|
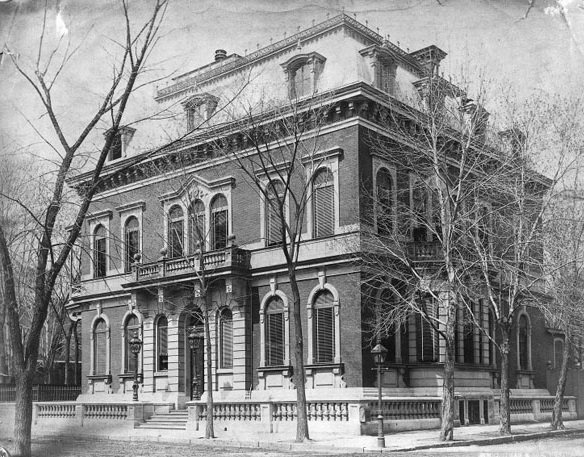
Saint James's Club Of Montreal
The Saint James's Club of Montreal (French: ''Club Saint-James de Montréal'') is a private social club in Montreal, Quebec. The club was founded in 1857 as a gentlemen's club, but since 1979 has been mixed-sex. As with many upper-class Montreal institutions, the Saint James's Club underwent a significant upheaval during the Quiet Revolution of the 1960s and 1970s, when much of the city's Anglo-Scottish establishment relocated to Toronto. In recent decades the club has reinvented itself as a predominantly Francophone institution. History In 1864 the club opened its original clubhouse, designed by John William Hopkins and Frederick Lawford, at the northwest corner of Dorchester Boulevard and University Avenue. The clubhouse was demolished in 1961 to make way for the construction of Place Ville Marie. In 1960 the club partnered with the Yale Building Corporation to construct a combination club and office building, designed by Durnford Bolton Chadwick and Ellwood, at 620 Dorche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple-peaked hill around which the early city of Ville-Marie is built. The city is centred on the Island of Montreal, which obtained its name from the same origin as the city, and a few much smaller peripheral islands, the largest of which is Île Bizard. The city is east of the national capital Ottawa, and southwest of the provincial capital, Quebec City. As of 2021, the city had a population of 1,762,949, and a metropolitan population of 4,291,732, making it the second-largest city, and second-largest metropolitan area in Canada. French is the city's official language. In 2021, it was spoken at home by 59.1% of the population and 69.2% in the Montreal Census Metropolitan Area. Overall, 85.7% of the population of the city of Montreal co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quiet Revolution
The Quiet Revolution (french: Révolution tranquille) was a period of intense socio-political and socio-cultural change in French Canada which started in Quebec after the election of 1960, characterized by the effective secularization of government, the creation of a state-run welfare state (''état-providence''), as well as realignment of politics into federalist and sovereigntist (or separatist) factions and the eventual election of a pro-sovereignty provincial government in the 1976 election. The Quiet Revolution typically refers to the efforts made by the Liberal government of Jean Lesage (elected in 1960) and sometimes Robert Bourassa (elected in 1970 after the Union Nationale's Daniel Johnson in 1966), though given the profound effect of the changes, most provincial governments since the early 1960s have maintained an orientation based on core concepts developed and implemented in that era. A primary change was an effort by the provincial government to take more dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, most populous city in Canada and the List of North American cities by population, fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the anchor of the Golden Horseshoe, an urban agglomeration of 9,765,188 people (as of 2021) surrounding the western end of Lake Ontario, while the Greater Toronto Area proper had a 2021 population of 6,712,341. Toronto is an international centre of business, finance, arts, sports and culture, and is recognized as one of the most multiculturalism, multicultural and cosmopolitanism, cosmopolitan cities in the world. Indigenous peoples in Canada, Indigenous peoples have travelled through and inhabited the Toronto area, located on a broad sloping plateau interspersed with Toronto ravine system, rivers, deep ravines, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Place Ville Marie
Place Ville Marie (PVM for short) is a large office and shopping complex skyscraper in Downtown Montreal, Quebec, Canada, comprising four office buildings and an underground shopping plaza. It serves as the main and official headquarters for Royal Bank of Canada, Canada's Largest Bank. The main building, 1 Place Ville Marie (formerly Royal Bank Tower from its anchor tenant), was built in the International style in 1962 as the headquarters for the Royal Bank of Canada, which it still is presently. It is a , 47-storey, cruciform office tower. The complex is a nexus for Montreal's Underground City, the world's busiest, with indoor access to over 1,600 businesses, numerous subway stations, a suburban transportation terminal, and tunnels extending throughout downtown. A counter-clockwise rotating beacon on the rooftop lights up at night, illuminating the surrounding sky with up to four white horizontal beams that can be seen as far as away. The light is not for airplanes. Buildi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Gentlemen's Clubs In Canada
The following list is of gentlemen's clubs that operated in Canada. A gentlemen's club is a private social club that serves as places for men to dine, drink, read, and socialize. They originated in the 18th century as a type of British social institution and flourished particularly in the 19th century. History As a part of the British Empire, Canadians adopted the gentlemen's club tradition enthusiastically. Most of Canada's clubs were founded during the Victorian era and used similar rules to their British counterparts, including: a proscription on discussions about politics and religion, silence in reading rooms, and a ban on smoking in dining areas. Moreover, clubs oriented towards businessmen prohibited briefcases in dining rooms. Wallace Clement described Canada's gentlemen's clubs as "one of the key institutions which form an interacting and active national upper class."Clement, Wallace. ''The Canadian Corporate Elite: An Analysis of Economic Power''. Toronto: McClelland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
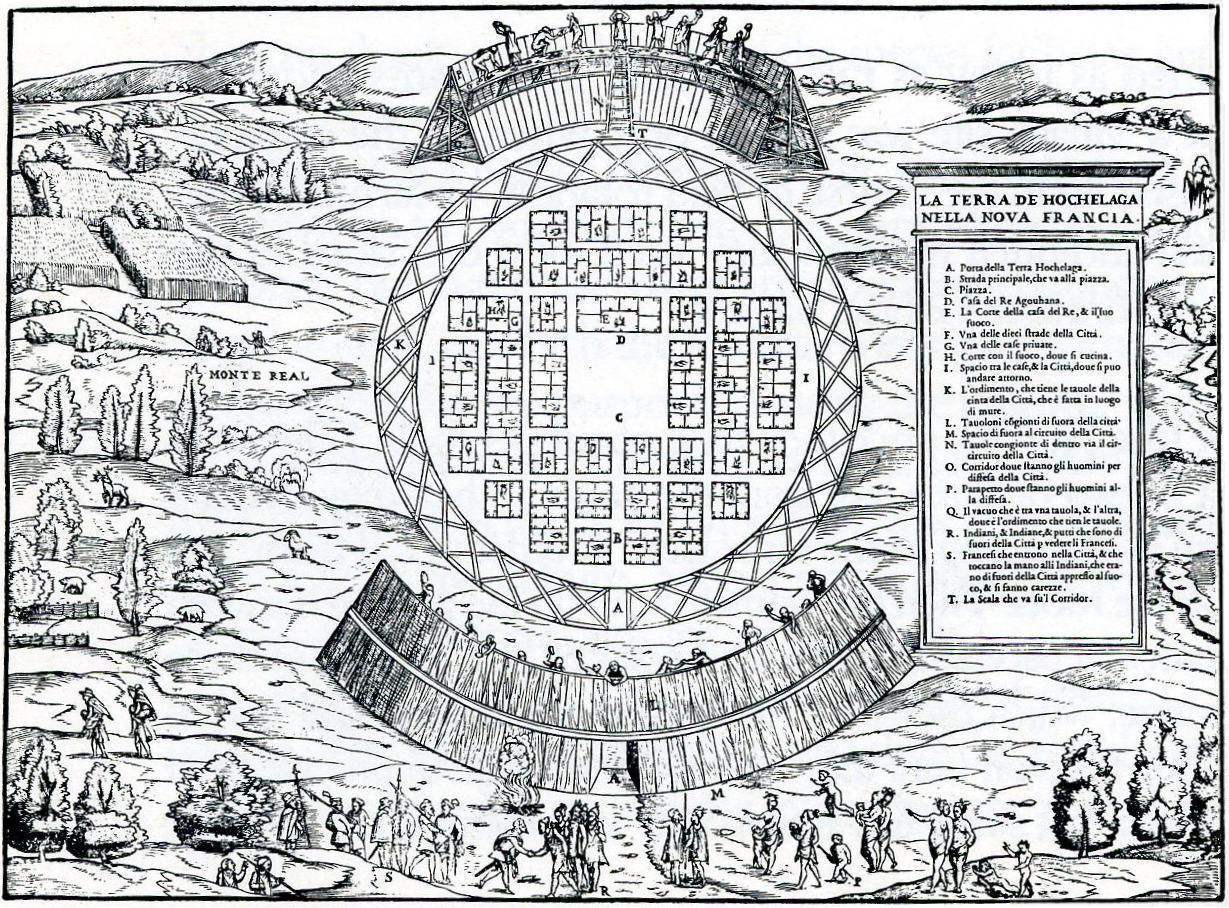
History Of Montreal
The history of the area around what is now known as Montreal, Montreal itself was established in 1642, located in what is now known as the province of Quebec, Canada, spans about 8,000 years. At the time of European contact, the area was inhabited by the St. Lawrence Iroquoians, a discrete and distinct group of Iroquoian-speaking indigenous people. They spoke Laurentian. Jacques Cartier became the first European to reach the area now known as Montreal in 1535 when he entered the village of '' Hochelaga'' on the Island of Montreal while in search of a passage to Asia during the Age of Exploration. Seventy years later, Samuel de Champlain unsuccessfully tried to create a fur trading post but the Mohawk of the Iroquois defended what they had been using as their hunting grounds. A fortress named Ville Marie was built in 1642 as part of a project to create a French colonial empire. Ville Marie became a centre for the fur trade and French expansion into New France until 1760, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Quebec
Quebec was first called ''Canada'' between 1534 and 1763. It was the most developed colony of New France as well as New France's centre, responsible for a variety of dependencies (ex. Acadia, Plaisance, Louisiana, and the Pays d'en Haut). Common themes in Quebec's early history as ''Canada'' include the fur trade -because it was the main industry- as well as the exploration of North America, war against the English, and alliances or war with Native American groups. Following the Seven Years' War, Quebec became a British colony in the British Empire. It was first known as the Province of Quebec (1763–1791), then as Lower Canada (1791–1841), and then as Canada East (1841–1867) as a result of the Lower Canada Rebellion. During this period, the inferior socio-economic status of francophones (because anglophones dominated the natural resources and industries of Quebec), the Catholic church, resistance against cultural assimilation, and isolation from non English-speaki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)