|
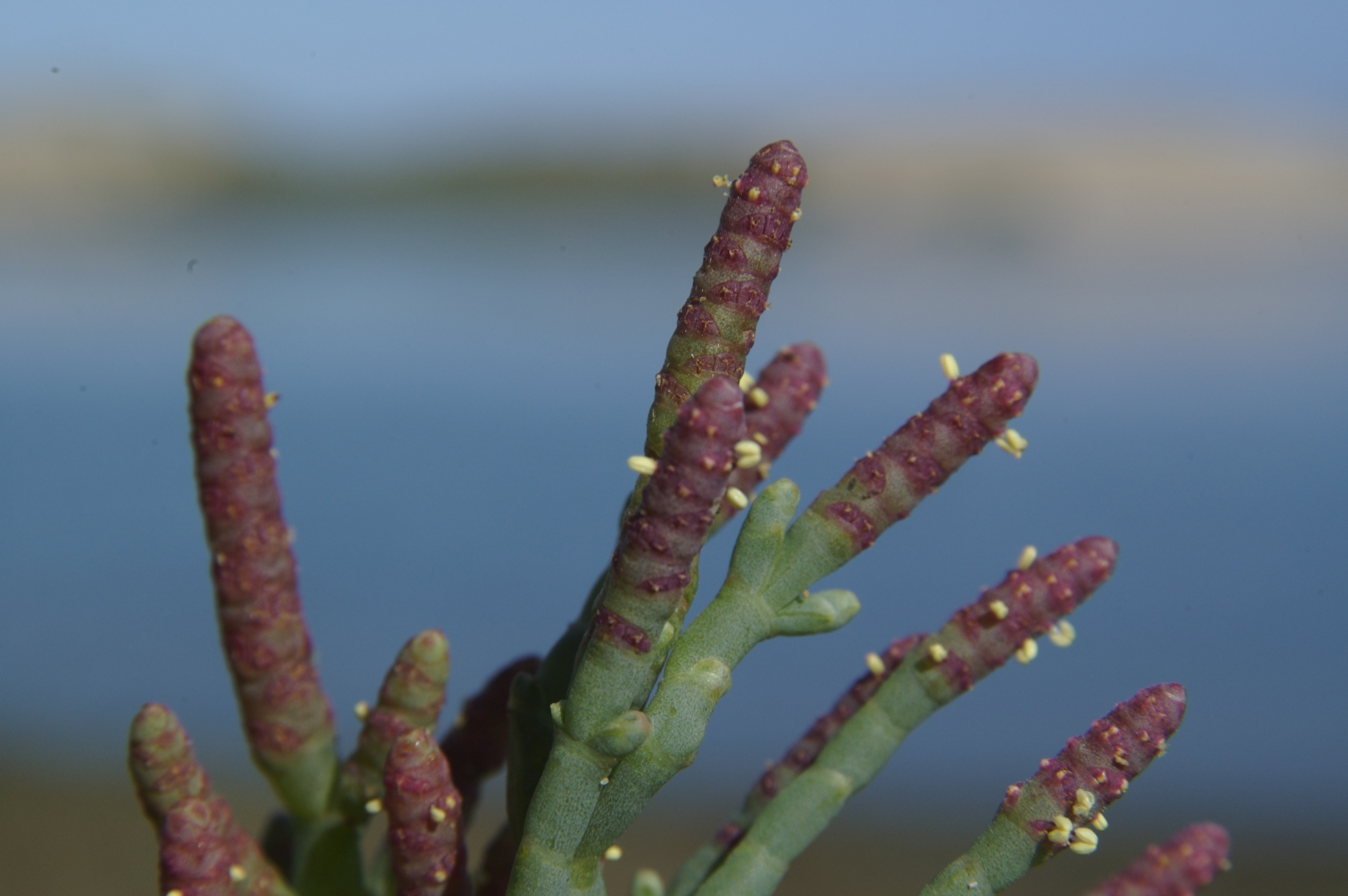
Sarcocornia Capensis
''Sarcocornia'' is a formerly recognized genus of flowering plants in the amaranth family, Amaranthaceae. Species are known commonly as samphires, glassworts, or saltworts. Molecular phylogenetic studies have shown that when separated from ''Salicornia'', the genus is paraphyletic, since ''Salicornia'' is embedded within it, and ''Sarcocornia'' has now been merged into a more broadly circumscribed ''Salicornia''. When separated from ''Salicornia'', the genus has a cosmopolitan distribution, and is most diverse in the Cape Floristic Region of South Africa. Description Species formerly placed in ''Sarcocornia'' are perennial herbs, subshrubs or shrubs. They are taking an erect or prostrate, creeping form. The new stems are fleshy and divided into joint-like segments. Older stems are woody and not segmented. The oppositely arranged leaves are borne on fleshy, knobby petioles, their base decurrent and connate (thus forming the segments), the blades forming small, triangular tips ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flowering Plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. They include all forbs (flowering plants without a woody stem), grasses and grass-like plants, a vast majority of broad-leaved trees, shrubs and vines, and most aquatic plants. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ἀγγεῖον / ('container, vessel') and σπέρμα / ('seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed within a fruit. They are by far the most diverse group of land plants with 64 orders, 416 families, approximately 13,000 known genera and 300,000 known species. Angiosperms were formerly called Magnoliophyta (). Angiosperms are distinguished from the other seed-producing plants, the gymnosperms, by having flowers, xylem consisting of vessel elements instead of tracheids, endosperm within their seeds, and fruits that completely envelop the seeds. The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from the common ance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perianth
The perianth (perigonium, perigon or perigone in monocots) is the non-reproductive part of the flower, and structure that forms an envelope surrounding the sexual organs, consisting of the calyx (sepals) and the corolla (petals) or tepals when called a perigone. The term ''perianth'' is derived from Greek περί (, "around") and άνθος (, "flower"), while ''perigonium'' is derived from περί () and γόνος (, "seed, sex organs"). In the mosses and liverworts (Marchantiophyta), the perianth is the sterile tubelike tissue that surrounds the female reproductive structure (or developing sporophyte). Flowering plants In flowering plants, the perianth may be described as being either dichlamydeous/heterochlamydeous in which the calyx and corolla are clearly separate, or homochlamydeous, in which they are indistinguishable (and the sepals and petals are collectively referred to as tepals). When the perianth is in two whorls, it is described as biseriate. While the ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
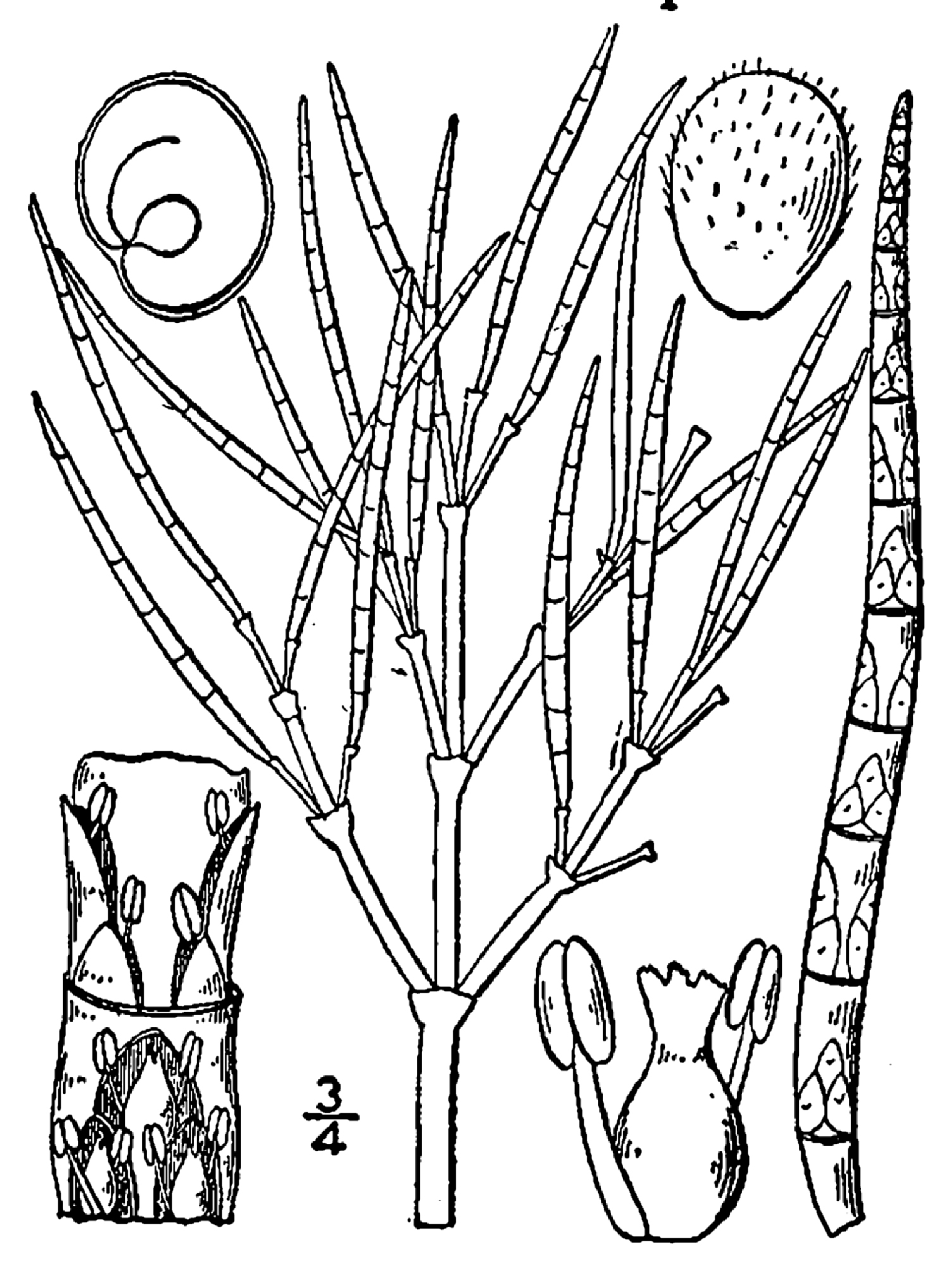
Salicornia Capensis
''Salicornia'' is a genus of succulent, halophytic (salt tolerant) flowering plants in the family Amaranthaceae that grow in salt marshes, on beaches, and among mangroves. ''Salicornia'' species are native to North America, Europe, Central Asia, and southern Africa. Common names for the genus include glasswort, pickleweed, picklegrass, and marsh samphire; these common names are also used for some species not in ''Salicornia''. To French speakers in Atlantic Canada, they are known colloquially as ''titines de souris'' ('mouse tits'). The main European species is often eaten, called marsh samphire in Britain, and the main North American species is occasionally sold in grocery stores or appears on restaurant menus as sea beans, samphire greens or sea asparagus. Description The ''Salicornia'' species are small annual herbs. They grow prostrate to erect, their simple or branched stems are succulent, hairless, and appear to be jointed. The opposite leaves are strongly reduced to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salicornia Blackiana
''Salicornia blackiana'', synonym ''Sarcocornia blackiana'', commonly known as thick-head glasswort, is a species of succulent halophytic shrub. It is widespread in southern and western Australia, including Tasmania. Its preferred habitats are estuaries, swamps and periodically waterlogged saline areas. Description It grows as an erect or decumbent perennial herb In general use, herbs are a widely distributed and widespread group of plants, excluding vegetables and other plants consumed for macronutrients, with savory or aromatic properties that are used for flavoring and garnishing food, for medicina ... with succulent, stem-like leaves, growing up to 0.8 m in height. It is very similar to the better known beaded glasswort but is a larger plant and differs in having a thicker fruiting spike, 4–9 mm in diameter, and seeds with blunt hairs or papillae. References External links * blackiana Flora of Tasmania Flora of New South Wales Flora of V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salicornia Andina
''Salicornia'' is a genus of succulent, halophytic (salt tolerant) flowering plants in the family Amaranthaceae that grow in salt marshes, on beaches, and among mangroves. ''Salicornia'' species are native to North America, Europe, Central Asia, and southern Africa. Common names for the genus include glasswort, pickleweed, picklegrass, and marsh samphire; these common names are also used for some species not in ''Salicornia''. To French speakers in Atlantic Canada, they are known colloquially as ''titines de souris'' ('mouse tits'). The main European species is often eaten, called marsh samphire in Britain, and the main North American species is occasionally sold in grocery stores or appears on restaurant menus as sea beans, samphire greens or sea asparagus. Description The ''Salicornia'' species are small annual herbs. They grow prostrate to erect, their simple or branched stems are succulent, hairless, and appear to be jointed. The opposite leaves are strongly reduced to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salicornia Ambigua
''Salicornia'' is a genus of succulent, halophytic A halophyte is a salt-tolerant plant that grows in soil or waters of high salinity, coming into contact with saline water through its roots or by salt spray, such as in saline semi-deserts, mangrove swamps, marshes and sloughs and seashores. T ... (salt tolerant) flowering plants in the family Amaranthaceae that grow in salt marshes, on beaches, and among mangroves. ''Salicornia'' species are native to North America, Europe, Central Asia, and southern Africa. Common names for the genus include glasswort, pickleweed, picklegrass, and marsh samphire; these common names are also used for some species not in ''Salicornia''. To French speakers in Atlantic Canada, they are known colloquially as ''titines de souris'' ('mouse tits'). The main European species is often eaten, called marsh samphire in Britain, and the main North American species is occasionally sold in grocery stores or appears on restaurant menus as sea beans, samphir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salicornia Alpini
''Salicornia'' is a genus of succulent, halophytic (salt tolerant) flowering plants in the family Amaranthaceae that grow in salt marshes, on beaches, and among mangroves. ''Salicornia'' species are native to North America, Europe, Central Asia, and southern Africa. Common names for the genus include glasswort, pickleweed, picklegrass, and marsh samphire; these common names are also used for some species not in ''Salicornia''. To French speakers in Atlantic Canada, they are known colloquially as ''titines de souris'' ('mouse tits'). The main European species is often eaten, called marsh samphire in Britain, and the main North American species is occasionally sold in grocery stores or appears on restaurant menus as sea beans, samphire greens or sea asparagus. Description The ''Salicornia'' species are small annual herbs. They grow prostrate to erect, their simple or branched stems are succulent, hairless, and appear to be jointed. The opposite leaves are strongly reduced to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plants Of The World Online
Plants of the World Online (POWO) is an online database published by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. It was launched in March 2017 with the ultimate aim being "to enable users to access information on all the world's known seed-bearing plants by 2020". The initial focus was on tropical African Floras, particularly Flora Zambesiaca, Flora of West Tropical Africa and Flora of Tropical East Africa. The database uses the same taxonomical source as Kew's World Checklist of Selected Plant Families, which is the International Plant Names Index, and the World Checklist of Vascular Plants (WCVP). POWO contains 1,234,000 global plant names and 367,600 images. See also *Australian Plant Name Index The Australian Plant Name Index (APNI) is an online database of all published names of Australian vascular plants. It covers all names, whether current names, synonyms or invalid names. It includes bibliographic and typification details, informati ... * Convention on Biological Diversity * W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago and the Russian Far East to the east. The continental landmass is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean and Africa to the west, the Pacific Ocean to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and by Africa, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Indian Ocean to the south. The division between Europe and Asia as two continents is a historical social construct, as many of their borders are over land; thus, in some parts of the world, Eurasia is recognized as the largest of the six, five, or four continents on Earth. In geology, Eurasia is often considered as a single rigid megablock. However, the rigidity of Eurasia is debated based on paleomagnetic data. Eurasia covers around , or around 36.2% of the Earth's total land area. It is also home to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salicornia Perennis
''Salicornia perennis'', synonym ''Sarcocornia perennis'', otherwise known as perennial glasswort, is a species of halophytic perennial plant within the family Amaranthaceae Amaranthaceae is a family of flowering plants commonly known as the amaranth family, in reference to its type genus '' Amaranthus''. It includes the former goosefoot family Chenopodiaceae and contains about 165 genera and 2,040 species, making i .... It has a widespread but patchy native distribution, being found in parts of Western Europe, northern and southern Africa, North America from southeast Alaska to south Mexico, the Caribbean, and South America. It is native to the coasts of southern Britain and Ireland, where it is classified as nationally scarce. The species flowers between July and October. References perennis Flora of Southwestern Europe Flora of Southeastern Europe Flora of Africa Flora of North America Flora of South America {{Amaranthaceae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ploidy
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively, in each homologous chromosome pair, which chromosomes naturally exist as. Somatic cells, tissues, and individual organisms can be described according to the number of sets of chromosomes present (the "ploidy level"): monoploid (1 set), diploid (2 sets), triploid (3 sets), tetraploid (4 sets), pentaploid (5 sets), hexaploid (6 sets), heptaploid or septaploid (7 sets), etc. The generic term polyploid is often used to describe cells with three or more chromosome sets. Virtually all sexually reproducing organisms are made up of somatic cells that are diploid or greater, but ploidy level may vary widely between different organisms, between different tissues within the same organism, and at different stages in an organism's life cycle. Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |