|
Samuel Wilbert Tucker
Samuel Wilbert Tucker (June 18, 1913 – October 19, 1990) was an American lawyer and a cooperating attorney with the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP). His civil rights career began as he organized a 1939 sit-in at the then-segregated Alexandria, Virginia public library. A partner in the Richmond, Virginia, firm of Hill, Tucker and Marsh (formerly Hill, Martin and Robinson), Tucker argued and won several civil rights cases before the Supreme Court of the United States, including '' Green v. County School Board of New Kent County'' which, according to ''The Encyclopedia of Civil Rights In America'', "did more to advance school integration than any other Supreme Court decision since ''Brown''." Early life and education Tucker was born in Alexandria, Virginia, on June 18, 1913. His father, Samuel A. Tucker, a real estate agent and NAACP member, and teacher mother saw to his formal and informal education. Tucker later said: "I got involved in the ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
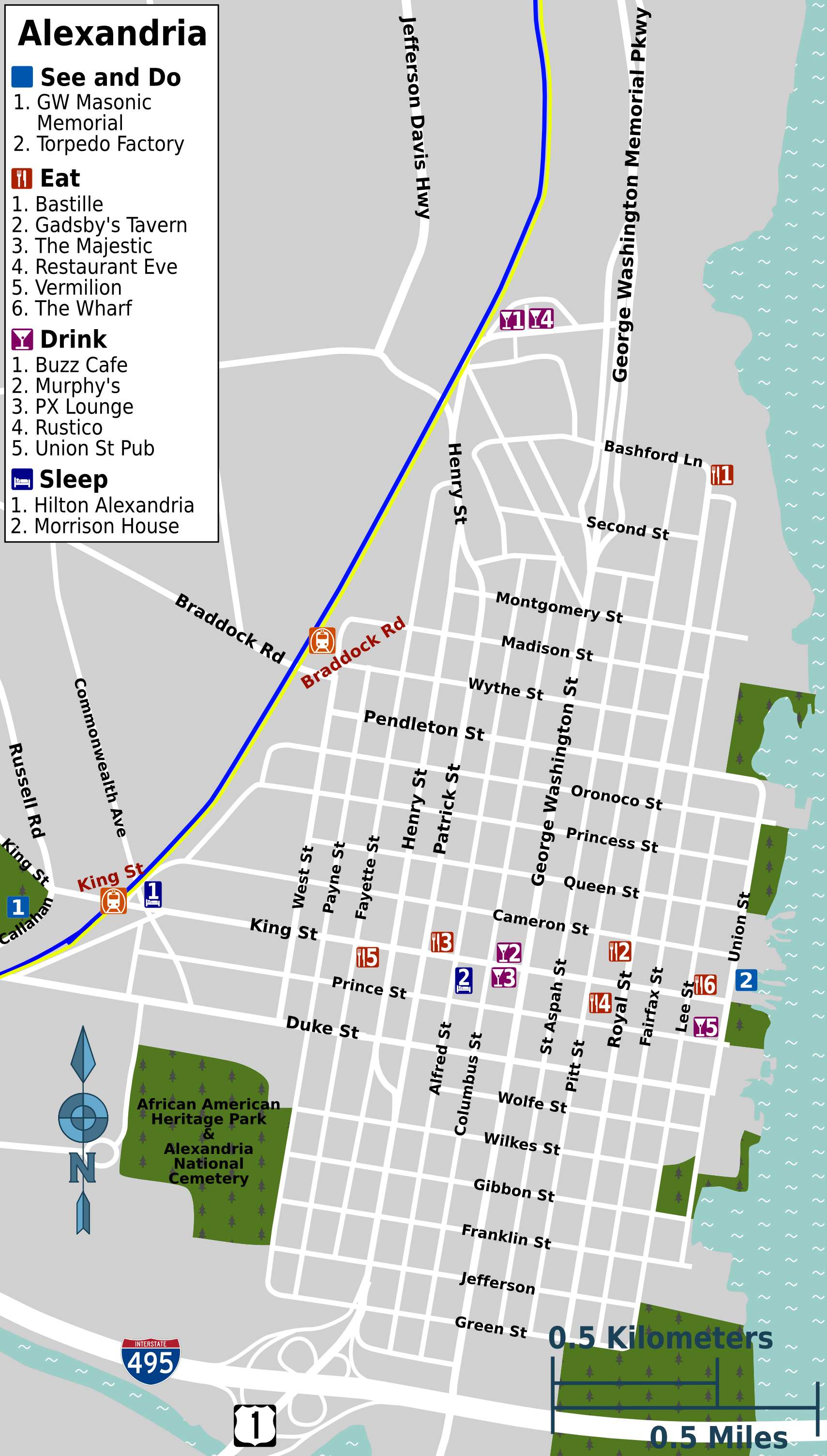
Alexandria, Virginia
Alexandria is an independent city (United States), independent city in Northern Virginia, United States. It lies on the western bank of the Potomac River approximately south of Washington, D.C., D.C. The city's population of 159,467 at the 2020 census made it the List of cities in Virginia, sixth-most populous city in Virginia and List of United States cities by population, 169th-most populous city in the U.S. Alexandria is a principal city of the Washington metropolitan area, which is part of the larger Washington–Baltimore combined statistical area. Like the rest of Northern Virginia and Central Maryland, present-day Alexandria has been influenced by its proximity to the U.S. capital. It is largely populated by professionals working in the United States federal civil service, federal civil service, in the United States Armed Forces, U.S. military, or for one of the many private companies which contract to Government contractor, provide services to the Federal government of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howard Thurman
Howard Washington Thurman (November 18, 1899 – April 10, 1981) was an American author, philosopher, theologian, Christian mystic, educator, and civil rights leader. As a prominent religious figure, he played a leading role in many social justice movements and organizations of the twentieth century. Thurman's theology of radical nonviolence influenced and shaped a generation of civil rights activists, and he was a key mentor to leaders within the civil rights movement, including Martin Luther King Jr. Thurman served as dean of Andrew Rankin Memorial Chapel, Frederick Douglass Memorial Hall, Founders Library, Rankin Chapel at Howard University from 1932 to 1944 and as dean of Marsh Chapel at Boston University from 1953 to 1965. In 1944, he co-founded, along with Alfred Fisk, the first major interracial, interdenominational church in the United States. Early life and education Howard Thurman was born in 1899 in Daytona Beach, Florida, Florida in Daytona Beach. He spent most of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandria Black History Museum
The Alexandria Black History Museum, located at 902 Wythe St., Alexandria, Virginia, is operated by the City of Alexandria. The building was formerly the Robert Robinson Library, originally constructed in 1940 as the first "separate but equal" library for African Americans in the segregated city. History In 1794, Alexandria Library opened as a private lending library, calling itself the Alexandria Library Company. In 1937, Dr. Robert South Barrett donated funds to build Alexandria's Public Library. The Library Company cooperated in this effort, contracting with the Alexandria City Council to turn over its collections to City of Alexandria as the City agreed to include the public library's operating expenses in its budget. Since the library's budget was collected from the taxes paid by every American Citizen regardless their race, the lawyer Samuel Wilbert Tucker organized in 1939 a pacific sit-in at the new and "whites only" Alexandria, Virginia public library (Kate Waller B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Separate But Equal
Separate but equal was a legal doctrine in United States constitutional law, according to which racial segregation did not necessarily violate the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, which nominally guaranteed "equal protection" under the law to all people. Under the doctrine, as long as the facilities provided to each race were equal, state and local governments could require that services, facilities, public accommodations, housing, medical care, education, employment, and transportation be segregated by race, which was already the case throughout the states of the former Confederacy. The phrase was derived from a Louisiana law of 1890, although the law actually used the phrase "equal but separate". The doctrine was confirmed in the '' Plessy v. Ferguson'' Supreme Court decision of 1896, which allowed state-sponsored segregation. Though segregation laws existed before that case, the decision emboldened segregation states during the Jim Crow era, which had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afro-American (newspaper)
The ''Baltimore Afro-American'', commonly known as ''The Afro'' or ''Afro News'', is a weekly African-American newspaper published in Baltimore, Maryland. It is the flagship newspaper of the ''AFRO-American'' chain and the longest-running African-American family-owned newspaper in the United States, established in 1892. History Initially the ''Afro-American'' was known as the ''Home Protector'' which was established and edited by Reverend William Alexander in 1889. With the help of a group of investors, including John R. Cole, Charles H. Richardson, James E. Johnson, and William H. Daly, the ''Home Protector'' became the ''Afro-American'' on August 13, 1892. In the spring of 1895, the Northwestern Family Supply Company (NFSC), assumed control of the ''Afro-American''. Although this seemed to be a turn for the best, that prominent business firm went bankrupt leading to near end of the newspaper. In 1897, the machinery used to print the ''Afro-American'' went up for sale. J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-examination
In law, cross-examination is the interrogation of a witness by one's opponent. It is preceded by direct examination (known as examination-in-chief in Law of the Republic of Ireland, Ireland, the Law of the United Kingdom, United Kingdom, Australian legal system, Australia, Law of Canada, Canada, Law of South Africa, South Africa, Law of India, India and Law of Pakistan, Pakistan) and may be followed by a Redirect examination, redirect (known as re-examination in the aforementioned countries). A redirect examination, performed by the attorney or pro se individual who performed the direct examination, clarifies the witness' testimony provided during cross-examination including any subject matter raised during cross-examination but not discussed during direct examination. Recross examination addresses the witness' testimony discussed in redirect by the opponent. Depending on the judge's discretion, opponents are allowed multiple opportunities to redirect and recross examine witnesse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African-American Newspapers
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa. African Americans constitute the second largest ethno-racial group in the U.S. after White Americans. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of Africans enslaved in the United States. In 2023, an estimated 48.3 million people self-identified as Black, making up 14.4% of the country’s population. This marks a 33% increase since 2000, when there were 36.2 million Black people living in the U.S. African-American history began in the 16th century, with Africans being sold to European slave traders and transported across the Atlantic to the Western Hemisphere. They were sold as slaves to European colonists and put to work on plantations, particularly in the southern colonies. A few were able to achieve freedom through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago Defender
''The Chicago Defender'' is a Chicago-based online African-American newspaper. It was founded in 1905 by Robert S. Abbott and was once considered the "most important" newspaper of its kind. Abbott's newspaper reported and campaigned against Jim Crow-era violence and urged black people in the American South to settle in the north in what became the Great Migration. Abbott worked out an informal distribution system with Pullman porters who surreptitiously (and sometimes against southern state laws and mores) took his paper by rail far beyond Chicago, especially to African American readers in the southern United States. Under his nephew and chosen successor, John H. Sengstacke, the paper dealt with racial segregation in the United States, especially in the U.S. military, during World War II. Copies of the paper were passed along in communities, and it is estimated that at its most successful, each copy was read by four to five people. In 1919–1922, the ''Defender'' attracted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington Post
''The Washington Post'', locally known as ''The'' ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'' or ''WP'', is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C., the national capital. It is the most widely circulated newspaper in the Washington metropolitan area and has a national audience. As of 2023, the ''Post'' had 130,000 print subscribers and 2.5 million digital subscribers, both of which were the List of newspapers in the United States, third-largest among U.S. newspapers after ''The New York Times'' and ''The Wall Street Journal''. The ''Post'' was founded in 1877. In its early years, it went through several owners and struggled both financially and editorially. In 1933, financier Eugene Meyer (financier), Eugene Meyer purchased it out of bankruptcy and revived its health and reputation; this work was continued by his successors Katharine Graham, Katharine and Phil Graham, Meyer's daughter and son-in-law, respectively, who bought out several rival publications. The ''Post ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armistead Boothe
Armistead Lloyd Boothe (September 23, 1907 – February 14, 1990) was a Virginia Democratic legislator representing Alexandria, Virginia: first as a delegate in the Virginia General Assembly and later as a State Senator from the newly created 36th District. A lifelong Democrat, Boothe helped lead his party's progressive faction, particularly as they opposed the Byrd Organization's policy of Massive Resistance to racial integration in Virginia's public schools. Early life and education Boothe was born in Alexandria, Virginia, on September 23, 1907, to Gardner Lloyd and Eleanor Harrison Carr Boothe. He attended Episcopal High School and graduated from the University of Virginia, receiving his A.B. in 1928. He was chosen as a Rhodes scholar in 1929 and received a B.A. in Jurisprudence from Oxford University in 1931. In 1934 Boothe married Elizabeth Ravenel Peelle of Washington, D.C., and they ultimately had three daughters, Julie Perry, Eleanor Smith and Elizabeth Davis. Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kate Waller Barrett
Kate Waller Barrett (January 24, 1857 – February 23, 1925), née Katherine Harwood Waller, was a prominent Virginia physician, humanitarian, philanthropist, sociologist and social reformer, best known for her leadership of the National Florence Crittenton Mission, which she founded in 1895 with Charles Nelson Crittenton. Her causes included helping the "outcast woman, the mistreated prisoner, those lacking in educational and social opportunity, the voteless woman, and the disabled war veteran." Although comparatively little known today, she was " e of the most prominent women of her time". Biography Barrett was born Katherine Harwood Waller at her family's historic estate, Clifton, in Widewater, Virginia, to Ann Eliza Stribbling Waller and Withers Waller on January 24, 1857. Her family owned slaves on several large plantations, and Barrett's two young black playmates named Jane and Lucy were "given" to young Kate as a birthday gift on her sixth birthday by her grandmother. La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandria Library Sit-In 1939
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile Delta, Nile River delta. Founded in 331 BC by Alexander the Great, Alexandria grew rapidly and became a major centre of Hellenic civilisation, eventually replacing Memphis, Egypt, Memphis, in present-day Greater Cairo, as Egypt's capital. Called the "Bride of the Mediterranean" and "Pearl of the Mediterranean Coast" internationally, Alexandria is a popular tourist destination and an important industrial centre due to its natural gas and petroleum, oil pipeline transport, pipelines from Suez. The city extends about along the northern coast of Egypt and is the largest city on the Mediterranean, the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second-largest in Egypt (after Cairo), the List of largest cities in the Arab world, fourth- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |