|
SLC38A10
Putative sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter 10, also known as solute carrier family 38 member 10, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC38A10'' gene. Cellular localization Cellular localization study of SLC38A10 protein was investigated on different cell lines and primary cortex neuronal cells using Immunocytochemistry and GFP SLC38A10 vector. SLC38A10 localized on Golgi apparatus and ER organelles. Recent study on SLC38A10 knockout model provided some insight on possible association with p53 protein and cell survival. Cancer A SLC38A family member has been observed progressively downregulated in Human papillomavirus Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and r ...-positive neoplastic keratinocytes derived from uterine cervical preneoplastic lesion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solute Carrier Family
The solute carrier (SLC) group of membrane transport proteins include over 400 members organized into 66 families. Most members of the SLC group are located in the cell membrane. The SLC gene nomenclature system was originally proposed by the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC) and is the basis for the official HGNC names of the genes that encode these transporters. A more general transmembrane transporter classification can be found in TCDB, TCDB database. Solutes that are transported by the various SLC group members are extremely diverse and include both charged and uncharged organic molecules as well as inorganic ions and the gas Ammonia transporter, ammonia. As is typical of integral membrane proteins, SLCs contain a number of hydrophobic transmembrane Alpha helix, alpha helices connected to each other by hydrophilic intra- and extra-cellular loops. Depending on the SLC, these transporters are functional as either monomers or obligate homo- or hetero-oligomers. Many SLC fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
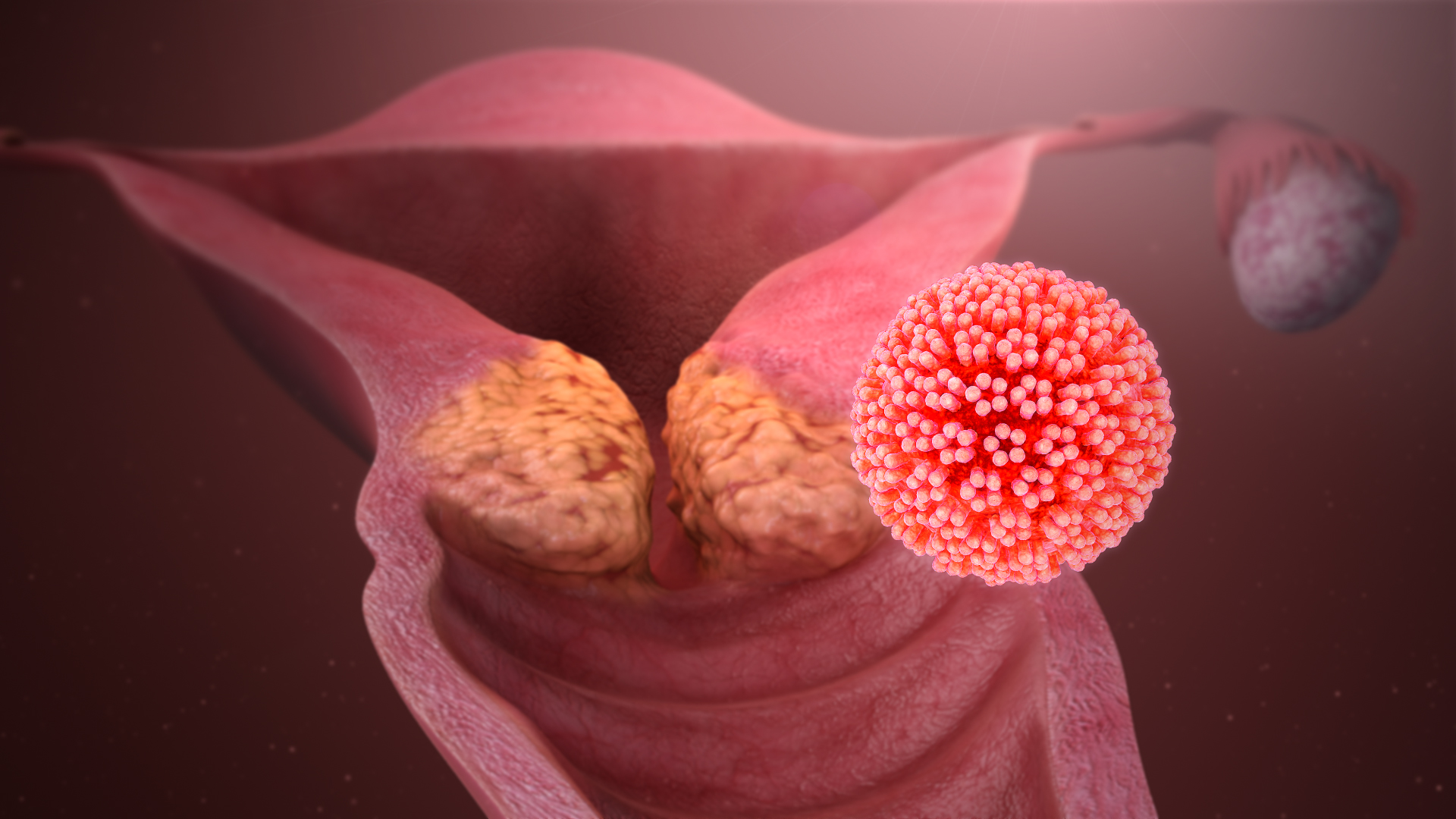
Human Papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and results in either warts or precancerous lesions. All warts are caused by HPV. These lesions, depending on the site affected, increase the risk of cancer of the cervical cancer, cervix, vulva cancer, vulva, vaginal cancer, vagina, penis cancer, penis, anal cancer, anus, oropharyngeal cancer, mouth, tonsils, or throat. Nearly all cervical cancer is due to HPV, and two strains – HPV16 and HPV18 – account for 70% of all cases. HPV16 is responsible for almost 90% of HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers. Between 60% and 90% of the other cancers listed above are also linked to HPV. HPV6 and HPV11 are common causes of genital warts and laryngeal papillomatosis. An HPV infection is caused by the ''human papillomavirus'', a DNA virus from the papi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoplasm
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, which may be called a tumour or tumor.'' ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, such as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word neoplasm is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), also known as cervical dysplasia, is the abnormal growth of cells on the surface of the cervix that could potentially lead to cervical cancer. More specifically, CIN refers to the potentially Precancerous condition, precancerous transformation of cells of the cervix. CIN most commonly occurs at the Transformation zone, squamocolumnar junction of the cervix, a transitional area between the Squamous epithelial cell, squamous epithelium of the vagina and the columnar epithelium of the endocervix. It can also occur in vaginal walls and vulvar epithelium. CIN is graded on a 1–3 scale, with 3 being the most abnormal (see classification section below). Human papillomavirus (Human papillomavirus infection, HPV) infection is necessary for the development of CIN, but not all with this infection develop cervical cancer. Many women with HPV infection never develop CIN or cervical cancer. Typically, HPV resolves on its own. However, those with an HPV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |