|
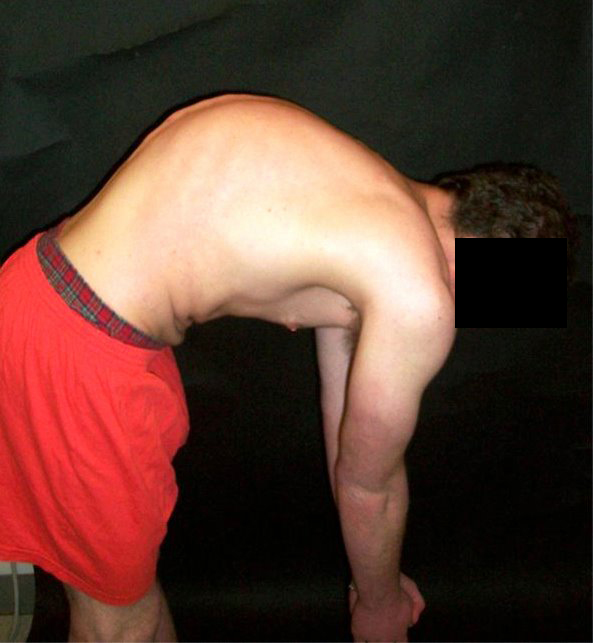
Scheuermann's Kyphosis
Scheuermann's disease is a skeletal disorder. It describes a condition where the vertebrae grow unevenly with respect to the sagittal plane; that is, the posterior angle is often greater than the anterior. This uneven growth results in the signature "wedging" shape of the vertebrae, causing kyphosis. It is named after Danish surgeon Holger Scheuermann. Signs and symptoms Scheuermann's disease is considered to be a form of osteochondrosis of the spine. It typically develops during adolescence and presents a significantly worse deformity than postural kyphosis. Patients with Scheuermann’s kyphosis cannot consciously correct their posture. The apex of their curve, located in the thoracic vertebrae, is quite rigid. Scheuermann's disease is notorious for causing lower and mid-level back and neck pain, which can be severe and disabling. The individual may feel pain at the apex of the curve, which is aggravated by physical activity and by periods of standing or sitting; this can ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthopaedics
Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics ( alternative spelling orthopaedics) is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors and congenital disorders. Etymology Nicholas Andry coined the word in French as ', derived from the Ancient Greek words ("correct", "straight") and ("child"), and published ''Orthopedie'' (translated as ''Orthopædia: Or the Art of Correcting and Preventing Deformities in Children'') in 1741. The word was assimilated into English as ''orthopædics''; the ligature ''æ'' was common in that era for ''ae'' in Greek- and Latin-based words. As the name implies, the discipline was initially developed with attention to children, but the correction of spinal and bone deformities in all stages of life eventually became the cornerstone of orthopedic pra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forced Vital Capacity
Spirometry (meaning ''the measuring of breath'') is the most common of the pulmonary function tests (PFTs). It measures lung function, specifically the amount (volume) and/or speed (flow) of air that can be inhaled and exhaled. Spirometry is helpful in assessing breathing patterns that identify conditions such as asthma, pulmonary fibrosis, cystic fibrosis, and Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, COPD. It is also helpful as part of a system of Public health surveillance, health surveillance, in which breathing patterns are measured over time. Spirometry generates pneumotachographs, which are charts that plot the volume and flow of air coming in and out of the lungs from one inhalation and one exhalation. Testing Spirometer The spirometry test is performed using a device called a spirometer, which comes in several different varieties. Most spirometers display the following graphs, called spirograms: * a ''volume-time curve'', showing volume (litres) along the Y-axis and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barrel Chest
Barrel chest generally refers to a wikt:broad, broad, deep chest found on a patient (or other person). A barrel chested person will usually have a naturally large ribcage, very round (i.e., vertically cylindrical) torso, large lung capacity, and can potentially have great upper body strength. It can sometimes be found alongside acromegaly (an enlargement of the extremities resulting from excess levels of human growth hormone (HGH) in the body). Barrel chest, as a medical condition, is most commonly related to osteoarthritis as individuals age. Arthritis can stiffen the chest causing the ribs to become fixed in their most expanded position, giving the appearance of a barrel chest. Barrel chest refers to an increase in the anteroposterior diameter of the chest wall resembling the shape of a barrel, most often associated with emphysema. There are two main causes of the barrel chest phenomenon in emphysema: # Increased lung compliance, compliance of the lungs leads to the accumulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |