|
Sack Of Magadha
The Khalji Raids into Magadh, was a significant military campaign of the Ghurid Empire led by the Ghurid commander Bakhtiyar Khalji. He successfully captured Bihar, incorporating it into the Ghurid Empire, before proceeding with his invasion of Bengal. The Conquest Muhammad Bakhtiyar Khalji advanced towards Bihar with a mere 200 soldiers, yet he accomplished the relatively easy capture of one of its most heavily fortified forts, Udantapuri. While local inhabitants did resist the Ghurid general and his forces, resulting in significant casualties on both sides. Despite emerging from his fort to engage in battle with great courage, the ruler was ultimately defeated and killed in the ensuing confrontation with the Khalji Commander. Destruction of Nalanda and Vikramshila It is highly likely that during this particular conquest, as recorded by the Tibetan chronicler Taranath in the 15th century, Bakhtiyar also seized the monastic cities of Vikramsila and Nalanda, and proceeded to raz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghurid Empire
The Ghurid dynasty (also spelled Ghorids; ; self-designation: , ''Šansabānī'') was a Persianate dynasty of eastern Iranian peoples, Iranian Tajik people, Tajik origin, which ruled from the 8th-century in the region of Ghor, and became an Empire from 1175 to 1215. The Ghurids were centered in the hills of the Ghor region in the present-day central Afghanistan, where they initially started out as local chiefs. They gradually converted to Sunni Islam after the conquest of Ghor by the Ghaznavid ruler Mahmud of Ghazni in 1011. The Ghurids eventually overran the Ghaznavids when Muhammad of Ghor Siege of Lahore (1186), seized Lahore and expelled the Ghaznavids from their last stronghold. The Ghurids initially ruled as vassals of the Ghaznavids and later of the Seljuk Empire, Seljuks. However, during the early twelfth century the long-standing rivalry between the Seljuks and Ghaznavids created a power vacuum in eastern Afghanistan and Punjab, Panjab which the Ghurids took advantage o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
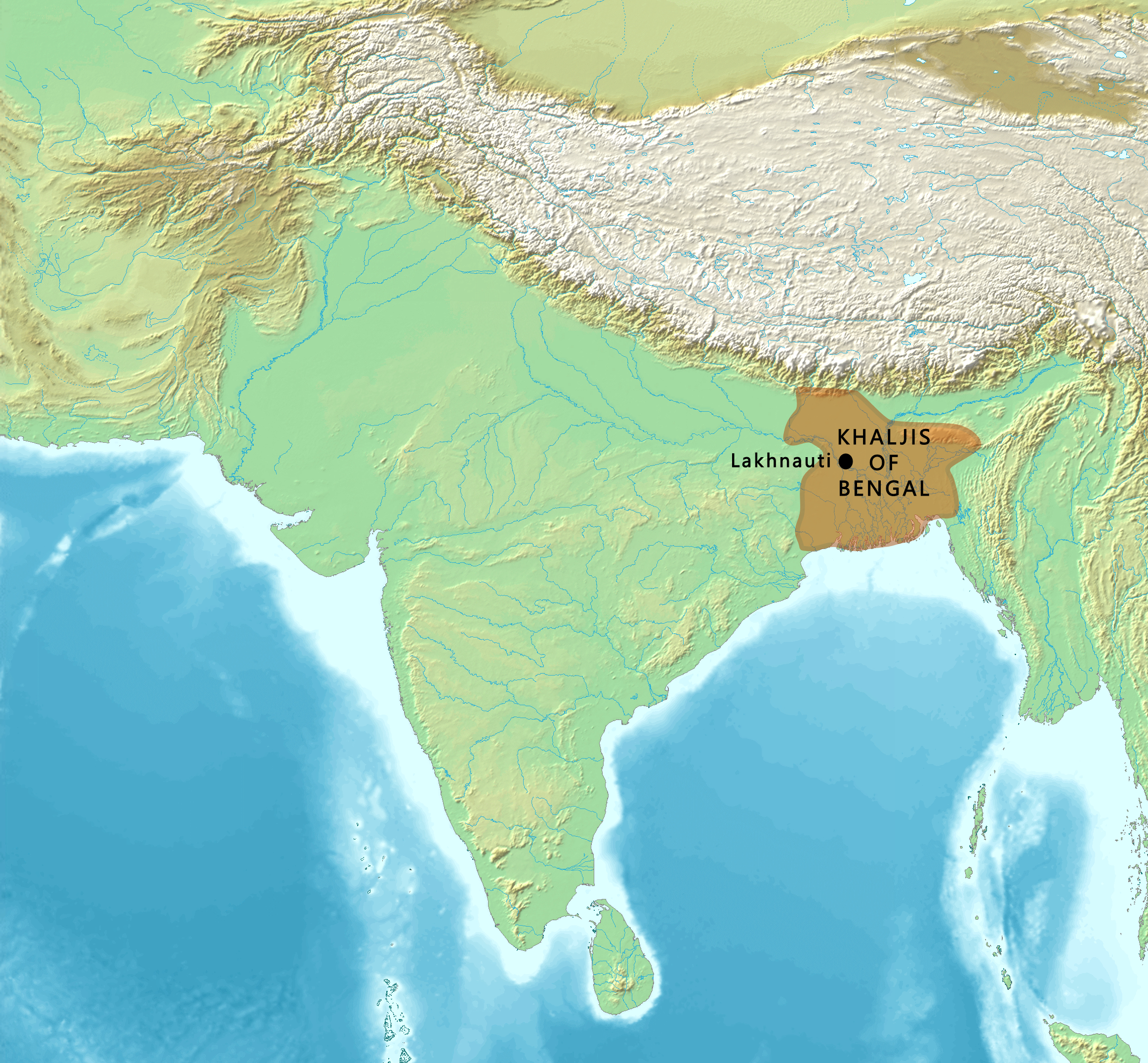
Bakhtiyar Khalji
Ikhtiyār al-Dīn Muḥammad Bin Bakhtiyār Khaljī, also known as Bakhtiyar Khalji, was a Turko-Afghan Military General of the Ghurid ruler Muhammad of Ghor, who led the Muslim conquests of the eastern Indian regions of Bengal and parts of Bihar and established himself as their deputy-ruler/governor, He was the founder of the Khalji dynasty of Bengal, ruling Bengal for a short period, from 1203 to 1227 CE. Khalji's invasions of the Indian subcontinent between A.D. 1197 and 1206 led to mass flight and massacres of monks, and caused damage to the traditional Buddhist institutions of higher learning in Northern India. In Bengal, Khalji's reign was responsible for the displacement of Buddhism. The leading centre of teaching for Mahayana Buddhism was Nalanda. At the end of the 12th century, Bakhityar Khalji demolished the monastery in a brutal sacking . His rule is said to have begun the Muslim rule in Bengal, most notably those of Bengal Sultanate and Mughal Bengal. Bakhtiya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by area, 12th largest by area, and the List of Indian states and union territories by GDP, 14th largest by GDP in 2024. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West Bengal to the east, and Jharkhand to the south. Bihar is split by the river Ganges, which flows from west to east. On 15 November 2000, a large chunk of southern Bihar was ceded to form the new state of Jharkhand. Around 11.27% of Bihar's population live in urban areas as per a 2020 report. Additionally, almost 58% of Bihari people, Biharis are below the age of 25, giving Bihar the highest proportion of young people of any Indian state. The official language is Hindi, which shares official status alongside that of Urdu. The main native languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghurid Invasion Of Bengal
The Ghurid invasion of Bengal in 1202 was a military campaign of Ghurid dynasty led by Muhammad Bhakhtiyar Khalji against the Sena dynasty. Bakhtiyar Khalji emerged victorious in the campaign and subsequently annexed Nabadwip, a significant portion of the territory controlled by the Sena Dynasty. Following their defeat, Lakshmana Sena, the ruler of the Sena dynasty, retreated to the southeastern region of Bengal. Background Bhakhtiyar Khalji, after the successful annexation of Bihar to the Ghurid dynasty, learned about the Sena Dynasty and its illustrious ruler, Lakshmana Sena. Despite Sena's advanced age and reputation, Khalji was determined to extend his conquests further into Bengal. Upon hearing of Khalji's intent to invade Bengal, many Brahmins and traders decided to leave the Sena capital in search of safer locations. However, in a display of resilience, Lakshmana Sena chose to remain in Nadiya, ready to defend his realm. The siege Bakhtiyar, leading his forces fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The End Of Buddhist Monks, A
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vikramsila
Vikramashila (IAST: ) was a Buddhist monastery situated in what is now modern-day Bihar in India. It was founded by King Dharmapala between the late eighth and early ninth century. It was one of the three most important Buddhist Mahaviharas of its time in India, along with Nalanda and Odantapuri. Its location is now the site of Antichak village near Kahalgaon, Bhagalpur district in Bihar. It was one of the largest Buddhist mahaviharas, with more than one hundred teachers and about one thousand students. It produced eminent scholars who were often invited by foreign countries to spread Buddhist learning, culture and religion including Atiśa and Ratnākaraśānti. Vikramashila was established by the Pala emperor Dharmapala (783 to 820 CE) in response to a supposed decline in the quality of scholarship at Nalanda. It was destroyed by the forces of Muhammad bin Bakhtiyar Khalji around 1193. History A number of monasteries grew up during the Pāla period in medieval Bengal and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nalanda
Nalanda (International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: , ) was a renowned Buddhism, Buddhist ''mahavihara'' (great monastery) in medieval Magadha (Mahajanapada), Magadha (modern-day Bihar), eastern India. Widely considered to be among the greatest Ancient higher-learning institutions, centres of learning in the ancient world and often referred to as "the world's first residential university", it was located near the city of Rajagriha (now Rajgir), roughly southeast of Pataliputra (now Patna). Operating for almost a thousand years from 427 CE until around 1400 CE, Nalanda mahavihara played a vital role in promoting the patronage of arts, culture and academics during the 5th and 6th century CE, a period that has since been described as the "Golden Age of India" by scholars. Nalanda was established by emperor Kumaragupta I of the Gupta Empire around 427 CE, and was supported by numerous Indian and Javanese patrons – both Buddhists and non-Buddhists. Nalanda continue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qutubuddin Aibak
Qutb ud-Din Aibak (; 1150 – 4 November 1210) was a Turkic general of the Ghurid emperor Muhammad Ghori. He was in charge of the Ghurid territories in northern India, and after Muhammad Ghori's assassination in 1206, he established his own independent rule in Lahore, and laid the foundations for the Sultanate of Delhi. A native of Turkestan, Aibak was sold into slavery as a child. He was purchased by a Qazi at Nishapur in Persia, where he learned archery and horse-riding among other skills. He was subsequently resold to Muhammad Ghori in Ghazni, where he rose to the position of the officer of the royal stables. During the Khwarazmian-Ghurid wars, he was captured by the scouts of Sultan Shah; after the Ghurid victory, he was released and highly favoured by Muhammad Ghori. After the Ghurid victory in the Second Battle of Tarain in 1192, Muhammad Ghori made Aibak in charge of his Indian territories. Aibak expanded the Ghurid power in northern India by conquering and raiding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Later Guptas
The Later Gupta dynasty, also known as the Later Guptas of Magadha, were the rulers of Magadha and Malwa from the 6th to 8th centuries CE. The Later Guptas emerged after the disintegration of the Imperial Guptas. However, there is no evidence to connect the two dynasties and the Later Guptas may have adopted the -gupta suffix to link themselves with the Imperial Guptas. There are several important sources of information regarding the Later Guptas including two epigraphs, the Aphsad inscription of Ādityasena, which sets out the genealogy of the ruling family from Kṛṣṇagupta to Ādityasena, and the Deo Baranark inscription of Jīvitagupta II. The Harshacharita of Bāṇabhaṭṭa is also an important source of information as are the records of the Chinese pilgrims Xuanzang and Yijing which also mentions them. The Gaudavaho of Vākpatirāja refers to the victory of King Yashovarman of the Varman dynasty against the king of Magadha, with the scholarly consensus being tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1200s Conflicts
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, Numeral (linguistics), numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest Positive number, positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit (measurement), unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In Digital electronics, digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghurid Dynasty
The Ghurid dynasty (also spelled Ghorids; ; self-designation: , ''Šansabānī'') was a Persianate dynasty of eastern Iranian Tajik origin, which ruled from the 8th-century in the region of Ghor, and became an Empire from 1175 to 1215. The Ghurids were centered in the hills of the Ghor region in the present-day central Afghanistan, where they initially started out as local chiefs. They gradually converted to Sunni Islam after the conquest of Ghor by the Ghaznavid ruler Mahmud of Ghazni in 1011. The Ghurids eventually overran the Ghaznavids when Muhammad of Ghor seized Lahore and expelled the Ghaznavids from their last stronghold. The Ghurids initially ruled as vassals of the Ghaznavids and later of the Seljuks. However, during the early twelfth century the long-standing rivalry between the Seljuks and Ghaznavids created a power vacuum in eastern Afghanistan and Panjab which the Ghurids took advantage of and began their territorial expansion. Ala al-Din Husayn ended the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |