|
Sanjak Of Gaza
Gaza Sanjak (), known in Arabic as Bilād Ghazza (the Land of Gaza), was a sanjak of the Damascus Eyalet of the Ottoman Empire centered in Gaza City, Gaza, and spread northwards up to the Yarkon River. In the 16th century it was divided into ''nawahi'' (singular: ''nahiya''; third-level subdivisions): Gaza in the south and Ramla in the north along the Nahr Rūbīn/Wādī al-Ṣarār. Gaza Sanjak "formed a passageway connecting Egypt and the Levant, precipitating bi-directional trade, conquest and Human migration, population movements". Situated in the southern part of the Levantine coastal plain, Gaza Sanjak received less precipitation and was more prone to drought and nomadic incursion than more northerly regions. Roy Marom, Marom and Itamar Taxel, Taxel have shown that during the seventeenth to eighteenth centuries, nomadic economic and security pressures led to settlement abandonment around Majdal ‘Asqalān, and the southern coastal plain in general. The population of abando ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanjak
A sanjak or sancak (, , "flag, banner") was an administrative division of the Ottoman Empire. The Ottomans also sometimes called the sanjak a liva (, ) from the name's calque in Arabic and Persian. Banners were a common organization of nomadic groups on the Eurasian Steppe including the early Turks, Mongols, and Manchus and were used as the name for the initial first-level territorial divisions at the formation of the Ottoman Empire. Upon the empire's expansion and the establishment of eyalets as larger provinces, sanjaks were used as the second-level administrative divisions. They continued in this purpose after the eyalets were replaced by vilayets during the Tanzimat reforms of the 19th century. Sanjaks were typically headed by a bey or sanjakbey. The Tanzimat reforms initially placed some sanjaks under kaymakams and others under mutasarrifs; a sanjak under a mutasarrif was known as a mutasarriflik. The districts of each sanjak were known as kazas. These were ini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Town
A town is a type of a human settlement, generally larger than a village but smaller than a city. The criteria for distinguishing a town vary globally, often depending on factors such as population size, economic character, administrative status, or historical significance. In some regions, towns are formally defined by legal charters or government designations, while in others, the term is used informally. Towns typically feature centralized services, infrastructure, and governance, such as municipal authorities, and serve as hubs for commerce, education, and cultural activities within their regions. The concept of a town varies culturally and legally. For example, in the United Kingdom, a town may historically derive its status from a market town designation or City status in the United Kingdom, royal charter, while in the United States, the term is often loosely applied to incorporated municipality, municipalities. In some countries, such as Australia and Canada, distinction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yibna
Yibna (; ''Jabneh'' or ''Jabneel'' in Biblical times; ''Jamnia'' in Roman empire, Roman times; ''Lordship of Ibelin, Ibelin'' to the Crusades, Crusaders), or Tel Yavne, is an archaeological site and List of villages depopulated during the Arab–Israeli conflict, depopulated Palestinian town. The ruins are located southeast of the modern Israeli city of Yavne. The town had a population of 5,420 in 1948, located 15 kilometers southwest of Ramla.Khalidi, 1992, p.421 Most of the population fled after the fall of al-Qubayba, Hebron, al-Qubeiba and Zarnuqa in late May, but armed males were forced back. Israeli army took the town on June 5 and expelled the remaining population. It is a significant site for post-biblical Jewish history, as it was the location of the Council of Jamnia, considered the birthplace of modern Rabbinic Judaism. It is also significant in the history of the Crusades, as the location of the House of Ibelin. Name In many English translations of the Bible, it is k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Tina
Al-Tina, or Khirbet et-Tineh was a Palestinian Arab village in the Ramle Subdistrict of Mandatory Palestine. The village was located between the Shfela and southern Israeli coastal plain. It was depopulated during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War on July 8, 1948, by the Givati Brigade under Operation An-Far. It was located 20. km south of Ramla. The hill on which the village was built stands today next to the Kiryat Mal'akhi – Yoav railway station and next to Highway 6. Archeological excavations at the site revealed the remains of a Byzantine settlement. History Based on the archaeological excavation in the eastern foot of the hill on which the village used to stand, a settlement was established in the site as early as the Byzantine era. Pottery, glassware and coins allowed the researchers to date this settlement to a short period between roughly 375 to 425 CE. The excavation has revealed remains of what may be a storehouse, with many broken wine jars. The structure included ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
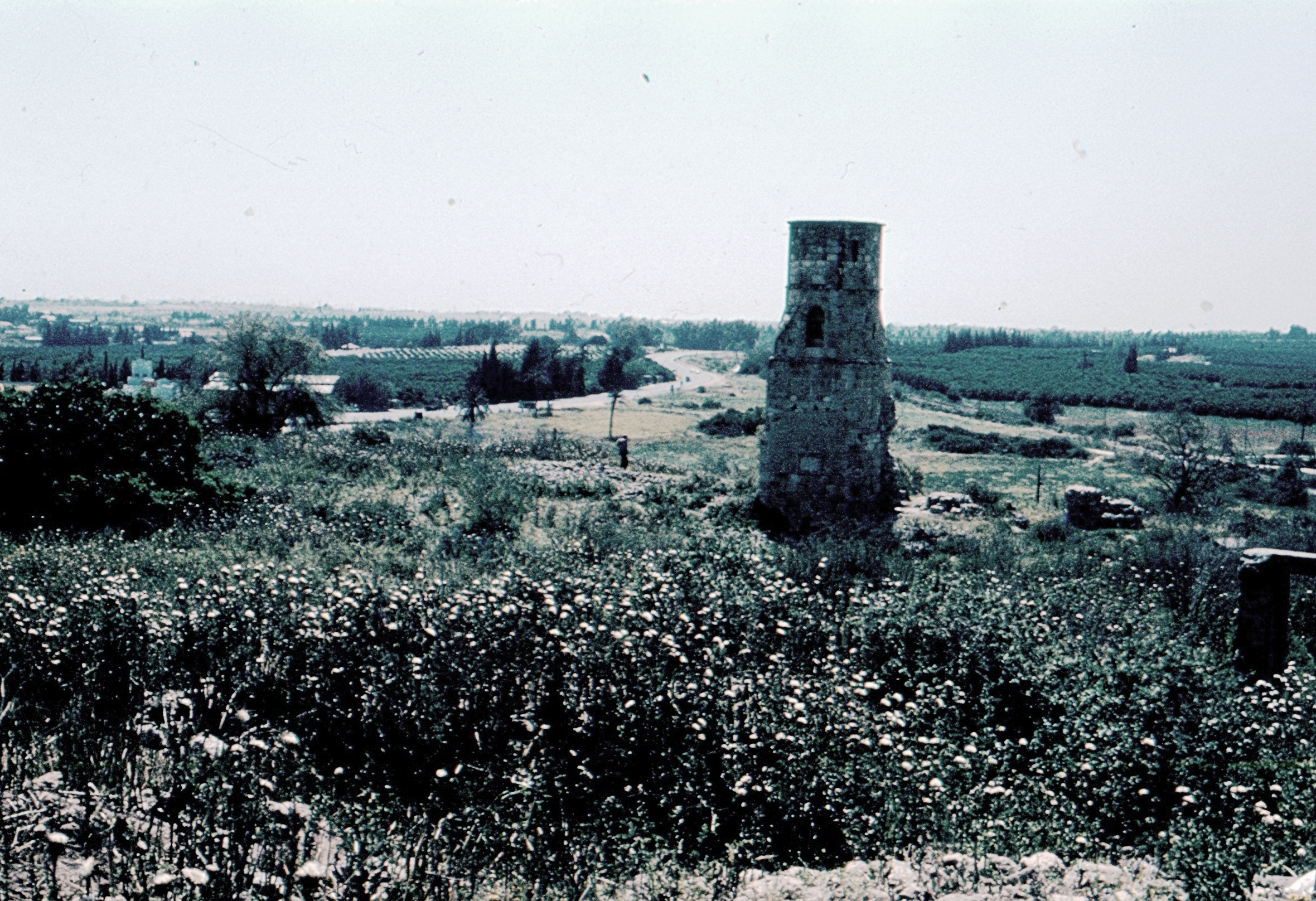
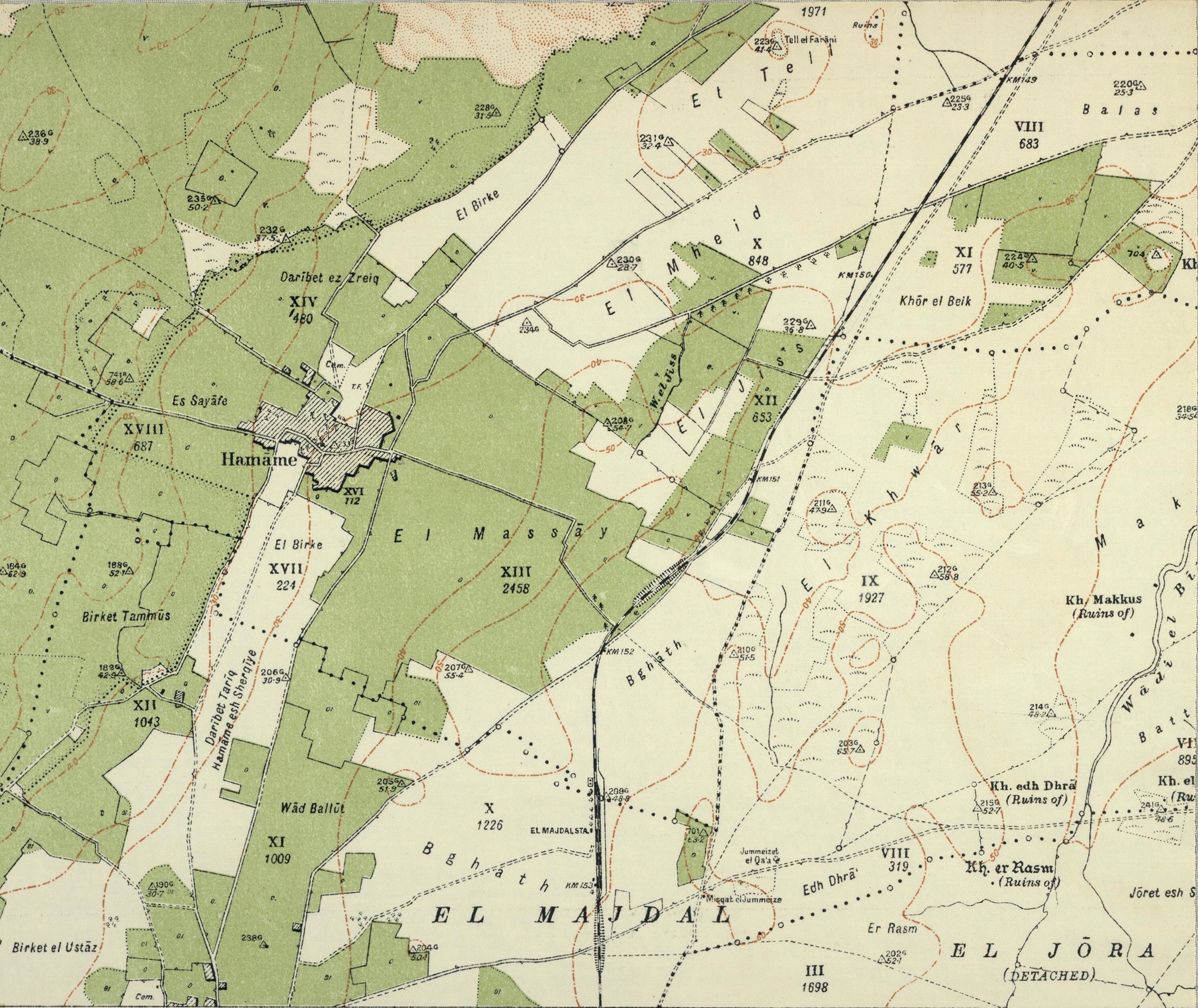
Hamama
Hamama (; also known in Byzantine times as ''Peleia'') was a Palestinian people, Palestinian town of over 5,000 inhabitants that was depopulated during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War. It was located 24 kilometers north of Gaza City, Gaza. It was continuously inhabited from the Mamluk Sultanate, Mamluk period (in the 13th century) until 1948. Its ruins are today in the north of the Israeli city of Ashkelon. Etymology Hamama's earliest recorded name is ''Peleia,'' dating to the Roman period. It translates as "dove", and when the Arabs conquered it through the Rashidun Caliphate in the seventh century, the town received its Arabic language, Arabic name ''Hamama'' meaning "dove", reflecting its Byzantine roots. Underlying Hamama's Late Ottoman Empire, Ottoman and Mandatory Palestine, British Mandate toponymy, is a limited stratum of pre-Ottoman village names. To this pre-existing stratum, residents added new place names referring in cases to Family, families living in or around the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
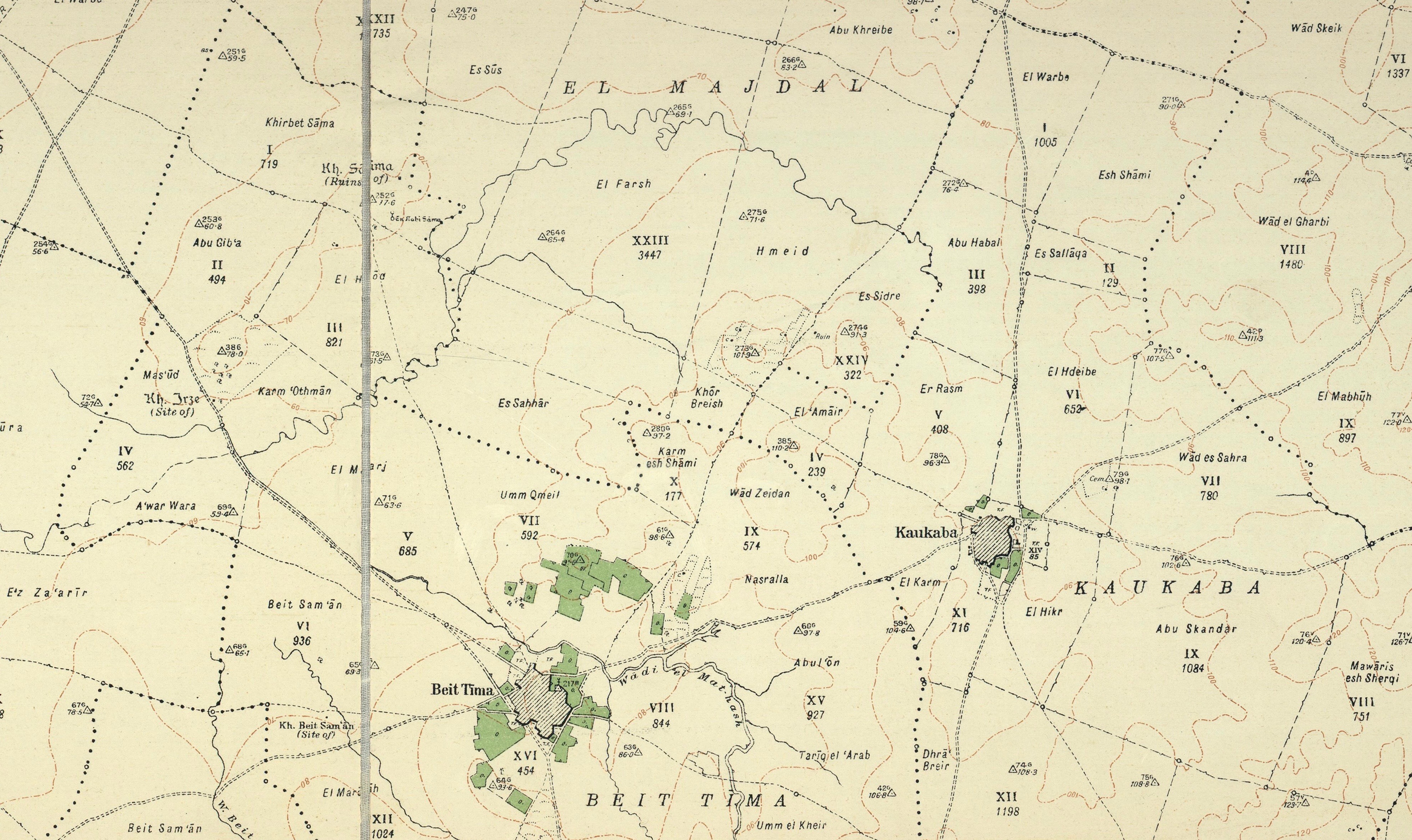
Bayt Tima
Bayt Tima () was a Palestinian Arab village in the Gaza Subdistrict, located northeast of Gaza and some from the coastline. It was situated in flat terrain on the southern coastal plain of Palestine. Bayt Tima was depopulated during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War. Its population in 1945 was 1,060.Khalidi, 1992, p.89. History During the Mandate period the village was inspected by the Department of Antiquities, and a number of ancient remains were noted, in addition to two Arabic inscriptions built into the mosque. In the cemetery located just south of Bayt Tima lies a worn mosaic pavement, suggesting an Ancient Roman or Byzantine presence at the site. A 14th-century Mamluk-era mosque existed on the site dedicated to a certain prophet or local saint named "Nabi Tima". In the courtyard of the mosque and near it are imitations of Corinthian capitals and columns of gray stone. The remainder of the building was built in local ''kurkar'' stone. There is no mention of Bayt Tima in ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Sawafir Al-Sharqiyya
Al-Sawafir al-Sharqiyya was a Palestinian people, Palestinian Arab village in the Gaza Subdistrict, Mandatory Palestine, Gaza Subdistrict. It was depopulated during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, 1948 War on May 18, 1948, as part of the second stage of Operation Barak. The village was located 32 km northeast of Gaza City, Gaza. It is one of three namesake villages, alongside Al-Sawafir al-Gharbiyya and Al-Sawafir al-Shamaliyya. History Remains from the late Roman Empire, Roman (third–fourth centuries CE), Byzantine Empire, Byzantine (fifth–beginning of seventh centuries CE), and Abbasid Caliphate, Abbasid eras have been found here. Columns and fragments were noted near the Water well, well. 12th century, 12 century Crusades, Crusader Catholic Church, church endowments and land deeds mention Latin settlement in Zeophir/al-Sawāfīr. However, it is not clear which village of three Sawafirs these records pertain to. Ottoman era Al-Sawafir al-Sharqiyya was like the rest of Pale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nahiyah
A nāḥiyah ( , plural ''nawāḥī'' ), also nahiyeh, nahiya or nahia, is a regional or local type of administrative division that usually consists of a number of villages or sometimes smaller towns. In Tajikistan, it is a second-level division while in Syria, Iraq, Lebanon, Jordan, Xinjiang, and the former administrative divisions of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Empire, where it was also called a ''bucak (administrative unit), bucak'', it is a third-level or lower division. It can constitute a division of a ''qadaa'', ''mintaqah'' or other such district-type division and is sometimes translated as "subdistrict". Ottoman Empire The nahiye () was an administrative territorial entity of the Ottoman Empire, smaller than a . The head was a (governor) who was appointed by the Pasha. The was a subdivision of a Selçuk Akşin Somel. "Kazâ". ''The A to Z of the Ottoman Empire''. Volume 152 of A to Z Guides. Rowman & Littlefield, 2010. p. 151. and corresponded roughly to a city w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daftar
A ''defter'' was a type of tax register and land cadastre in the Ottoman Empire. Etymology The term is derived from Greek , literally 'processed animal skin, leather, fur', meaning a book, having pages of goat parchment used along with papyrus as paper in Ancient Greece, borrowed into Arabic as '':'' , meaning a register or a notebook. Description The information collected could vary, but ''tahrir defterleri'' typically included details of villages, dwellings, household heads (adult males and widows), ethnicity/religion (because these could affect tax liabilities/exemptions), and land use. The defter-i hakâni was a land registry, also used for tax purposes. Each town had a defter and typically an officiator or someone in an administrative role to determine whether the information should be recorded. The officiator was usually some kind of learned man who had knowledge of state regulations. The defter was used to record family interactions such as marriage and inheritance. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiqh
''Fiqh'' (; ) is the term for Islamic jurisprudence.Fiqh Encyclopædia Britannica ''Fiqh'' is often described as the style of human understanding, research and practices of the sharia; that is, human understanding of the divine Islamic law as revealed in the Quran and the sunnah (the teachings and practices of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his companions). Fiqh expands and develops Shariah through interpretation (''ijtihad'') of the Quran and ''Sunnah'' by Islamic jurists (''ulama'') and is implemented by the rulings (''fatwa'') of jurists on questions presented to them. Thus, whereas ''sharia'' is considered immutable and infallible by Muslims, ''fiqh'' is considered fallible and changeable. ''Fiqh'' deals with the observance of rituals, morals and social legislation in Islam as well as econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shafi'i School
The Shafi'i school or Shafi'i Madhhab () or Shafi'i is one of the four major schools of fiqh (Islamic jurisprudence), belonging to the Ahl al-Hadith tradition within Sunni Islam. It was founded by the Muslim scholar, jurist, and traditionist al-Shafi'i (), "the father of Muslim jurisprudence", in the early 9th century. The other three schools of Sunnī jurisprudence are Ḥanafī, Mālikī and Ḥanbalī. Like the other schools of fiqh, Shafii recognize the First Four Caliphs as the Islamic prophet Muhammad's rightful successors and relies on the Qurʾān and the "sound" books of Ḥadīths as primary sources of law. The Shafi'i school affirms the authority of both divine law-giving (the Qurʾān and the Sunnah) and human speculation regarding the Law. Where passages of Qurʾān and/or the Ḥadīths are ambiguous, the school seeks guidance of Qiyās (analogical reasoning). The Ijmā' (consensus of scholars or of the community) was "accepted but not stressed". The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God in Abrahamic religions, God of Abraham (or ''Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the last Islamic prophet. Alongside the Quran, Muslims also believe in previous Islamic holy books, revelations, such as the Tawrat (Torah), the Zabur (Psalms), and the Injeel (Gospel). These earlier revelations are associated with Judaism and Christianity, which are regarded by Muslims as earlier versions of Islam. The majority of Muslims also follow the teachings and practices attributed to Muhammad (''sunnah'') as recorded in traditional accounts (hadith). With an estimated population of almost 2 billion followers, Muslims comprise around 26% of the world's total population. In descending order, the percentage of people who identify as Muslims on each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |