|
Samuel Gibbs (British Army Officer)
Sir Samuel Gibbs (1770–1815) was an English officer in the British Army during the Napoleonic Wars and the War of 1812, rising to the rank of major-general.Rapson 1890, p. 269. Gibbs was second-in-command under Edward Pakenham at the Battle of New Orleans and died of wounds received while leading one of the main columns in the failed British assault. Life Samuel Gibbs was born on 21 February 1770, the son of Colonel Samuel Gibbs of Horsley Park, Surrey, by his wife Arabella, daughter of Sir William Rowley, admiral of the fleet, and widow of William Martin (), naval officer.Rapson & Harfield 2008. His half-brother was Sir George Martin, admiral of the fleet. Gibbs was appointed an ensign in the 102nd Foot in October 1783. He removed in 1788 to the 60th, with which he served in Upper Canada, until he was promoted in 1792 to a lieutenancy in the 11th. He joined this regiment at Gibraltar, and returned with it to England in February 1793, when he was appointed aide-de-camp to L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Westmacott
Sir Richard Westmacott (15 July 17751 September 1856) was a British sculptor. Life and career Westmacott studied with his father, also named Richard Westmacott, at his studio in Mount Street, off Grosvenor Square in London before going to Rome in 1793 to study under Antonio Canova. Westmacott devoted all his energies to the study of classical sculpture, and throughout his life his real sympathies were with pagan rather than with Christian art. Within a year of his arrival in Rome he won the first prize for sculpture offered by the Florentine Academy of Arts, and in the following year he gained the papal gold medal awarded by the Academy of St Luke with his bas-relief of Joseph and his brothers. On returning to England in 1797, he set up a studio, where John Edward Carew and Musgrave Watson gained experience. Westmacott had his own foundry at Pimlico, in London, where he cast both his own works, and those of other sculptors, including John Flaxman's statue of Sir John ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
102nd Foot
The 102nd Regiment of Foot (Royal Madras Fusiliers) was a regiment of the British Army raised by the Honourable East India Company in 1742. It transferred to the command of the British Army in 1862. Under the Childers Reforms it amalgamated with the 103rd Regiment of Foot in 1881 to form the Royal Dublin Fusiliers. History Formation The regiment was raised by the Honourable East India Company as the Madras Europeans from independent companies in 1742 – "European" indicating it was composed of British soldiers, not Indian sepoys. It saw action at the siege of Arcot in autumn 1751 during the Second Carnatic War and went on to fight at the Battle of Plassey in June 1757, the Battle of Condore in December 1758 and the Battle of Wandiwash in January 1760 during the Seven Years' War. It also fought at the siege of Pondicherry in September 1760 during the Third Carnatic War. It became the 1st Madras Europeans, on formation of the 2nd and 3rd Madras Europeans, in 1766. It went o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
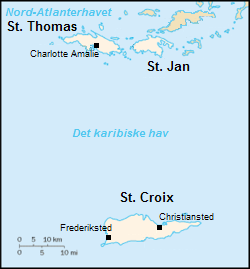
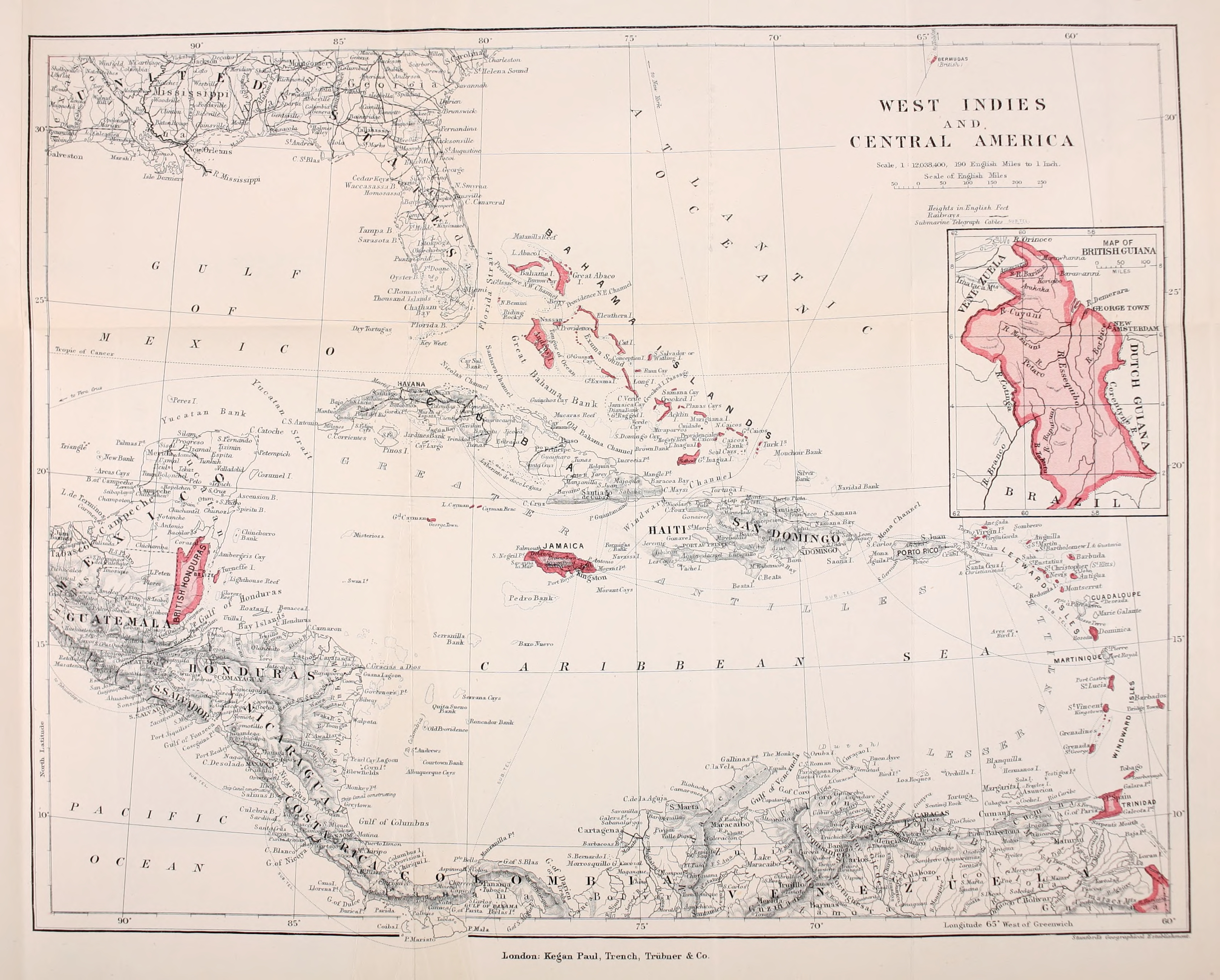
Danish West Indies
The Danish West Indies () or Danish Virgin Islands () or Danish Antilles were a Danish colony in the Caribbean, consisting of the islands of Saint Thomas with , Saint John () with , Saint Croix with , and Water Island. The islands of St Thomas, St John, and St Croix were purchased by United States in 1917 and became known as the United States Virgin Islands. Water Island was sold in 1905 to the Danish East Asiatic Company and bought by the U.S. Government in 1944. In 1996, it also became part of the U.S. Virgin Islands. Historical overview Acquisition The Danish West India-Guinea Company annexed uninhabited St. Thomas in 1672. It annexed St. John in 1718 and bought St. Croix from France (King Louis XV) on 28 June 1733. When the Danish West India-Guinea Company went bankrupt in 1754, King Frederik V of Denmark–Norway assumed direct control of the three islands. Although, during the Napoleonic Wars, Britain twice occupied the Danish West Indies, first in 1801� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Martin (island)
Saint Martin is an island in Leeward Islands of the Lesser Antilles in the northeastern Caribbean, approximately east of Puerto Rico. The island is divided roughly 60:40 between the France, French Republic () and the Kingdom of the Netherlands (), but the Dutch part is more populated than the French. Divided since 1648, the northern French part comprises the Collectivity of Saint Martin and is an overseas collectivity of the French Republic. The southern Dutch part comprises Sint Maarten and is one of Kingdom of the Netherlands#Constituent countries, four constituent countries that form the Kingdom of the Netherlands. Even though the island is an overseas possession of two European Union member states, only the French part of the island is part of the EU. On 1 January 2019, the population of the whole island was 73,777 inhabitants, with 41,177 living on the Dutch side and 32,489 on the French side. Note that the figure for the French side is based on censuses that took place af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British West Indies
The British West Indies (BWI) were the territories in the West Indies under British Empire, British rule, including Anguilla, the Cayman Islands, the Turks and Caicos Islands, Montserrat, the British Virgin Islands, Bermuda, Antigua and Barbuda, the Bahamas, Barbados, Dominica, Grenada, Jamaica, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, British Honduras, British Guiana and Trinidad and Tobago. The Kingdom of England first English overseas possessions, established colonies in the region during the 17th century. Financed by valuable extractive commodities such as sugar production, the colonies were also at the centre of the Atlantic slave trade, with around 2.3 million slaves being brought to the British West Indies. The colonies also served as bases to project the power of the British Empire through the Royal Navy and Britain's Merchant Marine, and to expand and protect British overseas trade. Before the decolonization of the Americas in the later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostend
Ostend ( ; ; ; ) is a coastal city and municipality in the province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It comprises the boroughs of Mariakerke, Raversijde, Stene and Zandvoorde, and the city of Ostend proper – the largest on the Belgian coast. History Middle Ages In the Early Middle Ages, Ostend was a small village built on the east-end () of an island (originally called Testerep) between the North Sea and a beach lake. Although small, the village rose to the status of "town" around 1265, when the inhabitants were allowed to hold a market and to build a market hall. The major source of income for the inhabitants was fishing. The North Sea coastline has always been rather unstable due to the power of the water. In 1395 the inhabitants decided to build a new Ostend behind large dikes and further away from the always-threatening sea. 15th–18th centuries The strategic position on the North Sea coast had major advantages for Ostend as a harbour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
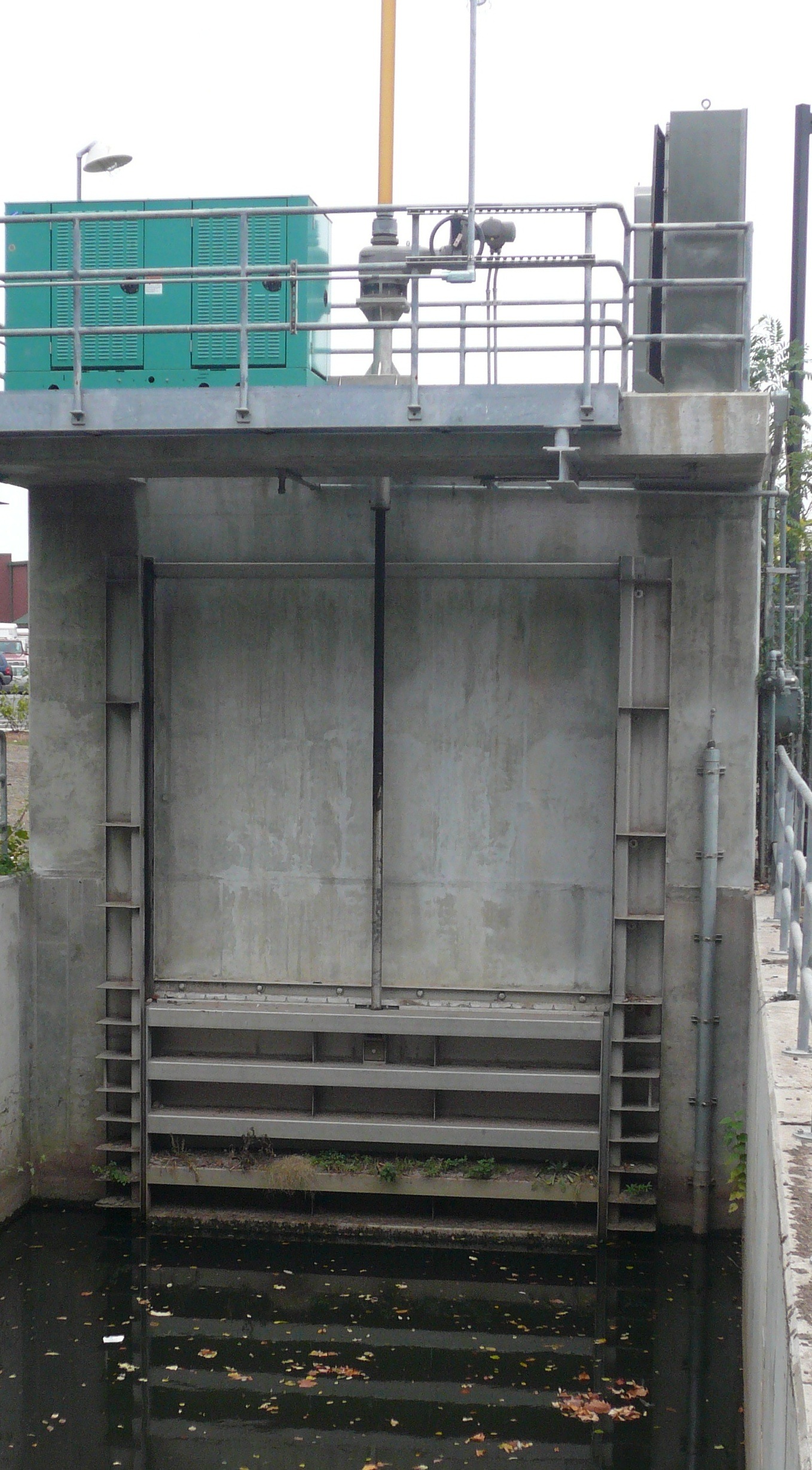
Sluice
A sluice ( ) is a water channel containing a sluice gate, a type of lock to manage the water flow and water level. There are various types of sluice gates, including flap sluice gates and fan gates. Different depths are calculated when design sluice gates. Sluices are used for channeling water toward a water mill, including for transporting logs from steep hillsides. Different terms are used regionally for sluices; the terms ''sluice'', ''sluice gate'', ''knife gate'', and ''slide gate'' are used interchangeably in the water and wastewater control industry. Etymology The term "sluice" originates from the Middle English word scluse, which derived from the Old French escluse (modern French: écluse). This, in turn, came from the Late Latin exclusa, a shortening of aqua exclusa, meaning "excluded water" or "a shut-off water channel." The Latin exclusa is the feminine past participle of excludere ("to shut out, exclude"), from *ex-* ("out") and claudere ("to close"). Regional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
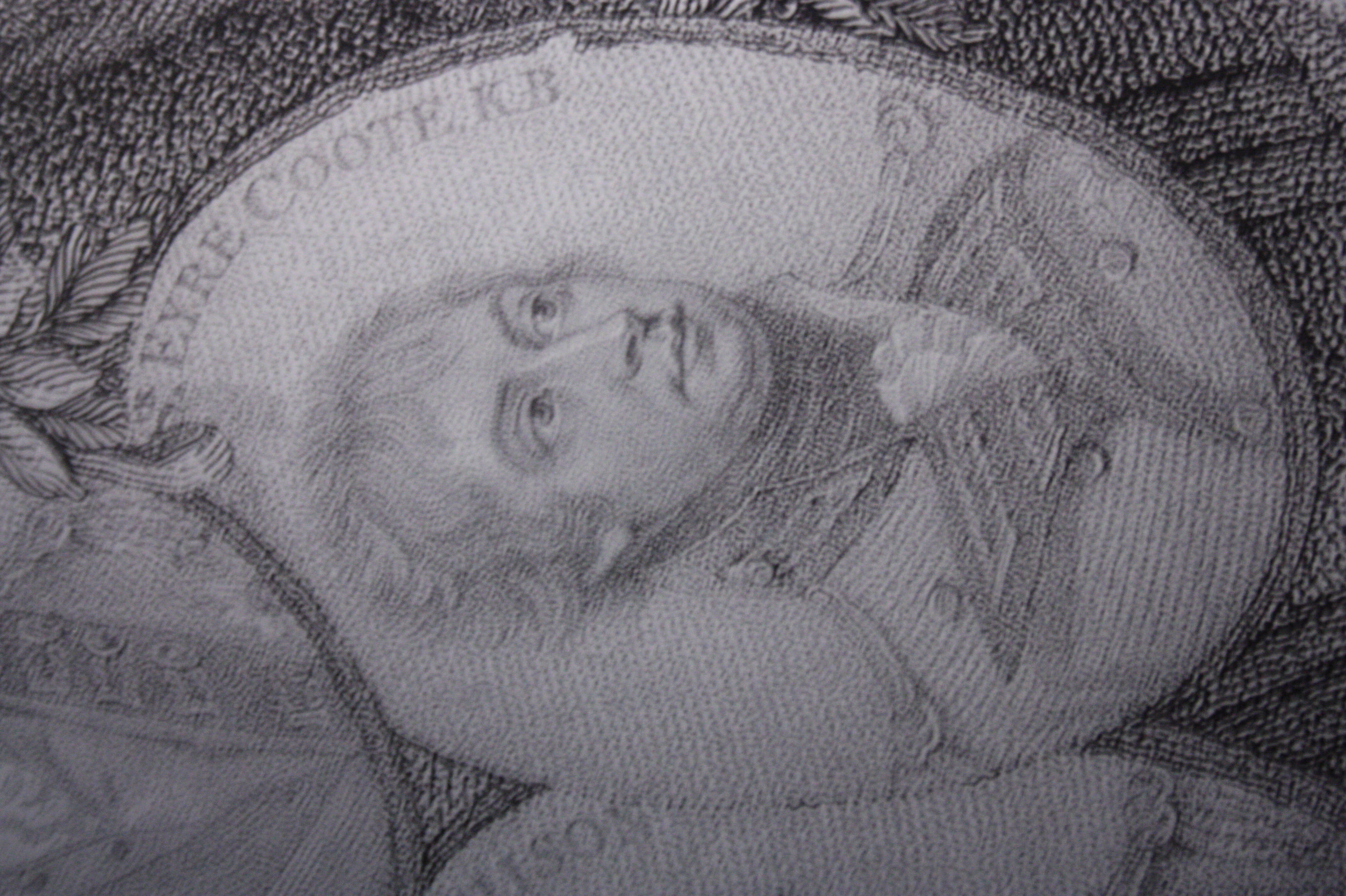
Eyre Coote (British Army Officer, Born 1762)
General (United Kingdom), General Eyre Coote (20 May 1762 – 10 December 1823) was a British Army officer, politician and colonial administrator who served as the governor of Jamaica from 1806 to 1808. He attained the rank of general in the British army and was created a Knight Grand Cross of the Order of the Bath before being stripped of his rank and honours in 1816 after Conduct unbecoming, conduct unbecoming an officer and a gentleman. Background He was the second son of the Very Rev. Charles Coote (1713 – 12 February 1776), DD, Dean of Kilfenora and wife (m. 31 July 1753) Grace Tilson (- 1 January 1767), brother of Charles Henry Coote, 2nd Baron Castle Coote, Charles Henry Coote (1754–1823), who succeeded the last Earl of Mountrath as 2nd Baron Castle Coote in 1802, and nephew of Eyre Coote (East India Company officer), Sir Eyre Coote, KB, the celebrated Indian General, to whose vast estates in England and Ireland he eventually succeeded. Career Following studies at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Company (military Unit)
A company is a Military organization#Commands, formations, and units, military unit, typically consisting of 100–250 soldiers and usually commanded by a Major (rank), major or a Captain (armed forces), captain. Most companies are made up of three to seven platoons, although the exact number may vary by country, unit type, and structure. Usually several companies are grouped as a battalion or regiment, the latter of which is sometimes formed by several battalions. Occasionally, ''independent'' or ''separate'' companies are organized for special purposes, such as the Air Naval Gunfire Liaison Company, 1st Air Naval Gunfire Liaison Company or the 3rd Force Reconnaissance Company. These companies are not organic to a battalion or regiment, but rather report directly to a higher level organization such as a Marine Expeditionary Force headquarters (i.e., a corps-level command). Historical background The modern military company became popularized during the reorganization of the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Hood, 1st Viscount Hood
Admiral (Royal Navy), Admiral Samuel Hood, 1st Viscount Hood (12 December 1724 – 27 January 1816) was a Royal Navy officer and politician. As a junior officer he saw action during the War of the Austrian Succession. While in temporary command of , Hood drove a French ship ashore in Audierne, Audierne Bay, and captured two privateers in 1757 during the Seven Years' War. He held senior command as North America and West Indies Station, Commander-in-Chief, North American Station and then as Leeward Islands Station, Commander-in-Chief, Leeward Islands Station. During the American Revolutionary War, Hood led the British fleet to victory at the Battle of the Mona Passage in April 1782. He went on to be Commander-in-Chief, Portsmouth, then First Sea Lord, First Naval Lord and, after briefly returning to the Portsmouth command, became Mediterranean Fleet, Commander-in-Chief, Mediterranean Fleet during the French Revolutionary Wars. His younger brother was Admiral Alexander Hood, 1st Vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Grant (British Army Officer, Born 1720)
James Grant, 4th of Ballindalloch (1720–1806) was a British Army officer who served as a major general during the American War of Independence. He served as Governor of East Florida from 1763 to 1771, and between 1773 and 1802 he had seats in the House of Commons. Early career Grant was born on the family estate of Ballindalloch in Banffshire in the Northeast of Scotland. He began his military career by purchasing a commission as captain in the Royal Scots on 24 October 1744. The regiment was shipped to the Continent and Grant fought with them in the Battle of Fontenoy during the War of the Austrian Succession. French and Indian War By 1757, Grant was a major of the 77th Regiment of Foot (Montgomerie's Highlanders), fighting in the French and Indian War in the British Thirteen Colonies. In 1758, he led part of the regiment in an expedition led by General John Forbes. On this expedition, he became acquainted with others who would also play larger parts in the American Revolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gibraltar
Gibraltar ( , ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory and British overseas cities, city located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula, on the Bay of Gibraltar, near the exit of the Mediterranean Sea into the Atlantic Ocean (Strait of Gibraltar). It has an area of and is Gibraltar–Spain border, bordered to the north by Spain (Campo de Gibraltar). The landscape is dominated by the Rock of Gibraltar, at the foot of which is a densely populated town area. Gibraltar is home to some 34,003 people, primarily Gibraltarians. Gibraltar was founded as a permanent watchtower by the Almohad Caliphate, Almohads in 1160. It switched control between the Nasrids, Crown of Castile, Castilians and Marinids in the Late Middle Ages, acquiring larger strategic clout upon the destruction of nearby Algeciras . It became again part of the Crown of Castile in 1462. In 1704, Anglo-Dutch forces Capture of Gibraltar, captured Gibraltar from Spain during the War of the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |