|
Salix OS
Salix OS is a multi-purpose Linux distribution based on Slackware. Goals Salix OS retains full backwards compatibility with Slackware. This enables Slackware users to benefit from Salix repositories, which they can use as an "extra" source of software for their distribution. However, while in the KISS principle that Slackware adheres to, "Simple" refers to the system design, Salix OS applies it to daily use as well. It aims to be simple, fast and easy to use. To paraphrase the words of a journalist: the target audience for Salix OS might well be described as "lazy Slackers", users familiar with Linux in general and Slackware in particular who do not mind having additional tools to reduce their workload, while maintaining the maximum compatibility with Slackware possible. Salix OS adds automated dependency resolution, enhanced internationalization and localization, a larger repository of applications, and a well equipped suite of native administration and configuration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses the name "GNU/Linux" to emphasize the importance of GNU software, causing some controversy. Popular Linux distributions include Debian, Fedora Linux, and Ubuntu, the latter of which itself consists of many different distributions and modifications, including Lubuntu and Xubuntu. Commercial distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux and SUSE Linux Enterprise. Desktop Linux distributions include a windowing system such as X11 or Wayland, and a desktop environment such as GNOME or KDE Plasma. Distributions intended for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
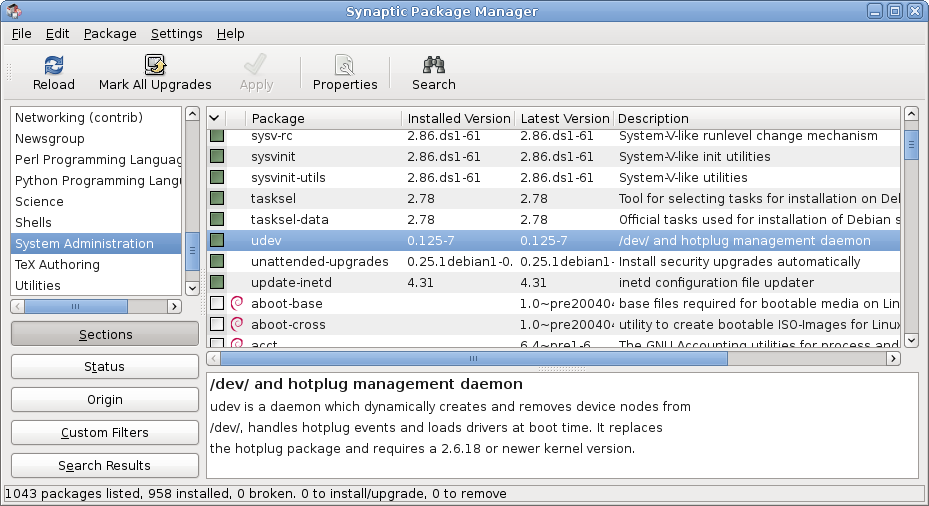
Package Management
A package manager or package-management system is a collection of software tools that automates the process of installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing computer programs for a computer in a consistent manner. A package manager deals with ''packages'', distributions of software and data in archive files. Packages contain metadata, such as the software's name, description of its purpose, version number, vendor, checksum (preferably a cryptographic hash function), and a list of dependencies necessary for the software to run properly. Upon installation, metadata is stored in a local package database. Package managers typically maintain a database of software dependencies and version information to prevent software mismatches and missing prerequisites. They work closely with software repositories, binary repository managers, and app stores. Package managers are designed to eliminate the need for manual installs and updates. This can be particularly useful for large ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SourceForge
SourceForge is a web service that offers software consumers a centralized online location to control and manage open-source software projects and research business software. It provides source code repository hosting, bug tracking, mirroring of downloads for load balancing, a wiki for documentation, developer and user mailing lists, user-support forums, user-written reviews and ratings, a news bulletin, micro-blog for publishing project updates, and other features. SourceForge was one of the first to offer this service free of charge to open-source projects. Since 2012, the website has run on Apache Allura software. SourceForge offers free hosting and free access to tools for developers of free and open-source software. , the SourceForge repository claimed to host more than 502,000 projects and had more than 3.7 million registered users. Concept SourceForge is a web-based source code repository. It acts as a centralized location for free and open-source softwar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zenwalk
Zenwalk GNU/Linux is a desktop-focused Linux distribution founded by Jean-Philippe Guillemin. It is based on Slackware with very few modifications at system level making it 100% compatible with Slackware. Zenwalk aims to be a modern and multi-purpose Linux distribution by focusing on internet applications, multimedia and programming tools. Zenwalk comes with many specialized tools, designed for beginner through advanced users, as it offers system configuration via both graphical and command-line operations. History Zenwalk was originally called Minislack up to version 1.1 It was renamed starting with version 1.2 which was released on 12 August 2005. Originally using KDE as its desktop environment, Zenwalk moved to Xfce starting with version 0.3, although GNOME and KDE packages have always been available separately. Aims The Zenwalk Project aims to create a lightweight Linux distribution (through using only one application per task on the release ISO image), optimization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disk Partitioning
Disk partitioning or disk slicing is the creation of one or more regions on secondary storage, so that each region can be managed separately. These regions are called partitions. It is typically the first step of preparing a newly installed disk, before any file system is created. The disk stores the information about the partitions' locations and sizes in an area known as the partition table that the operating system reads before any other part of the disk. Each partition then appears to the operating system as a distinct "logical" disk that uses part of the actual disk. System administrators use a program called a partition editor to create, resize, delete, and manipulate the partitions. Partitioning allows the use of different filesystems to be installed for different kinds of files. Separating user data from system data can prevent the system partition from becoming full and rendering the system unusable. Partitioning can also make backing up easier. A disadvantage is that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bootloader
A bootloader, also spelled as boot loader or called boot manager and bootstrap loader, is a computer program that is responsible for booting a computer. When a computer is turned off, its softwareincluding operating systems, application code, and dataremains stored on non-volatile memory. When the computer is powered on, it typically does not have an operating system or its loader in random-access memory (RAM). The computer first executes a relatively small program stored in read-only memory (ROM, and later EEPROM, NOR flash) along with some needed data, to initialize RAM (especially on x86 systems), to access the nonvolatile device (usually block device, eg NAND flash) or devices from which the operating system programs and data can be loaded into RAM. Some earlier computer systems, upon receiving a boot signal from a human operator or a peripheral device, may load a very small number of fixed instructions into memory at a specific location, initialize at least one CPU, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LILO (boot Loader)
LILO (Linux Loader) is a boot loader for Linux and was the default boot loader for most Linux distributions in the years after the popularity of loadlin. Today, many distributions use GRUB as the default boot loader, but LILO and its variant ELILO are still in wide use. Further development of LILO was discontinued in December 2015 along with a request by Joachim Wiedorn for potential developers. ELILO For EFI-based PC hardware the now orphaned ELILO boot loader was developed, originally by Hewlett-Packard for IA-64 systems made, but later also for standard i386 and amd64 hardware with EFI support. On any version of Linux running on Intel-based Apple Macintosh The Mac (known as Macintosh until 1999) is a family of personal computers designed and marketed by Apple Inc. Macs are known for their ease of use and minimalist designs, and are popular among students, creative professionals, and software ... hardware, ELILO is one of the available bootloaders. It support ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livecd
A live CD (also live DVD, live disc, or live operating system) is a complete bootable computer installation including operating system which runs directly from a CD-ROM or similar storage device into a computer's memory, rather than loading from a hard disk drive. A live CD allows users to run an operating system for any purpose without installing it or making any changes to the computer's configuration. Live CDs can run on a computer without secondary storage, such as a hard disk drive, or with a corrupted hard disk drive or file system, allowing data recovery. As CD and DVD drives have been steadily phased-out, live CDs have become less popular, being replaced by live USBs, which are equivalent systems written onto USB flash drives, which have the added benefit of having writeable storage. The functionality of a live CD is also available with an external hard disk drive connected by USB. Many live CDs offer the option of persistence by writing files to a hard drive or USB ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X86-64
x86-64 (also known as x64, x86_64, AMD64, and Intel 64) is a 64-bit version of the x86 instruction set, first released in 1999. It introduced two new modes of operation, 64-bit mode and compatibility mode, along with a new 4-level paging mode. With 64-bit mode and the new paging mode, it supports vastly larger amounts of virtual memory and physical memory than was possible on its 32-bit predecessors, allowing programs to store larger amounts of data in memory. x86-64 also expands general-purpose registers to 64-bit, and expands the number of them from 8 (some of which had limited or fixed functionality, e.g. for stack management) to 16 (fully general), and provides numerous other enhancements. Floating-point arithmetic is supported via mandatory SSE2-like instructions, and x87/ MMX style registers are generally not used (but still available even in 64-bit mode); instead, a set of 16 vector registers, 128 bits each, is used. (Each register can store one or two double- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runlevel
A runlevel is a mode of operation in the computer operating systems that implements Unix System V-style initialization. Conventionally, seven runlevels exist, numbered from zero to six. ''S'' is sometimes used as a synonym for one of the levels. Only one runlevel is executed on startup; run levels are not executed one after another (i.e. only runlevel 2, 3, or 4 is executed, not more of them sequentially or in any other order). A runlevel defines the state of the machine after boot. Different runlevels are typically assigned (not necessarily in any particular order) to the single-user mode, multi-user mode without network services started, multi-user mode with network services started, system shutdown, and system reboot system states. The exact setup of these configurations varies between operating systems and Linux distributions. For example, runlevel 4 might be a multi-user GUI no-server configuration on one distribution, and nothing on another. Runlevels commonly follow the gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

.png)

