|
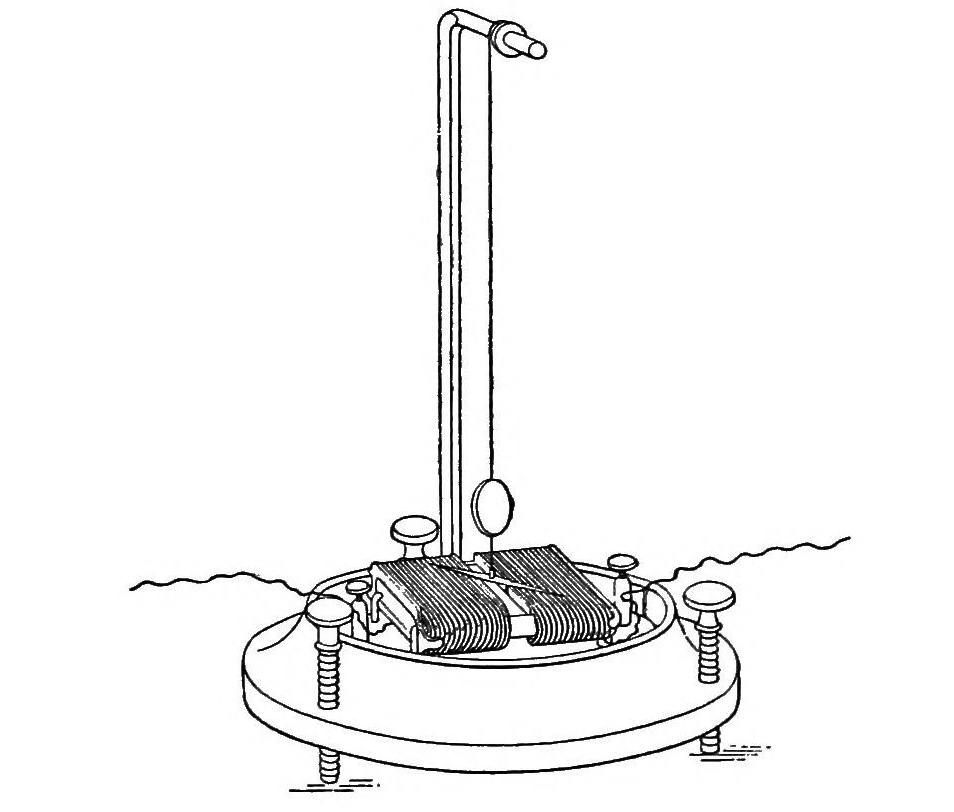
Schilling Telegraph
The Schilling telegraph is a needle telegraph invented by Pavel Schilling in the nineteenth century. It consists of a bank of needle instruments (six as developed for use in Russia) which between them display a binary code representing a letter or numeral. Signals were sent from a piano-like keyboard, and an additional circuit was provided for calling attention at the receiving end by setting off an alarm. The code was read from the position of paper discs suspended on threads. These had different colours on the two sides. Each disc was turned by electromagnetic action on a magnetised needle. Overview Schilling's telegraph is one of a type called needle telegraphs. These are telegraphs that use a coil of wire as an electromagnet to deflect a small magnet shaped like a compass needle. The position of the needle imparts the telegraphed information to the person receiving the message. Schilling's 1832 demonstration telegraph in St. Petersburg used six wires for signalling, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schilling One-needle Telegraph
Schilling may refer to: * Schilling (unit), an historical unit of measurement * Schilling (coin), the historical European coin ** Shilling, currency historically used in Europe and currently used in the East African Community ** Austrian schilling, the former currency of Austria * Schilling rudder, a type of rudder allowing extra manoeuvrability * A. Schilling & Company, an historical West Coast spice firm acquired in 1948 by McCormick & Company * Schilling Air Force Base * Schilling Power Station, an oil-fired power station near the nuclear power station at Stade, Germany * Schilling of Solothurn, a family of two Swiss chroniclers * The Schilling School for Gifted Children, a K-12 school in Cincinnati, Ohio People * Schilling (surname) See also * Schilling test in medicine * Schillings, a firm of UK lawyers * Schillings (surname) * Skilling (currency) The skilling (pronounced ''shilling'' in English) was the Scandinavian equivalent of the shilling. It was used as a subdivision ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Needle Telegraph
A needle telegraph is an electrical telegraph that uses indicating needles moved electromagnetically as its means of displaying messages. It is one of the two main types of electromagnetic telegraph, the other being the armature system, as exemplified by the telegraph of Samuel Morse in the United States. Needle telegraphs were widely used in Europe and the British Empire during the nineteenth century. Needle telegraphs were suggested shortly after Hans Christian Ørsted discovered that electric currents could deflect compass needles in 1820. Pavel Schilling developed a telegraph using needles suspended by threads. This was intended for installation in Russia for government use, but Schilling died in 1837 before it could be implemented. In 1833 Carl Friedrich Gauss and Wilhelm Eduard Weber in Göttingen built a telegraph line that was used for scientific study and communication between university sites. In 1837 Carl August von Steinheil adapted Gauss and Weber's rather cumbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavel Schilling
Baron Pavel Lvovitch Schilling (1786–1837), also known as Paul Schilling, was a Russian inventor, military officer and diplomat of Baltic German origin. The majority of his career was spent working for the imperial Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs as a language officer at the Russian embassy in Munich. As a military officer, he took part in the War of the Sixth Coalition against Napoleon. In his later career, he was transferred to the Asian department of the ministry and undertook a tour of Mongolia to collect ancient manuscripts. Schilling is best known for his pioneering work in electrical telegraphy, which he undertook at his own initiative. While in Munich, he worked with Samuel Thomas von Sömmerring who was developing an electrochemical telegraph. Schilling developed the first electromechanics, electromagnetic telegraph that was of practical use. Schilling telegraph, Schilling's design was a needle telegraph using magnetised needles suspended by a thread over a ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Code
A binary code represents plain text, text, instruction set, computer processor instructions, or any other data using a two-symbol system. The two-symbol system used is often "0" and "1" from the binary number, binary number system. The binary code assigns a pattern of binary digits, also known as bits, to each character, instruction, etc. For example, a binary string (computer science), string of eight bits (which is also called a byte) can represent any of 256 possible values and can, therefore, represent a wide variety of different items. In computing and telecommunications, binary codes are used for various methods of encoding data, such as character strings, into bit strings. Those methods may use fixed-width or variable-length code, variable-width strings. In a fixed-width binary code, each letter, digit, or other character is represented by a bit string of the same length; that bit string, interpreted as a binary number, is usually displayed in code tables in octal, decimal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. Electromagnets usually consist of wire (likely copper) wound into a electromagnetic coil, coil. A current through the wire creates a magnetic field which is concentrated along the center of the coil. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet. The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet, which needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field. Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as Electric motor, motor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compass Needle
A compass is a device that shows the cardinal directions used for navigation and geographic orientation. It commonly consists of a magnetized needle or other element, such as a compass card or compass rose, which can pivot to align itself with magnetic north. Other methods may be used, including gyroscopes, magnetometers, and GPS receivers. Compasses often show angles in degrees: north corresponds to 0°, and the angles increase clockwise, so east is 90°, south is 180°, and west is 270°. These numbers allow the compass to show azimuths or bearings which are commonly stated in degrees. If local variation between magnetic north and true north is known, then direction of magnetic north also gives direction of true north. Among the Four Great Inventions, the magnetic compass was first invented as a device for divination as early as the Chinese Han dynasty (since c. 206 BC), Li Shu-hua, p. 176 and later adopted for navigation by the Song dynasty Chinese during the 11th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris Electrical Exhibition
The first International Exposition of Electricity () ran from 15 August 1881 through to 15 November 1881 at the Palais de l'Industrie on the Champs-Élysées in Paris, France. It served to display the advances in electrical technology since the small electrical display at the 1878 Universal Exposition.K. G. Beauchamp, '' Exhibiting electricity'' IET, 1997 , pp.160-165 Exhibitors came from the United Kingdom, United States, Germany, Italy and the Netherlands, as well as from France. As part of the exhibition, the first International Congress of Electricians presented numerous scientific and technical papers, including definitions of the standard practical units volt, ohm and ampere. History Adolphe Cochery, Minister of Posts and Telegraphs of the time, had initially suggested that an international exposition should be held. This show was a great stir. The public could admire the dynamo of Zénobe Gramme, the incandescent light, the théâtrophone (with stereophonic sound), the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schilling Calling System
Schilling may refer to: * Schilling (unit), an historical unit of measurement * Schilling (coin), the historical European coin ** Shilling, currency historically used in Europe and currently used in the East African Community ** Austrian schilling, the former currency of Austria * Schilling rudder, a type of rudder allowing extra manoeuvrability * A. Schilling & Company, an historical West Coast spice firm acquired in 1948 by McCormick & Company * Schilling Air Force Base * Schilling Power Station, an oil-fired power station near the nuclear power station at Stade, Germany * Schilling of Solothurn, a family of two Swiss chroniclers * The Schilling School for Gifted Children, a K-12 school in Cincinnati, Ohio People * Schilling (surname) See also * Schilling test in medicine * Schillings, a firm of UK lawyers * Schillings (surname) * Skilling (currency) The skilling (pronounced ''shilling'' in English) was the Scandinavian equivalent of the shilling. It was used as a subdivision ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Thomas Von Sömmerring
Samuel Thomas von Sömmerring (28 January 1755 – 2 March 1830) was a German physician, anatomist, anthropologist, paleontologist and inventor. Sömmerring discovered the macula in the retina of the human eye. His investigations on the brain and the nervous system, on the sensory organs, on the embryo and its malformations, on the structure of the lungs, etc., made him one of the most important German anatomists. Career Sömmerring was born in Thorn (Toruń), Royal Prussia (a province of the Crown of Poland) as the ninth child of the physician Johann Thomas Sömmerring. In 1774 he completed his education in Thorn and began to study medicine at the University of Göttingen. He visited Petrus Camper lecturing at the University in Franeker. He became a professor of anatomy at the Collegium Carolinum (housed in the Ottoneum, now a Natural History Museum) in Kassel and, beginning in 1784, at the University of Mainz. There he was for five years the dean of the medical f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codepoint
A code point, codepoint or code position is a particular position in a table, where the position has been assigned a meaning. The table may be one dimensional (a column), two dimensional (like cells in a spreadsheet), three dimensional (sheets in a workbook), etc... in any number of dimensions. Technically, a code point is a unique position in a quantized n-dimensional space, where the position has been assigned a semantic meaning. The table has discrete (whole) and positive positions (1, 2, 3, 4, but not fractions). Code points are used in a multitude of formal information processing and telecommunication standards.ETSI TS 101 773 (section 4), https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_ts/101700_101799/101773/01.02.01_60/ts_101773v010201p.pdf For example ITU-T Recommendation T.35 contains a set of country codes for telecommunications equipment (originally fax machines) which allow equipment to indicate its country of manufacture or operation. In T.35, Argentina is represented by the code ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Alphabet
The Russian alphabet (, or , more traditionally) is the script used to write the Russian language. The modern Russian alphabet consists of 33 letters: twenty consonants (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , ), ten vowels (, , , , , , , , , ), a semivowel / consonant (), and two modifier letters or "signs" (, ) that alter pronunciation of a preceding consonant or a following vowel. History Russian alphabet is derived from the Cyrillic script, which was invented in the 9th century to capture accurately the phonology of the first Slavic literary language, Old Church Slavonic. The early Cyrillic alphabet was adapted to Old East Slavic from Old Church Slavonic and was used in Kievan Rus' from the 10th century onward to write what would become the modern Russian language. The last major reform of Russian orthography took place in 1917–1918. Letters : An alternative form of the letter De () closely resembles the Greek letter delta (). : An alternative form of the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Character Encoding
Character encoding is the process of assigning numbers to graphical character (computing), characters, especially the written characters of human language, allowing them to be stored, transmitted, and transformed using computers. The numerical values that make up a character encoding are known as code points and collectively comprise a code space or a code page. Early character encodings that originated with optical or electrical telegraphy and in early computers could only represent a subset of the characters used in written languages, sometimes restricted to Letter case, upper case letters, Numeral system, numerals and some punctuation only. Over time, character encodings capable of representing more characters were created, such as ASCII, the ISO/IEC 8859 encodings, various computer vendor encodings, and Unicode encodings such as UTF-8 and UTF-16. The Popularity of text encodings, most popular character encoding on the World Wide Web is UTF-8, which is used in 98.2% of surve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |