|
Sawai Madhopur
Sawai Madhopur (IAST: ''Savāī Mādhōpur'', IPA: əˈʋaːiː ˈmaːdʱoːpʊɾ is a city in the southeastern part of the Indian state of Rajasthan. It serves as the administrative headquarter of the Sawai Madhopur district, and forms a part of the Bharatpur division. The city is known for its historical significance, cultural heritage, and ecological importance. It is located near Ranthambore National Park, one of India's most prominent wildlife reserves, situated approximately from the city. The park is a major attraction for wildlife enthusiasts and tourists. Also located in the vicinity is the Ranthambore Fort, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, which adds to the city's cultural and architectural prominence. Etymology Sawai Madhopur is named after Maharaja Sawai Madho Singh I (born 20 May 1728 – March 5, 1768) (Reign: ), the ruler of Amer, who established the city in 1763 CE. In Sanskrit, the term "''pur''" (or "''pura''") is often employed to denote a city or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Indian Cities
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is an affinity group for contributors with shared goals within the Wikimedia movement. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sibling projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaipur
Jaipur (; , ) is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and the List of cities and towns in Rajasthan, largest city of the north-western States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan. , the city had a population of 3.1 million, making it the List of cities in India by population, tenth most populous city in the country. Located from the national capital New Delhi, Jaipur is also known as the ''Pink City'' due to the dominant color scheme of its buildings in the old city. Jaipur was founded in 1727 by Sawai Jai Singh, Sawai Jai Singh II, the Kachhwaha, Kachhwaha Rajput ruler of Amer, India, Amer, after whom the city is named. It is one of the earliest planned cities of modern India, designed by Vidyadhar Bhattacharya. During the British Raj, British colonial period, the city served as the capital of Jaipur State. After Independence of India, Indian independence in 1947, Jaipur became the capital of the newly formed state of Rajas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Alphabet Of Sanskrit Transliteration
The International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration (IAST) is a transliteration scheme that allows the lossless romanisation of Indic scripts as employed by Sanskrit and related Indic languages. It is based on a scheme that emerged during the 19th century from suggestions by Charles Trevelyan, William Jones, Monier Monier-Williams and other scholars, and formalised by the Transliteration Committee of the Geneva Oriental Congress, in September 1894. IAST makes it possible for the reader to read the Indic text unambiguously, exactly as if it were in the original Indic script. It is this faithfulness to the original scripts that accounts for its continuing popularity amongst scholars. Usage Scholars commonly use IAST in publications that cite textual material in Sanskrit, Pāḷi and other classical Indian languages. IAST is also used for major e-text repositories such as SARIT, Muktabodha, GRETIL, and sanskritdocuments.org. The IAST scheme represents more than a centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
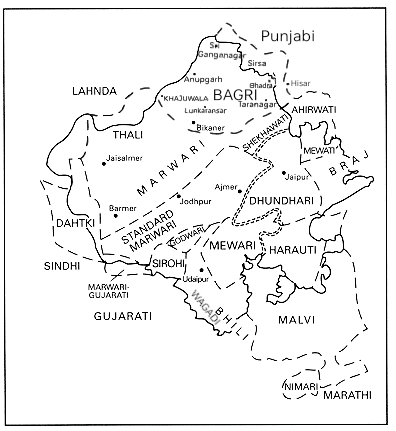
Dhundhari
Dhundhari (ढूंढाड़ी), also known as Jaipuri, is a Indo-Aryan language variety of the Rajasthani languages group. It is spoken in the Dhundhar region of northeastern Rajasthan state, India. Dhundari-speaking people are found in four districts – Jaipur, Sawai Madhopur, Dausa, Tonk and some parts of Sikar, Karauli and Gangapur District. With some 1.5 million speakers, it is not the largest speaking language variety in Rajasthan, though fairly used in the regions mentioned above. Dhundhari is spoken widely in and around Jaipur. MacAlister completed the grammatical analysis on 24 February 1884. Books on Jain philosophy, such as '' Moksha Marga Prakashak,'' have been written in Dhundari by Acharya Kalpa Pt. Todarmalji. The Serampore missionaries translated the New Testament into Jaipuri proper in 1815. Etymology It is called Dhundhari as it was mainly spoken in the Dhundhar region. The state was divided into-Marwar, Mewar, Dhundhar, Hadoti, and Vagad. These d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajasthani Languages
The Rajasthani languages are a group of Western Indo-Aryan languages, primarily spoken in Rajasthan and Malwa, and adjacent areas of Haryana, Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh in India and South Punjab and the adjacent areas of Sindh in Pakistan. They have also reached different corners of India, especially eastern and southern parts of India, due to the migrations of people of the Marwari community who use them for internal communication. Rajasthani languages are also spoken to a lesser extent in Nepal, where they are spoken by 25,394 people according to the 2011 Census of Nepal. The term Rajasthani is also used to refer to a literary language mostly based on Marwari.. Geographical distribution Most of the Rajasthani languages are chiefly spoken in the state of Rajasthan but are also spoken in Gujarat, Western Madhya Pradesh i.e. Malwa and Nimar, Haryana and Punjab. Rajasthani languages are also spoken in the Bahawalpur and Multan sectors of the Pakistani provinces of Pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government of India, alongside English language, English, and is the ''lingua franca'' of North India. Hindi is considered a Sanskritisation (linguistics), Sanskritised Register (sociolinguistics), register of Hindustani. Hindustani itself developed from Old Hindi and was spoken in Delhi and neighbouring areas. It incorporated a significant number of Persian language, Persian loanwords. Hindi is an Languages with official status in India, official language in twelve states (Bihar, Gujarat , Mizoram , Maharashtra ,Chhattisgarh, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand), and six Union territory, union territories (Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Delhi, Chandigarh, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi-arid Climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-arid climates, depending on variables such as temperature, and they give rise to different biomes. Defining attributes of semi-arid climates A more precise definition is given by the Köppen climate classification, which treats steppe climates (''BSh'' and ''BSk'') as intermediates between desert climates (BW) and humid climates (A, C, D) in ecological characteristics and agricultural potential. Semi-arid climates tend to support short, thorny or scrubby vegetation and are usually dominated by either grasses or shrubs as they usually cannot support forests. To determine if a location has a semi-arid climate, the precipitation threshold must first be determined. The method used to find the precipitation threshold (in millimeters): * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indicates a tropical rainforest climate. The system assigns a temperature subgroup for all groups other than those in the ''A'' group, indicated by the third letter for climates in ''B'', ''C'', ''D'', and the second letter for climates in ''E''. Other examples include: ''Cfb'' indicating an oceanic climate with warm summers as indicated by the ending ''b.'', while ''Dwb'' indicates a semi-Monsoon continental climate, monsoonal continental climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chauth Ka Barwara
Chauth Ka Barwara is a town and tehsil headquarters situated in Sawai Madhopur district, Rajasthan Rajasthan (; Literal translation, lit. 'Land of Kings') is a States and union territories of India, state in northwestern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the List of states and union territories of .... It is also known for Chauth Mata Temple in the region. References Villages in Sawai Madhopur district {{Bharatpurdivision-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niwai
Newai or Niwai is a town, and a municipality and tehsil in Tonk district in the Indian state of Rajasthan. The Tonk district is bounded in the north by Jaipur district, in the east by Sawai Madhopur district, in the southeast by Kota district, in the south by Bundi district, in the southwest by Bhilwara district, and in the west by Ajmer district. Jaipur, capital of Rajasthan is the closest major city to Newai. In 1783 Nepalia-Mathur Kayastha of Jaipur estate occupied it after defeating Nawab of Tonk in a bloody battle fought at the fort of Rakhtanchal. Since then it was a vassal state to the Jaipur estate until Jaipur became part of Independent India. Darbar of Daroga ji ruled Niwai under Maharaja of Jaipur. Demographics India census, Niwai had a population of 45,787. Males constitute 50.30% of the population and females 49.70%. Jaipur, the Pink city and Capital of Rajasthan is just away from Newai, Newai is a Tehsil Headquarter of District Tonk. Newai is surrounded by ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gangapur City
Gangapur City is a municipal council located in Sawai Madhopur district in the eastern part of Indian state of Rajasthan. It is situated 140 km (87 mi) east of Rajasthan's capital Jaipur, 76 km (47 mi) from Sawai Madhopur, 33 km (20 mi) from Karauli, 160 km (99 mi) from Agra of Uttar Pradesh. It is famous for its sweet cuisine ''Kheermohan'' and newly built ''Kushalgarh Baba Shyam Temple''. Gangapur City holds a strategic position due to its location on the Delhi–Mumbai railway route, making it an important transportation hub. The city is well-connected to major urban centers like Jaipur, Kota, and Agra. Its proximity to attractions like Ranthambore National Park adds to its importance in the area. History Gangapur was reportedly named Kushalgarh (Hindi: कुशालगढ़); by King Kushaliram Haldiya. Gangapur took its current name from Kushaliram's brother, Gangaram. Historically Gangapur City was the cultural capital of Jaipur State and was known as "The Jugad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheopur
Sheopur is a city in Madhya Pradesh state of central India. It is the administrative headquarters of Sheopur District. The City is situated on the right bank of the Seep River, a tributary of the Chambal. Thus the city derives its name from "Seep-pur" meaning "town on the Seep". Later, colloquially it came to be known as Sheopur. Sheopur is linked by narrow gauge rail to Gwalior (No longer in operation). Chambal River is just 25 km, which forms the boundary between Rajasthan and MP states. Sheopur can be reached via train and buses from Gwalior which is 211Km and via buses from Sawai Madhopur and Kota which are 61 km and 139 km from Sheopur. Sheopur is located at northern part of Madhya Pradesh. Some of the main locations are Vijaipur, Karahal and Badoda. Major tourist attraction is Palpur (kuno) wildlife sanctuary. The well-known Kaketo reservoir is located in this district. The art of woodcarving has flourished in district Sheopur and the beautifully e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |