|
SJ F
Littera F was a class of electric locomotives operated by the Swedish state railways (SJ) between 1942 and 1983. Twenty-four F-locomotives were constructed and delivered between 1942 and 1949. The design was a rigid-framed locomotive with quill drive and the axle arrangement 1′Do1′, inspired by the German type E 18. The F-locomotives pulled express passenger trains and express freight trains. History SJ decided in the late 1930s to rebuild the single-track mainline routes Stockholm-Gothenburg (Västra Stambanan) and Katrineholm-Malmö into double-track lines and hence increasing the maximum allowed speed to . At the time, no locomotive at SJ was capable of reaching that speed and SJ decided to develop a new rigid-framed electric locomotive with quill drive and the axle arrangement 1′Do1′, inspired by the German type E 18. A traditional design with jackshaft drive and connecting rods with 3 or 4 powered axles was considered, based on the type D-locomotive, but was aba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Railway Museum
The Swedish Railway Museum, ( sv, Sveriges Järnvägsmuseum), in Gävle, Gästrikland, Sweden is the national museum for Sweden's railway history. The Swedish Railway Museum is tasked with acquiring, preserving and supplying knowledge about Swedish railway history on the basis of the national collection. The museum is owned by Trafikverket (Swedish Transport Administration), which receives an annual sum for the museum's activities from the Government. History In 1915, the National Railway Board opened a railway museum in Stockholm. In 1942, a hall for locomotives and rolling stock was added at Tomteboda railway station in Stockholm. The Swedish Railway Museum has been located in Gävle since 1970. The Museum has the use of two yards with tracks and several large buildings, including two round loco sheds and a sizeable workshop. The complex covers a total area of some 16,000 square metres. Collections Some items for the collection had already been acquired by the end of the 19t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karlskrona
Karlskrona (, , ) is a locality and the seat of Karlskrona Municipality, Blekinge County, Sweden with a population of 66,675 in 2018. It is also the capital of Blekinge County. Karlskrona is known as Sweden's only baroque city and is host to Sweden's largest naval base and the headquarters of the Swedish Coast Guard. Historically, the city has been home to a German minority, thus enabling the formation of a German Congregational church. It also counted Jewish people in its population. In 1998, parts of the city, including the Karlskrona naval base, was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site. History The island on which Karlskrona was built, Trossö, was owned during the 17th century by the farmer Vittus Andersson. Under Danish rule, there was another, older town called Lyckå on the mainland a couple of kilometers away. A little further away, the Danes had started to build Kristianopel before Blekinge fell under Swedish rule in 1658. Until 1679, the island and the ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
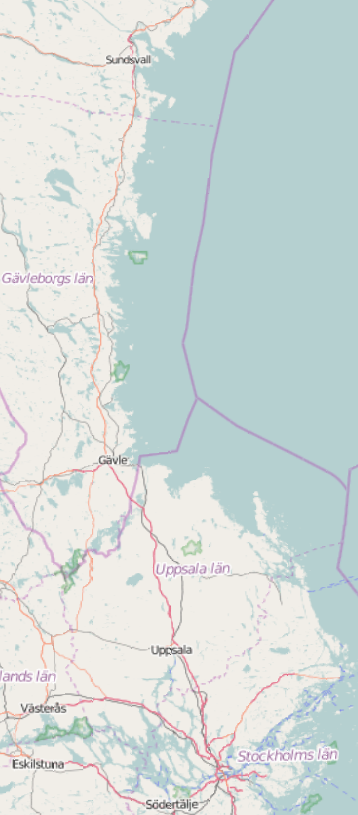
East Coast Line (Sweden)
The East Coast Line ( sv, Ostkustbanan) is a long mainline railway in Sweden, linking the cities of Stockholm, Uppsala, Gävle and Sundsvall, as well as the suburbs north of Stockholm. History At the construction of the first Swedish mainline railway network 1856–1891 there was a principle to avoid the coasts. This was for military reasons (protect against attacks, airplanes did not exist) and to bring steam powered transport to areas without any. The coasts already had steamboats. The Northern Main Line was built Stockholm–Uppsala–Avesta– Storvik–Ånge. Gävle, Söderhamn and Sundsvall which today are located along the East Coast Line were then connected by branches from the mainline. The first part of today's East Coast Line was the Stockholm–Uppsala part of the Northern Main Line, which opened on 20 September 1866. It was followed by the Uppsala–Gävle Railway, which was built by a private company and opened 1874. The railway Gävle–Sundsvall–Härnösand wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SJ Rc
The Rc class is the most used electric locomotive in Sweden. Rc is a universal locomotive used both in freight and passenger trains. The largest operator is Green Cargo, although SJ, Tågab, Hector Rail and the Swedish Transport Administration operate it as well. Previous operators include Veolia Transport. History The Rc-locomotive first appeared in 1967 to replace the older D-locomotives. The locomotives are notable for using thyristors instead of the older relay based system. Usage As of 2020, Rc-locomotives are still used all over Sweden in both passenger and freight lines, although on passenger trains they are slowly being replaced by new EMU, such as ER1. Versions Altogether, there have been eight versions of the Rc-locomotive in Sweden, including the freight locomotive Rm designed to pull iron ore trains. Rc1, Rc2, Rc4, and Rc5 have a maximum allowed speed of 135 km/h. Rc3 and Rc6 have a maximum allowed speed of 160 km/h. Rc7 was a rebuild of Rc6 meant t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandbox (locomotive)
A sandbox is a container on most locomotives, multiple units and trams that holds sand, which is dropped on the rail in front of the driving wheels in wet and slippery conditions and on steep grades to improve traction. Sand delivery The sand may be delivered by gravity, by a steam-blast (steam locomotives) or by compressed air. Gravity sanding requires that the sand be dry so that it runs freely. Locomotives use multiple sandboxes, so that their delivery pipes could be short and nearly vertical. Engine sheds in the UK were equipped with sand drying stoves, so that sandboxes could be refilled each morning with dry sand. Steam locomotives in the US had a single sandbox, called a sand dome, atop the boiler where the rising heat helped to dry the sand. Even with this arrangement, sand pipes tended to clog, and by the 1880s, pneumatic sanding systems were being proposed. Steam sanding The development of steam sanding was influential on locomotive design. As the sand could then be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bissel Truck
A Bissell or Bissel truck (also Bissel bogie or Pony truck) is a single-axle bogie which pivots towards the centre of a steam locomotive A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the loco ... to enable it to negotiate curves more easily. Invented in 1857 by and usually then known as a ''pony truck'', it is a very simple and common means of designing a carrying wheel. Name variants A pony truck in railway terminology, is a leading truck with only two wheels. Its invention is generally credited to Bissell, who devised one in 1857 in rail transport, 1857 and patented it the following year. Hence the term ''Bissel bogie'', ''Bissel truck'', or ''Bissel axle'' is used in continental Europe. In the UK, the term is Bissell truck. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Société Anonyme Des Ateliers De Sécheron
The (SAAS, in English translated as ''"Anonymous Society of Sécheron Workshops"'') was a joint-stock company based in Geneva, Switzerland. It specialized in electrical engineering, including the manufacture of electrical equipment and locomotives. In 1989, the company was split into four successor companies, ABB Sécheron SA, ABB Power Generation (closed in 1995), ABB Systèmes de Transport and Sécheron SA. History In 1879, Alfred de Meuron set up a small workshop in Geneva to manufacture electrical appliances. This workshop ultimately formed the basis for the establishment of SAAS on 9 July 1918. The following year, 1919, Brown Boveri & Cie (BBC) became SAAS's main shareholder. Five years later, SAAS resumed its independence. The company remained independent until 1969, when competitive pressures forced it to seek new partners. In 1970, BBC took over as sole shareholder. However, the company's name was changed only in 1982, when it became BBC Sécheron SA. In 198 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SJ D
D is a series of locomotives used by Swedish State Railways ( sv, Statens Järnvägar, SJ). 333 units were built by ASEA between 1925-43. It was used for both passenger and freight trains until it was taken out of service in 1988. History Though SJs first electric locomotive was the Oa series used on Malmbanan, it was not suitable for use on the main lines, due to low speeds. To solve this problem SJ surveyed a large section of locomotives abroad, before concluding with a design and placed an order with ASEA for 50 units. While ASEA was responsible for the electrical components, ASJ, NOHAB and Motala Verkstad were responsible for the mechanical parts. The first series consisted of two models, the Ds used for express trains and the Dg for freight trains. The former had 90 km/h as maximum speed while Dg only had 70 km/h. The first units were delivered in 1925 and tested on Malmbanan until Västra Stambanan between Stockholm and Göteborg was finished in 1926. Additional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jackshaft (locomotive)
A jackshaft is an intermediate shaft used to transfer power from a powered shaft such as the output shaft of an engine or motor to driven shafts such as the drive axles of a locomotive. As applied to railroad locomotives in the 19th and 20th centuries, jackshafts were typically in line with the drive axles of locomotives and connected to them by side rods. In general, each drive axle on a locomotive is free to move about one inch (2.5 cm) vertically relative to the frame, with the locomotive weight carried on springs. This means that if the engine, motor or transmission is rigidly attached to the locomotive frame, it cannot be rigidly connected to the axle. This problem can be solved by mounting the jackshaft on unsprung bearings and using side-rods or (in some early examples) chain drives.General Construction, Baldwin Gasoline Industrial LocomotiveBaldwin Locomotive Works Record No. 74, 1913; pages 7-9. Jackshafts were first used in early steam locomotives, although the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DRG Class E 18
The Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft (DRG) Class E 18 is a class of electric locomotives built in Germany and Austria between 1935 and 1955. With exception of Class E 19 it was Deutsche Reichsbahn's fastest electric locomotive. After 1945 most of the surviving locomotives were operated by Deutsche Bundesbahn (DB), although a few passed to Deutsche Reichsbahn (DR) and Österreichische Bundesbahnen (ÖBB). In addition to the 55 locomotives built in Germany, a further 8 locomotives of a modified design were built in Austria in 1939 as ''Class E 18.2'' (later ÖBB class 1018). Development dates back to the year 1881, when near Berlin the first public line was taken into service in Berlin. German WP article on electric traction Despite successful test runs with three-phase current electric railcars up to a top speed of in 1903, the German state railways decided to use single-phase alternating current because the overhead line of three-phase current was very complicated. The first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Västra Stambanan
The Western Main Line ( sv, Västra stambanan) is the main state-owned railway line between Stockholm and Gothenburg in Sweden. Its construction began in 1856 and it opened for service in 1862. Trafikverket. Retrieved 2019-03-02. Maintained by the Swedish Transport Administration, the Western Main Line is electrified and consists entirely of |
Quill Drive
A quill is a writing tool made from a moulted flight feather (preferably a primary wing-feather) of a large bird. Quills were used for writing with ink before the invention of the dip pen, the metal- nibbed pen, the fountain pen, and, eventually, the ballpoint pen. As with the earlier reed pen (and later dip pen), a quill has no internal ink reservoir and therefore needs to periodically be dipped into an inkwell during writing. The hand-cut goose quill is rarely used as a calligraphy tool anymore because many papers are now derived from wood pulp and would quickly wear a quill down. However, it is still the tool of choice for a few scribes who have noted that quills provide an unmatched sharp stroke as well as greater flexibility than a steel pen. Description The shaft of a flight feather is long and hollow, making it an obvious candidate for being crafted into a pen. The process of making a quill from a feather involves curing the shaft to harden it, then fashioning its tip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
.jpg)

