|
Saccular Acoustic Sensitivity
Saccular acoustic sensitivity is a measurement of the ear's affectability to sound. The saccule's normal function is to keep the body balanced, but it is believed to have some hearing function for special frequencies and tones. Saccular acoustic sensitivity is considered to be simply an extension of the sense of hearing through the use of the saccule. Effects Saccular acoustic sensitivity has a variety of physiological as well as mental/emotional effects. Physical effects Perhaps the most observable physical response is goose bumps. A similar effect is the manifestation of chills. Some sounds have been known to cause reflexive muscle movements like a twitch or even a jump. Since these physical effects are easily recorded and are linked consistently with strong emotion, they have been used in several types of psychological studies. Mental/Emotional effects Certain sounds, such as fingernails drawn down a blackboard, cause strong feelings of aversion or even fear in mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccule
The saccule is a bed of sensory cells in the inner ear The inner ear (internal ear, auris interna) is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in t .... It translates head movements into neural impulses for the brain to interpret. The saccule detects linear accelerations and head tilts in the vertical plane. When the head moves vertically, the sensory cells of the saccule are disturbed and the neurons connected to them begin transmitting impulses to the brain. These impulses travel along the vestibular portion of the eighth cranial nerve to the vestibular nuclei in the brainstem. The vestibular system is important in maintaining balance, or equilibrium. The vestibular system includes the saccule, utricle, and the three semicircular canals. The Vestibule of the ear, vestibule is the name of the fluid-filled, membrano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Salford
, caption = Coat of ArmsUniversity of Salford , mottoeng = "Let us seek higher things" , established = 1850 - Pendleton Mechanics Institute 1896 – Royal Technical Institute, Salford 1967 – gained university status by Royal charter , type = Public , endowment = £1.4m (2020) , city = Salford , country = England, United Kingdom , campus = Urban, Parkland , administrative_staff = 2,781 , chancellor = Lucy Meacock , vice_chancellor = Helen Marshall , students = () , undergrad = () , postgrad = () , colours = Black and Red , affiliations = University Alliance Association of Commonwealth Universities North West Universities Association Northern Consortium Universities UK , logo = , website = The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drums
A drum kit (also called a drum set, trap set, or simply drums) is a collection of drums, cymbals, and other auxiliary percussion instruments set up to be played by one person. The player (drummer) typically holds a pair of matching drumsticks, one in each hand, and uses their feet to operate a foot-controlled hi-hat and bass drum pedal. A standard kit may contain: * A snare drum, mounted on a stand * A bass drum, played with a beater moved by a foot-operated pedal * One or more tom-toms, including rack toms and/or floor toms * One or more cymbals, including a ride cymbal and crash cymbal * Hi-hat cymbals, a pair of cymbals that can be manipulated by a foot-operated pedal The drum kit is a part of the standard rhythm section and is used in many types of popular and traditional music styles, ranging from rock and pop to blues and jazz. __TOC__ History Early development Before the development of the drum set, drums and cymbals used in military and orchestral music sett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snoring
Snoring is the vibration of respiratory structures and the resulting sound due to obstructed air movement during breathing while sleeping. The sound may be soft or loud and unpleasant. Snoring during sleep may be a sign, or first alarm, of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Research suggests that snoring is one of the factors of sleep deprivation. Causes Snoring is the result of the relaxation of the uvula and soft palate. These tissues can relax enough to partially block the airway, resulting in irregular airflow and vibrations. Snoring can be attributed to one or more of the following: * Genetic predisposition, a proportion of which may be mediated through other heritable lifestyle factors such as body mass index, smoking and alcohol consumption. *Throat weakness, causing the throat to close during sleep. * Mispositioned jaw, often caused by tension in the muscles. * Obesity that has caused fat to gather in and around the throat. * Obstruction in the nasal passageway. * Obstruc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alarm Clock
An alarm clock (or sometimes just an alarm) is a clock that is designed to alert an individual or group of individuals at a specified time. The primary function of these clocks is to awaken people from their night's sleep or short naps; they are sometimes used for other reminders as well. Most use sound; some use light or vibration. Some have sensors to identify when a person is in a light stage of sleep, in order to avoid waking someone who is deeply asleep, which causes tiredness, even if the person has had adequate sleep. To turn off the sound or light, a button or handle on the clock is pressed; most clocks automatically turn off the alarm if left unattended long enough. A classic analog alarm clock has an extra hand or inset dial that is used to specify the time at which the alarm will ring. Alarm clocks are also used in mobile phones, watches, and computers. Many alarm clocks have radio receivers that can be set to start playing at specified times, and are known as ''clock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
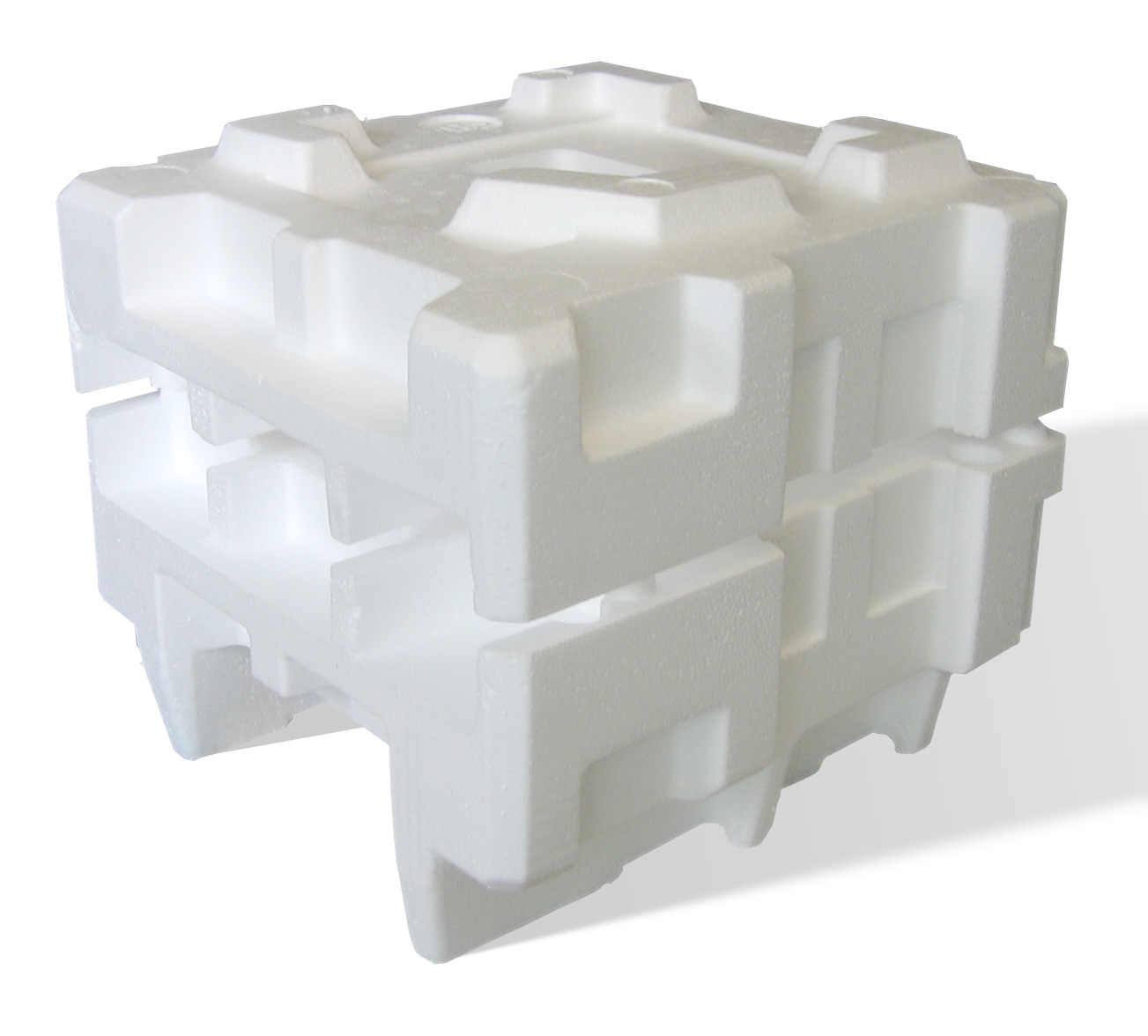
Polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a poor barrier to oxygen and water vapour and has a relatively low melting point. Polystyrene is one of the most widely used plastics, the scale of its production being several million tonnes per year. Polystyrene can be naturally transparent, but can be colored with colorants. Uses include protective packaging (such as packing peanuts and in the jewel cases used for storage of optical discs such as CDs and occasionally DVDs), containers, lids, bottles, trays, tumblers, disposable cutlery, in the making of models, and as an alternative material for phonograph records. As a thermoplastic polymer, polystyrene is in a solid (glassy) state at room temperature but flows if heated above about 100 °C, its glass transition temperature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages that can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex following three phases: an inhalation, a forced exhalation against a closed glottis, and a violent release of air from the lungs following opening of the glottis, usually accompanied by a distinctive sound. Frequent coughing usually indicates the presence of a disease. Many viruses and bacteria benefit, from an evolutionary perspective, by causing the host to cough, which helps to spread the disease to new hosts. Most of the time, irregular coughing is caused by a respiratory tract infection but can also be triggered by choking, smoking, air pollution, asthma, gastroesophageal reflux disease, post-nasal drip, chronic bronchitis, lung tumors, heart failure and medications such as angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors). Treatme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
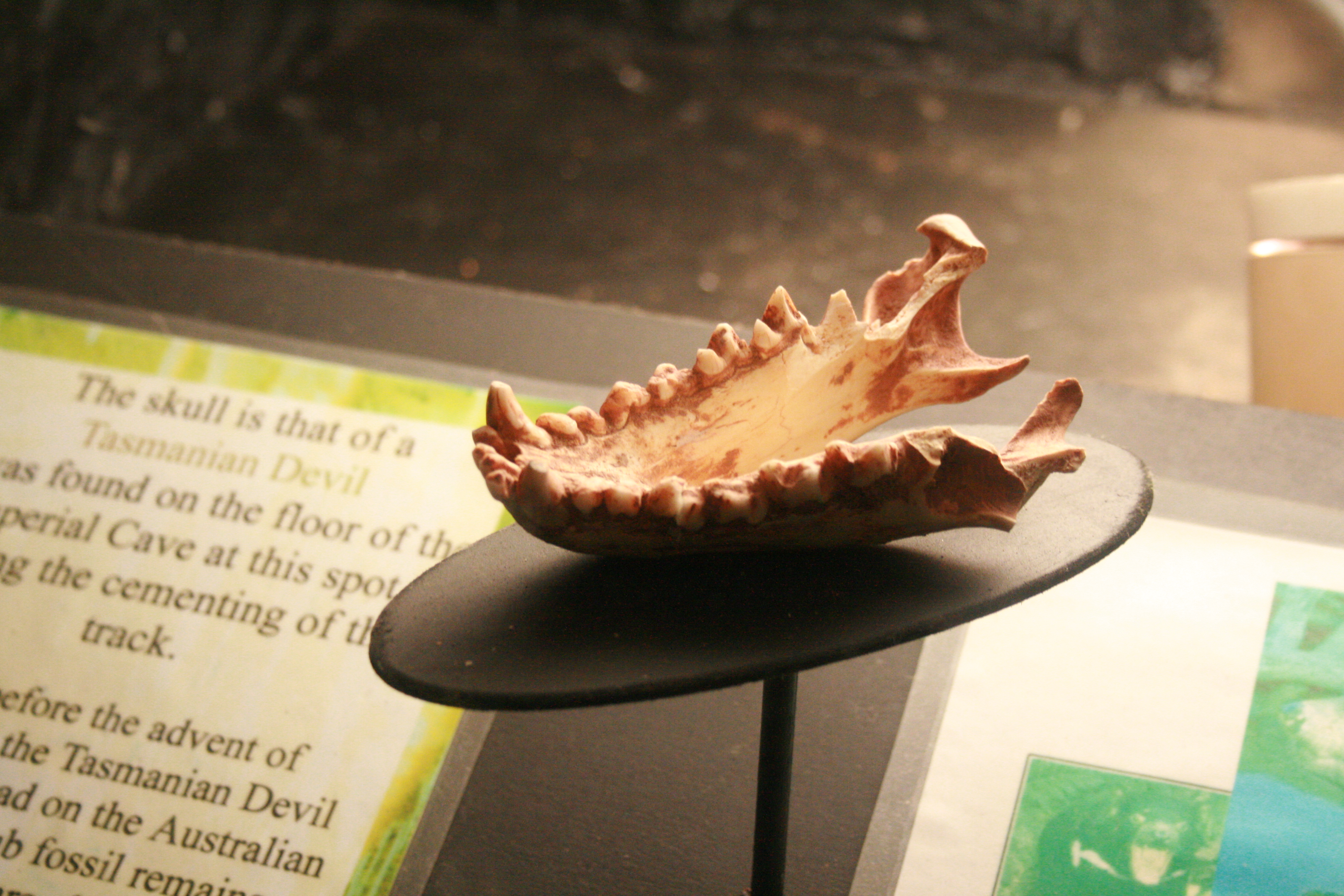
Tasmanian Devil
The Tasmanian devil (''Sarcophilus harrisii'') (palawa kani: purinina) is a carnivorous marsupial of the family Dasyuridae. Until recently, it was only found on the island state of Tasmania, but it has been reintroduced to New South Wales in mainland Australia, with a small breeding population. The size of a small dog, the Tasmanian devil became the largest carnivorous marsupial in the world following the extinction of the thylacine in 1936. It is related to quolls, and distantly related to the thylacine. It is characterised by its stocky and muscular build, black fur, pungent odour, extremely loud and disturbing screech, keen sense of smell, and ferocity when feeding. The Tasmanian devil's large head and neck allow it to generate among the strongest bites per unit body mass of any extant predatory land mammal. It hunts prey and scavenges on carrion. Although devils are usually solitary, they sometimes eat and defecate together in a communal location. Unlike most other da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mains Hum
Mains hum, electric hum, cycle hum, or power line hum is a sound associated with alternating current which is twice the frequency of the mains electricity. The fundamental frequency of this sound is usually double that of fundamental 50/60 Hz, ''i.e.''100/120Hz, depending on the local power-line frequency. The sound often has heavy harmonic content above 50/60Hz. Because of the presence of mains current in mains-powered audio equipment as well as ubiquitous AC electromagnetic fields from nearby appliances and wiring, 50/60Hz electrical noise can get into audio systems, and is heard as mains hum from their speakers. Mains hum may also be heard coming from powerful electric power grid equipment such as utility transformers, caused by mechanical vibrations induced by magnetostriction in magnetic core. Onboard aircraft (or spacecraft) the frequency heard is often higher pitched, due to the use of 400 Hz AC power in these settings because 400 Hz transformers are much smaller and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whoopee Cushion
A whoopee (or whoopie) cushion is a practical joke device involving flatulence humour, which produces a noise resembling human flatulence. It has also been referred to as a farting bag, pooting cushion, windy blaster and Razzberry Cushion. History and modern usage The whoopee cushion has reportedly been used since ancient times. Roman Emperor Elagabalus was said to enjoy practical jokes at his dinner parties and often placed whoopee cushions under the chairs of his more pompous guests. The 10th-century Aghlabid emir of Ifriqiya, Ziyadat Allah III, is said to have enjoyed hiding inflated animal bladders under the cushions of his palace for unsuspecting guests to sit on. The modern rubber version was invented in the 1930s by the JEM Rubber Co. of Toronto, Ontario, Canada, by employees who were experimenting with scrap sheets of rubber. The company's owner approached Samuel Sorenson Adams, inventor of numerous practical jokes and owner of S.S. Adams Co., with the newly invented ite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose. Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pregnancy, motion sickness, or hangover; or it can be an after effect of diseases such as brain tumors, elevated intracranial pressure, or overexposure to ionizing radiation. The feeling that one is about to vomit is called nausea; it often precedes, but does not always lead to vomiting. Impairment due to alcohol or anesthesia can cause inhalation of vomit, leading to suffocation. In severe cases, where dehydration develops, intravenous fluid may be required. Antiemetics are sometimes necessary to suppress nausea and vomiting. Self-induced vomiting can be a component of an eating disorder such as bulimia, and is itself now classified as an eating disorder on its own, purging disorder. Complications Aspiration Vomiting is dan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fight-or-flight Response
The fight-or-flight or the fight-flight-or-freeze response (also called hyperarousal or the acute stress response) is a physiological reaction that occurs in response to a perceived harmful event, attack, or threat to survival. It was first described by Walter Bradford Cannon. His theory states that animals react to threats with a general discharge of the sympathetic nervous system, preparing the animal for fighting or fleeing. More specifically, the adrenal medulla produces a hormonal cascade that results in the secretion of catecholamines, especially norepinephrine and epinephrine. The hormones estrogen, testosterone, and cortisol, as well as the neurotransmitters dopamine and serotonin, also affect how organisms react to stress. The hormone osteocalcin might also play a part. This response is recognised as the first stage of the general adaptation syndrome that regulates stress responses among vertebrates and other organisms. Name Originally understood as the fig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |