|
SW Sextantis Variable
SW Sextantis variable stars are a kind of cataclysmic variable star; they are double-star systems in which there is mass transfer from a red dwarf to a white dwarf forming a stable accretion disc around the latter. Unlike other non-magnetic cataclysmic variables, the emission lines from hydrogen and helium are not doubled, except briefly near phase 0.5. Characteristics SW Sextantis stars have an orbital period between 2.8 and 4 hours; most systems were discovered by surveys of eclipsing variables, so the orbit is nearly edge-on with respect to the Earth. Their spectra resemble those of a dwarf nova in outburst, with signs of a permanently ionised accretion disc. Material is constantly flowing into the disc from the companion star, and friction within the disc causes it to emit optical light. It is more difficult to find SW Sextantis systems with low inclination, since it is necessary to examine many stellar spectra without being able to restrict to eclipsing variables; howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cataclysmic Variable
In astronomy, cataclysmic variable stars (CVs) are stars which irregularly increase in brightness by a large factor, then drop back down to a quiescent state. They were initially called novae (), since ones with an outburst brightness visible to the naked eye and an invisible quiescent brightness appeared as new stars in the sky. Cataclysmic variable stars are binary stars that consist of two components; a white dwarf primary, and a mass transferring secondary. The stars are so close to each other that the gravity of the white dwarf distorts the secondary, and the white dwarf accretes matter from the companion. The tightest currently observed orbit in a hydrogen-rich system is 51 minutes in ZTF J1813+4251. Therefore, the secondary is often referred to as the ''donor star''. The infalling matter, which is usually rich in hydrogen, forms in most cases an accretion disk around the white dwarf. Strong UV and X-ray emission is often seen from the accretion disc, powered by the loss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Momentum
In physics, angular momentum (rarely, moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a conserved quantity—the total angular momentum of a closed system remains constant. Angular momentum has both a direction and a magnitude, and both are conserved. Bicycles and motorcycles, frisbees, rifled bullets, and gyroscopes owe their useful properties to conservation of angular momentum. Conservation of angular momentum is also why hurricanes form spirals and neutron stars have high rotational rates. In general, conservation limits the possible motion of a system, but it does not uniquely determine it. The three-dimensional angular momentum for a point particle is classically represented as a pseudovector , the cross product of the particle's position vector (relative to some origin) and its momentum vector; the latter is in Newtonian mechanics. Unlike linear momentum, angular mome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BB Doradus
BB Doradus or BB Dor is a cataclysmic variable In astronomy, cataclysmic variable stars (CVs) are stars which irregularly increase in brightness by a large factor, then drop back down to a quiescent state. They were initially called novae (), since ones with an outburst brightness visible to ..., a pre-nova star, thus a close pair binary star system. It is composed of a red dwarf and a white dwarf. Observations of the white dwarf's faint but certain accretion disk are consistent with it being at ~10° inclination (to the line of sight from the Earth). Its parallax (movement against background stars due to the Earth's orbit around the Sun) given by the ''Gaia'' space observatory's second data release puts the pair at about 3,000 light years away. References {{DEFAULTSORT:BB Doradus Cataclysmic variable stars Dorado Doradus, BB M-type main-sequence stars White dwarfs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LS Pegasi
LS may refer to: Businesses * LS Group, a Korean company * Jet2.com (IATA code: LS), a British airline Latin * Lewis and Short (abbr. "L&S"), authors of the 1879 work ''A Latin Dictionary'' * Lectori Salutem (L.S.), Latin for 'Greetings Reader' and used as opening words to a letter * ''locus sigilli'', Latin for 'place of the seal', used in notarized and legal documents; see: Seal (contract law) Organizations * Liberal Party of Croatia ( hr, Liberalna stranka or LS), a Croatian political party active from 1998–2006 * Lincoln-Sudbury Regional High School, Massachusetts, US * Lok Sabha, the lower house of the Parliament of India * Loyola Schools, the college unit of the Ateneo de Manila University in Quezon City, Philippines Places * Lesotho (ISO 3166-1 country code: LS), a country in southern Africa * LS postcode area, UK, covering Leeds * County Laois, Ireland Science, technology, and mathematics Astronomy * Light-second (ls), a unit of length in astro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DW Ursae Majoris
DW Ursae Majoris is an eclipsing binary star system in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major, abbreviated DW UMa. It is a cataclysmic variable of the SX Sextanis type, consisting of a compact white dwarf that is accreting matter from an orbiting companion star. The brightness of this source ranges from an apparent visual magnitude of 13.6 down to magnitude 18, which is too faint to be viewed with the naked eye. The distance to this system is approximately 1,920 light years based on parallax measurements. In 1982, R. F. Green and associates identified this star as a cataclysmic variable candidate with the Palomar–Green survey designation PG 1030+590. A. W. Shafter and F. V. Hessman in 1984 found this to be a close eclipsing binary system with a period of 3.27 hours. This is a nova-like binary where mass is being transferred from a late-type star to a white dwarf companion. This material is first accumulated in an accretion disk orbiting the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PX Andromedae
PX Andromedae (often abbreviated to PX And) is an eclipsing cataclysmic variable star in the constellation Andromeda. It has been classified as a SW Sextantis variable, and its apparent visual magnitude varies between 14.04 and 17. In 1982, Richard Green ''et al.'' listed PX Andromedae as a possible cataclysmic variable, based on spectra taken with the Hale Telescope. Observations in 1989 by Li Yong ''et al'', at the Beijing Observatory detected rapid variations of the star's brightness of up to 0.2 magnitudes, as well as eclipses which occur every 3.5 hours. In 1992 the star was given the variable star designation PX Andromedae. Spectrum The spectrum of PX Andromedae is variable, but typically shows a continuum with prominent broad emission lines of hydrogen and helium. Unlike many types of cataclysmic variable, the emission lines are generally single-peaked, although for a short time during each orbit they do show a double peak due to an absorption core within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nova
A nova (plural novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", which is Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. Causes of the dramatic appearance of a nova vary, depending on the circumstances of the two progenitor stars. All observed novae involve white dwarfs in close binary systems. The main sub-classes of novae are classical novae, recurrent novae (RNe), and dwarf novae. They are all considered to be cataclysmic variable stars. Classical nova eruptions are the most common type. They are likely created in a close binary star system consisting of a white dwarf and either a main sequence, subgiant, or red giant star. When the orbital period falls in the range of several days to one day, the white dwarf is close enough to its companion star to start drawing accreted matter onto the surface of the white dwarf, which creates a dense but shallow atmosphere. This atmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V728 Scorpii
V728 Scorpii, also known as Nova Scorpii 1862, was a nova that occurred in the constellation of Scorpius. It was discovered on 4 October 1862 by John Tebbutt, an astronomer living in New South Wales, Australia, while he was observing a comet. He reported that the star was in the constellation Ara. At the time of its discovery, the nova had an apparent magnitude of 5, making it visible to the unaided eye. Nine days later it had faded to below 11th magnitude, indicating that it was a very fast nova. Tappert ''et al.'' conducted an observing program from 2009 to 2011 to investigate nova candidates. Using photometric and spectroscopic observations, they identified the post-nova star corresponding to Nova Scorpii 1862. On 20 May 2009, the star had a visible-band magnitude of 18.5. They reported that the spectrum resembled that of a dwarf nova with a high orbital inclination, suggesting that it might be an eclipsing variable. Follow-up observations by the same te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
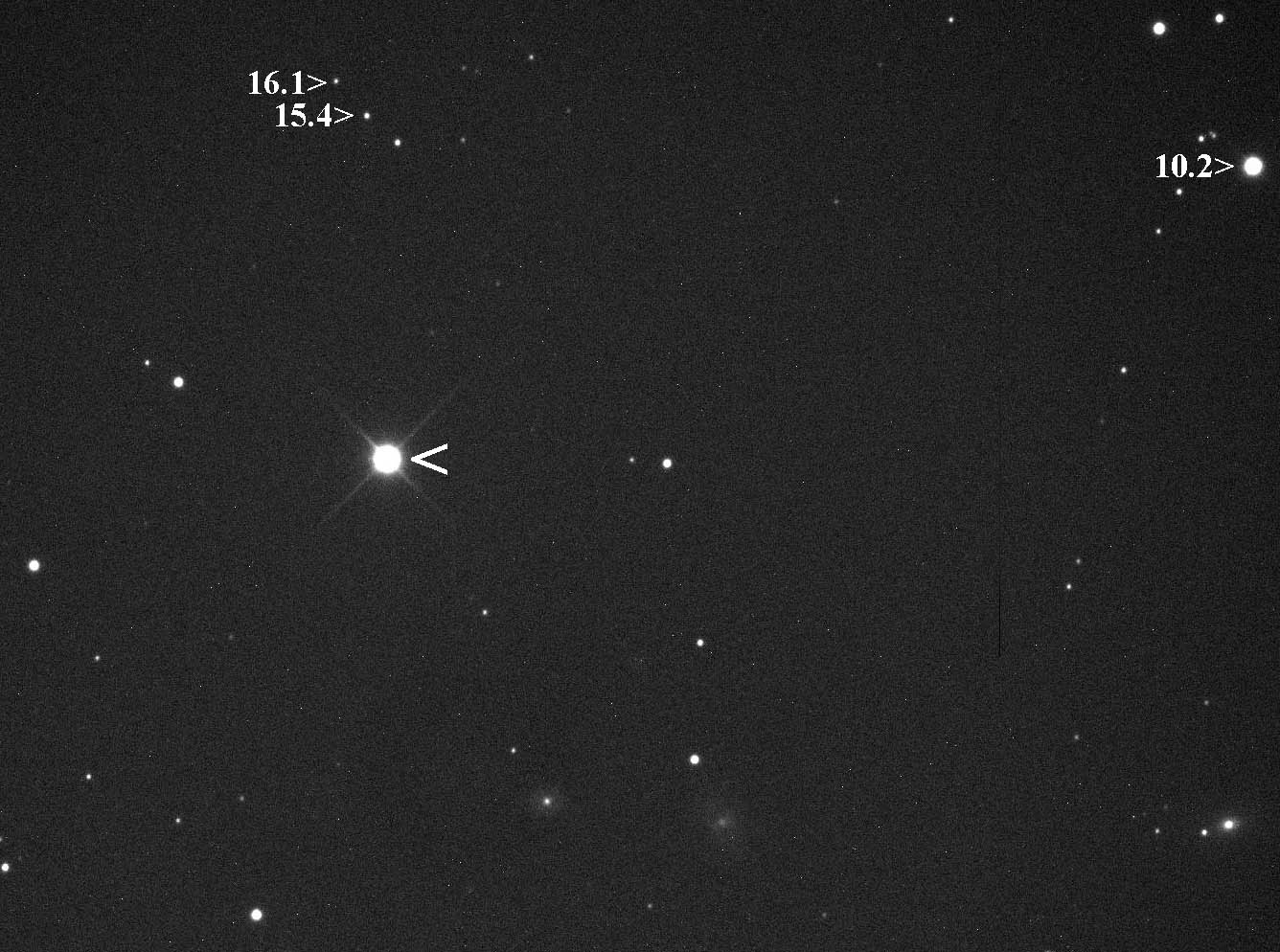
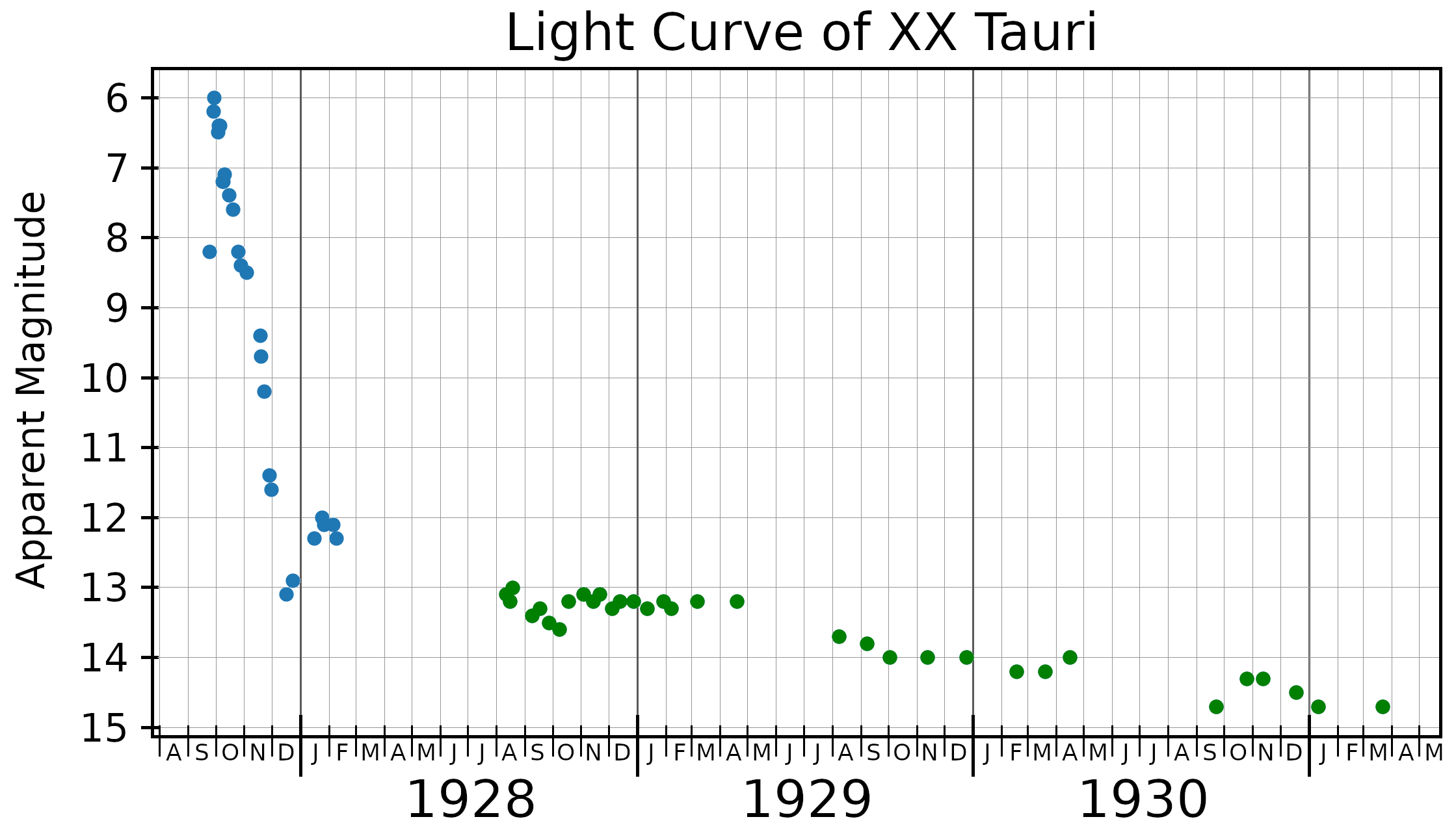
XX Tauri
XX Tauri (Nova Tauri 1927) was a nova, which appeared in the constellation Taurus in 1927. It was discovered by Arnold Schwassmann and Arno Arthur Wachmann at Hamburg Observatory on an objective prism photographic plate taken on 18 November 1927. Subsequent examination of pre-discovery photographic plates taken at the Harvard College Observatory showed that the peak brightness, magnitude 5.9, occurred on 1 October 1927, at which point it may have been faintly visible to the naked eye. By 1988 it had faded below magnitude 19.8. XX Tauri faded three magnitudes from peak brightness in just 43 days, making it a "fast nova". Its post eruption light curve shows small amplitude (~0.1 magnitude) variations of timescales of days, hours and minutes, which makes the determination of the orbital period of the binary system comprising the nova difficult. The orbital period may be 0.136±0.002 days. In 1984 a small (radius 2.2 arc second) nova remnant surrounding XX Tau was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
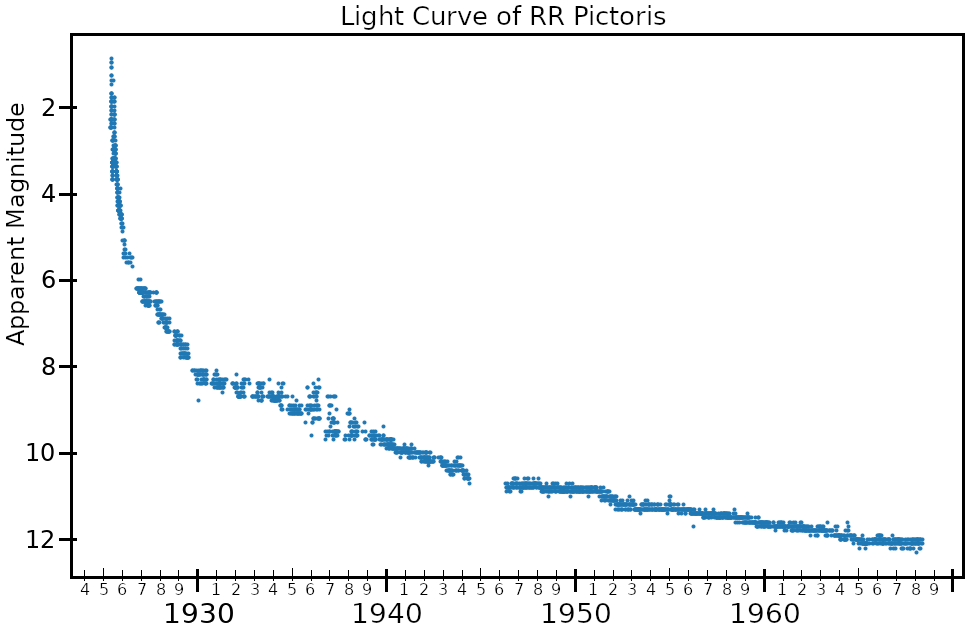
RR Pictoris
RR Pictoris, also known as Nova Pictoris 1925, is a cataclysmic variable star system that flared up as a nova that lit up in the constellation Pictor in 1925. It was discovered by South African amateur astronomer R. Watson who lived in Beaufort West. At 05:50 AM on 25 May 1925, Mr. Watson was walking to work and noticed a star that he did not recognize in line with the stars α Crucis and β Carinae. He consulted his copy of Norton's Star Atlas, and realized that the unfamiliar star was a nova. Fortuitously, Mr. Watson was employed as a telegraph operator, and he promptly sent a telegram describing his discovery to the Royal Observatory at Cape Town. This quick reporting of the event allowed southern observatories to obtain spectra of the nova before it had reached maximum brightness. At the time of its discovery, RR Pictoris had an apparent magnitude of 2.3. It continued to brighten to magnitude 1.2, which it reached on 9 June 1925. It dimmed to magnitude 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Braking (astronomy)
Magnetic braking is a theory explaining the loss of stellar angular momentum due to material getting captured by the stellar magnetic field and thrown out at great distance from the surface of the star. It plays an important role in the evolution of binary star systems. The problem The currently accepted theory of the solar system's evolution states that the Solar System originates from a contracting gas cloud. As the cloud contracts, the angular momentum L must be conserved. Any small net rotation of the cloud will cause the spin to increase as the cloud collapses, forcing the material into a rotating disk. At the dense center of this disk a protostar forms, which gains heat from the gravitational energy of the collapse. As the collapse continues, the rotation rate can increase to the point where the accreting protostar can break up due to centrifugal force at the equator. Thus the rotation rate must be braked during the first 100,000 years of the star's life to avoid this sce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |