solving systems of polynomial equations and computing the images of algebraic varieties under projections or rational maps. Gröbner basis computation can be seen as a multivariate, non-linear generalization of both Euclid's algorithm for computing polynomial greatest common divisors, and Gaussian elimination for linear systems. Gröbner bases were introduced by Bruno Buchberger in his 1965 Ph.D. thesis, which also included an algorithm to compute them ( Buchberger's alg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hook Length Formula
In combinatorics, combinatorial mathematics, the hook length formula is a formula for the number of Young tableau, standard Young tableaux whose shape is a given Young diagram. It has applications in diverse areas of mathematics, areas such as representation theory, probability theory, probability, and algorithm analysis; for example, the problem of longest increasing subsequences. A related formula gives the number of semi-standard Young tableaux, which is a specialization of a Schur polynomial. Definitions and statement Let \lambda=(\lambda_1\geq \cdots\geq \lambda_k) be a integer partition, partition of n=\lambda_1+\cdots+\lambda_k. It is customary to interpret \lambda graphically as a Young diagram, namely a left-justified array of square cells with k rows of lengths \lambda_1,\ldots,\lambda_k. A (standard) Young tableau of shape \lambda is a filling of the n cells of the Young diagram with all the integers \, with no repetition, such that each row and each column form incre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pieri's Formula
In mathematics, Pieri's formula, named after Mario Pieri, describes the product of a Schubert cycle by a special Schubert cycle in the Schubert calculus, or the product of a Schur polynomial by a complete symmetric function. In terms of Schur functions ''s''λ indexed by partitions λ, it states that :\displaystyle s_\mu h_r=\sum_\lambda s_\lambda where ''h''''r'' is a complete homogeneous symmetric polynomial and the sum is over all partitions λ obtained from μ by adding ''r'' elements, no two in the same column. By applying the ω involution on the ring of symmetric functions, one obtains the dual Pieri rule for multiplying an elementary symmetric polynomial In mathematics, specifically in commutative algebra, the elementary symmetric polynomials are one type of basic building block for symmetric polynomials, in the sense that any symmetric polynomial can be expressed as a polynomial in elementary sy ... with a Schur polynomial: :\displaystyle s_\ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skew Tableau
In mathematics, a Young tableau (; plural: tableaux) is a combinatorial object useful in representation theory and Schubert calculus. It provides a convenient way to describe the group representations of the symmetric and general linear groups and to study their properties. Young tableaux were introduced by Alfred Young, a mathematician at Cambridge University, in 1900. They were then applied to the study of the symmetric group by Georg Frobenius in 1903. Their theory was further developed by many mathematicians, including Percy MacMahon, W. V. D. Hodge, G. de B. Robinson, Gian-Carlo Rota, Alain Lascoux, Marcel-Paul Schützenberger and Richard P. Stanley. Definitions ''Note: this article uses the English convention for displaying Young diagrams and tableaux''. Diagrams A Young diagram (also called a Ferrers diagram, particularly when represented using dots) is a finite collection of boxes, or cells, arranged in left-justified rows, with the row lengths in non-increas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murnaghan–Nakayama Rule
In group theory, a branch of mathematics, the Murnaghan–Nakayama rule, named after Francis Murnaghan and Tadashi Nakayama, is a combinatorial method to compute irreducible character values of a symmetric group.Richard Stanley, ''Enumerative Combinatorics, Vol. 2'' There are several generalizations of this rule beyond the representation theory of symmetric groups, but they are not covered here. The irreducible characters of a group are of interest to mathematicians because they concisely summarize important information about the group, such as the dimensions of the vector spaces in which the elements of the group can be represented by linear transformations that “mix” all the dimensions. For many groups, calculating irreducible character values is very difficult; the existence of simple formulas is the exception rather than the rule. The Murnaghan–Nakayama rule is a combinatorial rule for computing symmetric group character values χ using a particular kind of Young tab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hall–Littlewood Polynomials
In mathematics, the Hall–Littlewood polynomials are symmetric functions depending on a parameter ''t'' and a partition λ. They are Schur functions when ''t'' is 0 and monomial symmetric functions when ''t'' is 1 and are special cases of Macdonald polynomials. They were first defined indirectly by Philip Hall using the Hall algebra, and later defined directly by Dudley E. Littlewood (1961). Definition The Hall–Littlewood polynomial ''P'' is defined by :P_\lambda(x_1,\ldots,x_n;t) = \left( \prod_ \prod_^ \frac \right) , where λ is a partition of at most ''n'' with elements λ''i'', and ''m''(''i'') elements equal to ''i'', and ''S''''n'' is the symmetric group In abstract algebra, the symmetric group defined over any set is the group whose elements are all the bijections from the set to itself, and whose group operation is the composition of functions. In particular, the finite symmetric grou ... of order ''n''!. As an example, : P_(x_1,x_ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giambelli's Formula
In mathematics, Giambelli's formula, named after Giovanni Giambelli, expresses Schubert classes as determinants in terms of special Schubert classes. It states :\displaystyle \sigma_\lambda= \det(\sigma_)_ where σλ is the Schubert class of a partition λ. Giambelli's formula may be derived as a consequence of Pieri's formula. The Porteous formula is a generalization to morphisms of vector bundles over a variety. In the theory of symmetric functions, the same identity, known as the first Jacobi-Trudi identity expresses Schur functions as determinants in terms of complete symmetric functions. There is also the dual second Jacobi-Trudi identity which expresses Schur functions as determinants in terms of elementary symmetric functions. The corresponding identity also holds for Schubert classes. There is another Giambelli identity, expressing Schur functions as determinants of matrices whose entries are Schur functions corresponding to ''hook partiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
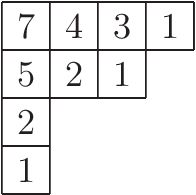
Conjugate Partition
In number theory and combinatorics, a partition of a non-negative integer , also called an integer partition, is a way of writing as a summation, sum of positive integers. Two sums that differ only in the order of their summands are considered the same partition. (If order matters, the sum becomes a composition (combinatorics), composition.) For example, can be partitioned in five distinct ways: : : : : : The only partition of zero is the empty sum, having no parts. The order-dependent composition is the same partition as , and the two distinct compositions and represent the same partition as . An individual summand in a partition is called a part. The number of partitions of is given by the Partition function (number theory), partition function . So . The notation means that is a partition of . Partitions can be graphically visualized with Young diagrams or Ferrers diagrams. They occur in a number of branches of mathematics and physics, including the study of symm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |