|
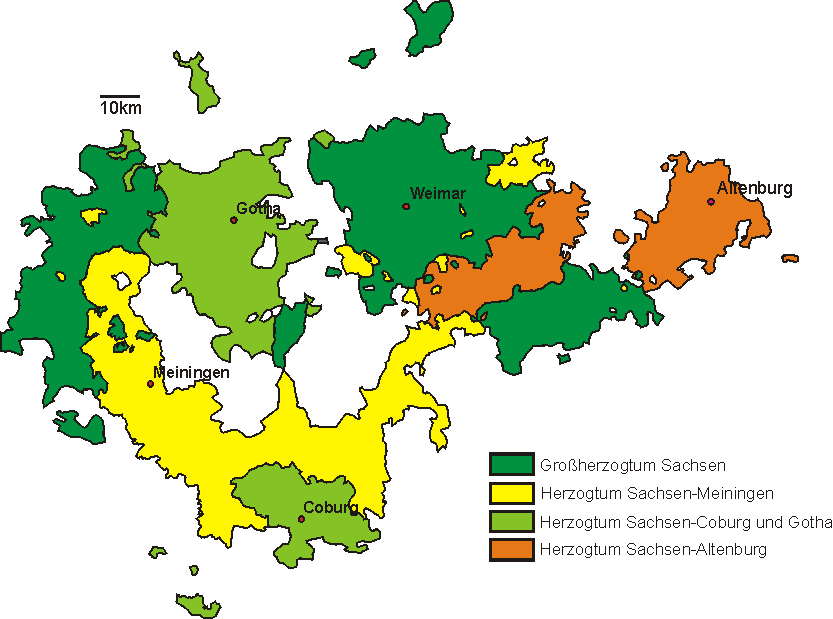
Saxe-Coburg And Gotha
Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (), or Saxe-Coburg-Gotha ( ), was an Ernestine duchy in Thuringia ruled by a branch of the House of Wettin, consisting of territories in the present-day states of Thuringia and Bavaria in Germany. It lasted from 1826 to 1918. In November 1918, Charles Edward, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, was forced to abdicate. In 1920, the northern part of the duchy (since 1918 the Free State of Gotha; culturally and linguistically Thuringian) was merged with six other Thuringian free states to form the Free State of Thuringia: Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach (until 1918 a grand duchy), Saxe-Altenburg and Saxe-Meiningen (until 1918 duchies), Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt and Schwarzburg-Sondershausen (until 1918 principalities), as well as the People's State of Reuss (until 1918 the principalities of Reuss-Gera and Reuss-Greiz). The southern part of the duchy (since 1918 the Free State of Coburg; culturally and linguistically Franconian), as southernmost of the Thuringian st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred, Duke Of Saxe-Coburg And Gotha
Alfred (Alfred Ernest Albert; 6 August 184430 July 1900) was sovereign Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha from 22 August 1893 until his death in 1900. He was the second son and fourth child of Queen Victoria and Prince Albert. He was known as the Duke of Edinburgh from 1866 until he succeeded his paternal uncle Ernest II as the reigning Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha in the German Empire. Early life Prince Alfred was born on 6 August 1844 at Windsor Castle to the reigning British monarch, Queen Victoria, and her husband, Prince Albert, the second son of Ernest I, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. Nicknamed Affie, he was second in the line of succession to the British throne behind his elder brother, Albert Edward, Prince of Wales. Alfred was baptised by the Archbishop of Canterbury, William Howley, at the Private Chapel in Windsor Castle on 6 September 1844. His godparents were his mother's first cousin, Prince George of Cambridge (represented by his father, the Duke of Cambridge); ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitutional Monarchy
Constitutional monarchy, also known as limited monarchy, parliamentary monarchy or democratic monarchy, is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in making decisions. Constitutional monarchies differ from absolute monarchies (in which a monarch is the only decision-maker) in that they are bound to exercise powers and authorities within limits prescribed by an established legal framework. A constitutional monarch in a parliamentary democracy is a hereditary symbolic head of state (who may be an emperor, king or queen, prince or grand duke) who mainly performs representative and civic roles but does not exercise executive or policy-making power. Constitutional monarchies range from countries such as Liechtenstein, Monaco, Morocco, Jordan, Kuwait, Bahrain and Bhutan, where the constitution grants substantial discretionary powers to the sovereign, to countries such as the United Kingdom and other Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papiermark
The Papiermark (; 'paper mark') was a derisive term for the Mark (currency sign, sign: ℳ︁) after it went off the gold standard, and most specifically with the era of Hyperinflation in the Weimar Republic, hyperinflation in Germany of 1922 and 1923. Formally, the same German mark (1871), German mark was used from 1871 to 1923. Like many countries, Germany departed the gold standard due to the outbreak of World War I, and stopped issuing gold coins backed in marks in August 1914. Precious metals rapidly disappeared from circulation, and inflation occurred as paper money was used to cover war debts in 1914 to 1918. Still, the papiermark is more associated with the early Weimar Republic era, when inflation grew out of control. By the time the mark was retired from circulation and renominated in December 1923, banknotes had amounts in the billions and trillions of marks by face value. History From 1914, the value of the mark fell. The rate of inflation rose following the en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt
Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt was a small historic state in present-day Thuringia, Germany, with its capital at Rudolstadt. History Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt was established in 1599 in the course of a resettlement of House of Schwarzburg, Schwarzburg dynasty lands. Since the 11th century, the ancestral seat of the comital family had been at Schwarzburg (municipality), Schwarzburg Castle, though after 1340, for most of its existence as a polity had the capital at the larger town of Rudolstadt. In 1583 Count Günther XLI, Count of Schwarzburg-Arnstadt, Günther XLI of Schwarzburg, the eldest son of Günther XL, Count of Schwarzburg, Günther XL the Rich and ruler over the united Schwarzburg lands, had died without issue. He was succeeded by his younger brothers, whereby Albrecht VII, Count of Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt, Albert VII received the territory around Rudolstadt. After their brother William I, Count of Schwarzburg-Frankenhausen had died in 1597, the surviving brothers Albrecht VII, Cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxe-Meiningen
Saxe-Meiningen ( ; ) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine duchies, Ernestine line of the House of Wettin, located in the southwest of the present-day Germany, German state of Thuringia. Established in 1681, by partition of the Ernestine Duchy of Saxe-Gotha among the seven sons of deceased Duke Ernest I, Duke of Saxe-Gotha, Ernest the Pious, the Saxe-Meiningen line of the House of Wettin lasted until the end of the German monarchies in 1918. History House of Wettin The House of Wettin, Wettiner had been the rulers of sizeable holdings in today's states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia since the Middle Ages. In the ''Treaty of Leipzig, Leipziger Teilung'' of 1485, the Wettiner were split into two branches named after their founding princes Albert III, Duke of Saxony, Albrecht and Ernest, Elector of Saxony, Ernst (''albertinisch'' and ''ernestinisch''). Thuringia was part of the Ernestine holdings of ''Kursachsen'' (the Electorate of Saxony). In 1572, the branc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxe-Altenburg
Saxe-Altenburg () was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the House of Wettin in present-day Thuringia. It was one of the smallest of the German states with an area of 1323 square kilometers and a population of 207,000 (1905) of whom about one fifth resided in the capital, Altenburg. The territory of the duchy consisted of two non-contiguous territories separated by land belonging to the Principality of Reuss-Gera. Its economy was based on agriculture, forestry, and small industry. The state had a constitutional monarchical form of government with a parliament composed of thirty members chosen by male taxpayers over 25 years of age. Territory Saxe-Altenburg had an area of 1,323 km2 (510 sq. mi.) and a population of 207,000 in 1905. Its capital was Altenburg. The duchy consisted of two separate areas: the Ostkreis, containing the cities of Altenburg, Schmölln, Gößnitz, Lucka und Meuselwitz (including the exclave of Mumsdorf), Roschütz, Hilbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach
Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach () was a German state, created as a duchy in 1809 by the merger of the Ernestine duchies of Saxe-Weimar and Saxe-Eisenach, which had been in personal union since 1741. It was raised to a grand duchy in 1815 by resolution of the Congress of Vienna. In 1903, it officially changed its name to the Grand Duchy of Saxony (), but this name was rarely used. The grand duchy came to an end in the German Revolution of 1918–19 with the other monarchies of the German Empire. It was succeeded by the Free State of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach, which was merged into the new Free State of Thuringia two years later. The full grand ducal style was Grand Duke of Saxe- Weimar- Eisenach, Landgrave in Thuringia, Margrave of Meissen, Princely Count of Henneberg, Lord of Blankenhayn, Neustadt and Tautenburg. The Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach branch has been the most genealogically senior extant branch of the House of Wettin since 1672. Geography The Grand Duchy of Saxe-Weimar-E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free State Of Thuringia
Thuringia (; officially the Free State of Thuringia, ) is one of Germany's 16 states. With 2.1 million people, it is 12th-largest by population, and with 16,171 square kilometers, it is 11th-largest in area. Erfurt is the capital and largest city. Other cities include Jena, Gera and Weimar. Thuringia is bordered by Bavaria, Hesse, Lower Saxony, Saxony, and Saxony-Anhalt. It has been known as "the green heart of Germany" () from the late 19th century due to its broad, dense forest. Most of Thuringia is in the Saale drainage basin, a left-bank tributary of the Elbe. Thuringia is home to the Rennsteig, Germany's best-known hiking trail. Its winter resort of Oberhof makes it a well-equipped winter sports destination – half of Germany's 136 Winter Olympic gold medals had been won by Thuringian athletes as of 2014. Thuringia was favoured by or was the birthplace of three key intellectuals and leaders in the arts: Johann Sebastian Bach, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thuringian
Thuringian is an East Central German dialect group spoken in much of the modern German Free State of Thuringia north of the Rennsteig ridge, southwestern Saxony-Anhalt and adjacent territories of Hesse and Bavaria. It is close to Upper Saxon spoken mainly in the state of Saxony, therefore both are also regarded as one Thuringian-Upper Saxon dialect group. Thuringian dialects are among the Central German dialects with the highest number of speakers. History Thuringian emerged during the medieval German '' Ostsiedlung'' migration from about 1100, when settlers from Franconia ( Main Franconia), Bavaria, Saxony, and Flanders settled in the areas east of the Saale River previously inhabited by Polabian Slavs. Characteristics The Thuringian dialect is characterized by a rounding of the vowels, the weakening of consonants of Standard German (the lenition of the consonants "p," "t," and "k"), a marked difference in the pronunciation of the "g" sound (which is most common in the areas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free State Of Gotha
The states of the Weimar Republic were the first-level administrative divisions and constituent states of the Weimar Republic. The states were established in 1918–1920 following the German Empire's defeat in World War I and the territorial losses that came with it. They were based on the 22 states and three city-states of the German Empire. During the revolution of 1918–1919, the states abolished their local monarchies and adopted republican constitutions. Several attempts were made to reorganize the states under the Weimar Republic, particularly because of Prussia's disproportionately large size and influence, but the attempts were unsuccessful. The one significant change was the formation of Thuringia from a number of smaller states. The Weimar Constitution created a federal republic with certain basic powers reserved for the federal government, some powers shared between the central government and the states, and the remainder in the hands of the states. The federal gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1918 In Germany
Events in the year 1918 in Germany. Incumbents National level Head of State * Kaiser – Wilhelm II, abdicated 9 November * Republic (from 9 November) – vacant Head of Government * Chancellor (Imperial) - Georg von Hertling to 30 September, then from 3 October Prince Maximilian of Baden to 9 November * Republic – from 9 November Friedrich Ebert, ''"Head of Government"'' State level Kingdoms * King of Bavaria – Ludwig III abdicated 7 November * King of Prussia – Wilhelm II, abdicated 9 November * King of Saxony – Frederick Augustus III, abdicated 13 November * King of Württemberg – William II, abdicated 30 November Grand Duchies * Grand Duke of Baden – Frederick II, abdicated 22 November * Grand Duke of Hesse – Ernest Louis, abdicated 9 November * Grand Duke of Mecklenburg-Schwerin - Frederick Francis IV, abdicated 14 November * Grand Duke of Mecklenburg-Strelitz – Adolphus Frederick VI, died 23 November, thereafter vacant * Grand Duke of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total land area of Germany, and with over 13.08 million inhabitants, it is the list of German states by population, second most populous German state, behind only North Rhine-Westphalia; however, due to its large land area, its population density is list of German states by population density, below the German average. Major cities include Munich (its capital and List of cities in Bavaria by population, largest city, which is also the list of cities in Germany by population, third largest city in Germany), Nuremberg, and Augsburg. The history of Bavaria includes its earliest settlement by Iron Age Celts, Celtic tribes, followed by the conquests of the Roman Empire in the 1st century BC, when the territory was incorporated into the provinces of Ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |