|
SARS-related Coronavirus
Severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus (SARSr-CoV or SARS-CoV'', Betacoronavirus pandemicum'')The terms ''SARSr-CoV'' and ''SARS-CoV'' are sometimes used interchangeably, especially prior to the discovery of SARS-CoV-2. This may cause confusion when some publications refer to SARS-CoV-1 as ''SARS-CoV''. is a species of virus consisting of many known strains. Two strains of the virus have caused outbreaks of severe respiratory diseases in humans: severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1 (SARS-CoV or SARS-CoV-1), the cause of the 2002–2004 outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the cause of the pandemic of COVID-19. There are hundreds of other strains of SARSr-CoV, which are only known to infect non-human mammal species: bats are a major reservoir of many strains of SARSr-CoV; several strains have been identified in Himalayan palm civets, which were likely ancestors of S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
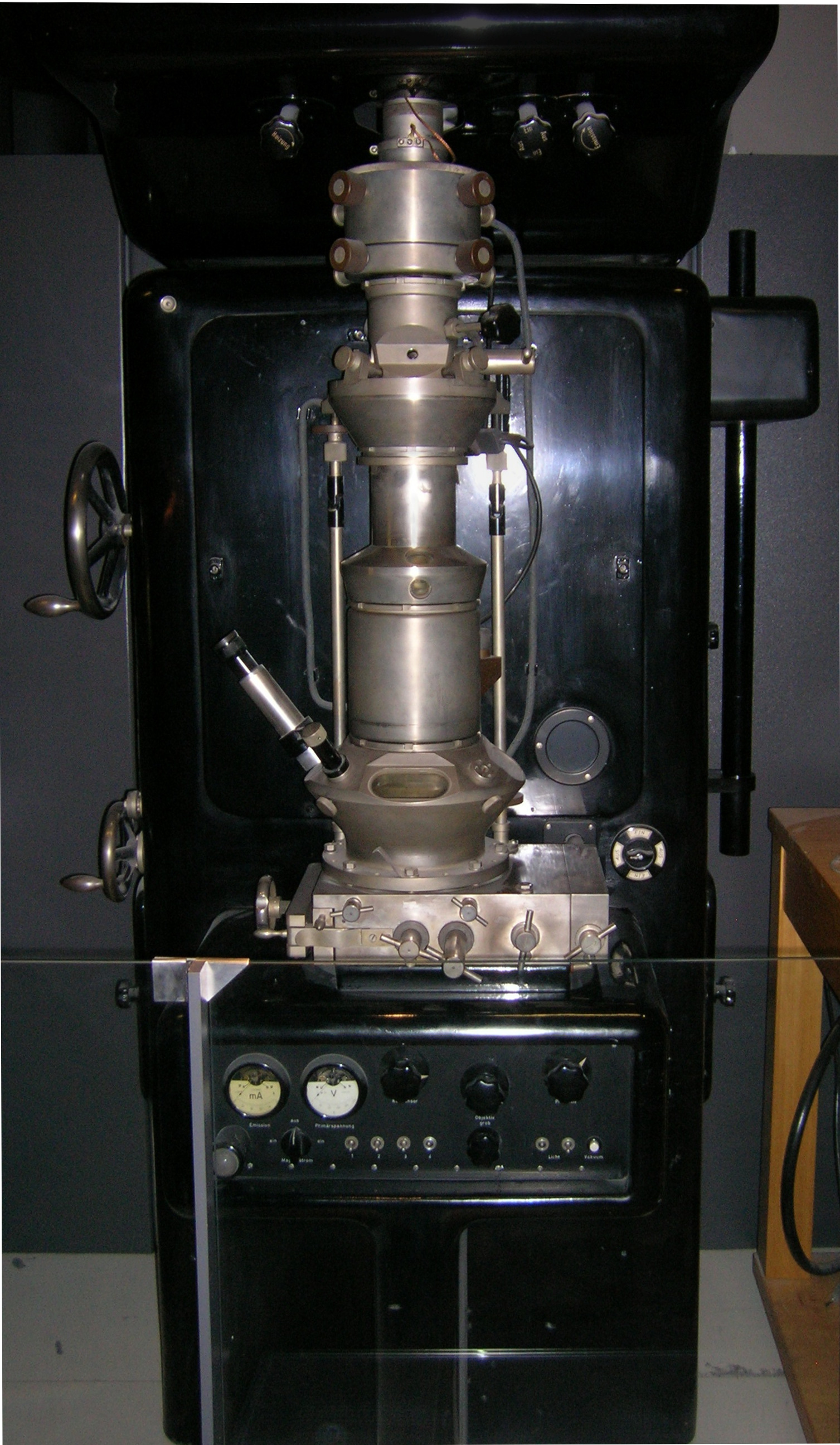
Transmission Electron Micrograph
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. The specimen is most often an ultrathin section less than 100 nm thick or a suspension on a grid. An image is formed from the interaction of the electrons with the sample as the beam is transmitted through the specimen. The image is then magnified and Focus (optics), focused onto an imaging device, such as a fluorescent screen, a layer of photographic film, or a Detectors for transmission electron microscopy, detector such as a scintillator attached to a charge-coupled device or a direct electron detector. Transmission electron microscopes are capable of imaging at a significantly higher Optical resolution, resolution than Optical microscope, light microscopes, owing to the smaller de Broglie wavelength of electrons. This enables the instrument to capture fine detail—even as small as a single column of atoms, which is thousands o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
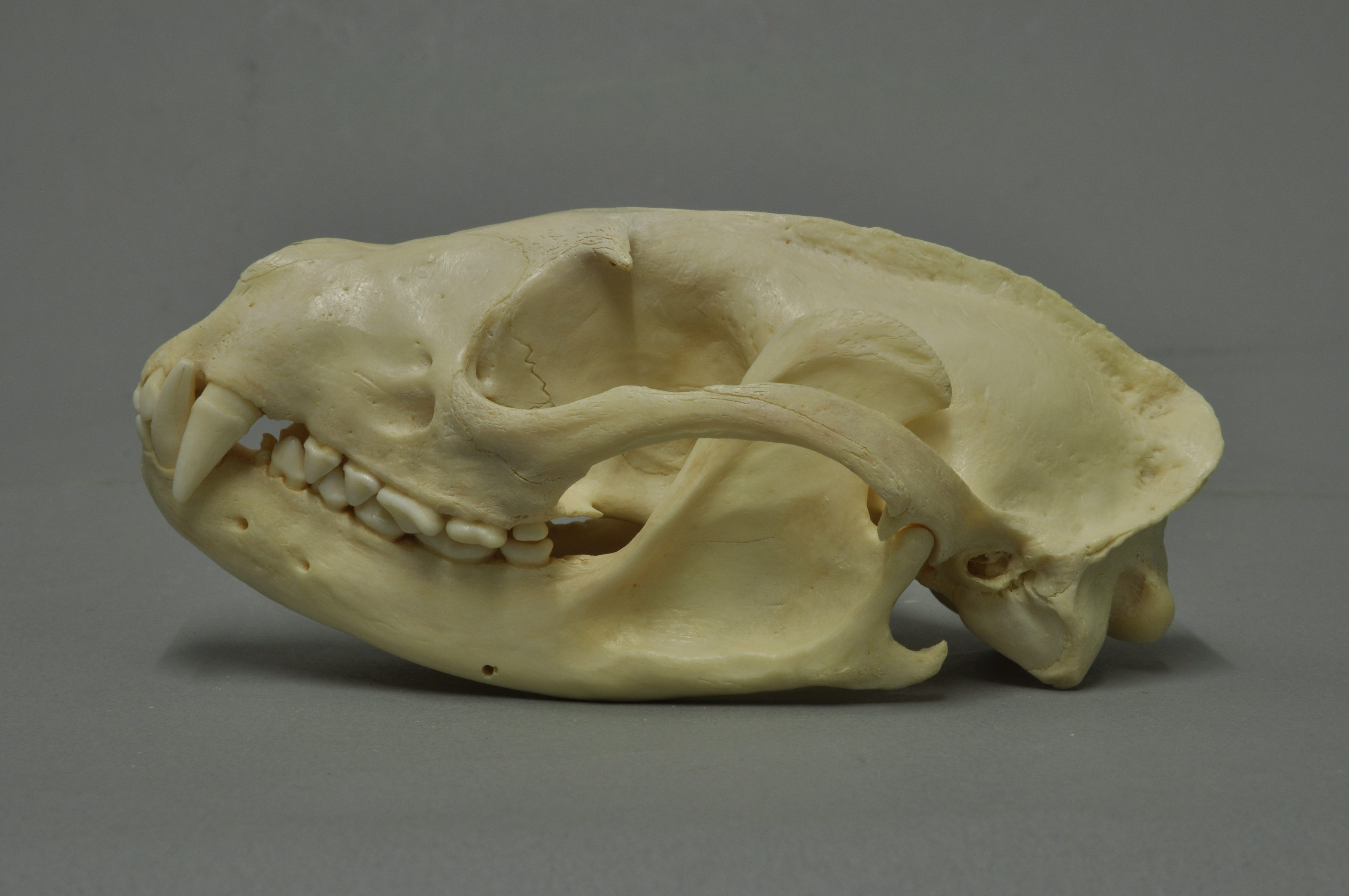
Himalayan Palm Civet
The masked palm civet (''Paguma larvata''), also called the gem-faced civet or Himalayan palm civet, is a viverrid species native to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. It has been listed as least concern on the IUCN Red List since 2008 as it occurs in many protected areas, is tolerant to some degree of habitat modification, and widely distributed with presumed large populations that are unlikely to be declining. The genus ''Paguma'' was first named and described by John Edward Gray in 1831. All described forms are regarded as a single species. In 2003, masked palm civets at a wildlife market in China were found to have been infected with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Characteristics The masked palm civet's fur is grayish to ochraceous, black on the head, shoulders and neck, and blackish brown on the tail and feet. It has a white blaze on the forehead; white marks above and below the eyes extend to the ears, forming a half-collar. In morpholo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphacoronavirus
Alphacoronaviruses (Alpha-CoV) are members of the first of the four genera (''Alpha''-, '' Beta-'', '' Gamma-'', and '' Delta-'') of coronaviruses. They are positive-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses that infect mammals, including humans. They have spherical virions with club-shaped surface projections formed by trimers of the spike protein, and a viral envelope. Alphacoronaviruses are in the subfamily ''Orthocoronavirinae'' of the family '' Coronaviridae''. Both the ''Alpha''- and ''Betacoronavirus'' lineages descend from the bat viral gene pool. Alphacoronaviruses were previously known as " phylogroup 1 coronaviruses". The Alphacoronavirus genus is very diverse, particularly in bats. Most bat originating strains haven't been successfully isolated and cultured in laboratory. Alphacoronaviruses infecting other mammal species have been much better studied, see List of Coronavirus live isolates. Etymology The name alphacoronavirus is derived from Ancient Greek ἄλφα ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embecovirus
''Embecovirus'' is a subgenus of coronaviruses in the genus '' Betacoronavirus''. The viruses in this subgenus, unlike other coronaviruses, have a hemagglutinin esterase (HE) gene. The viruses in the subgenus were previously known as group 2a coronaviruses. Taxonomy The subgenus contains the following species, listed by scientific name and followed by the exemplar virus of the species: * '' Betacoronavirus gravedinis'', Human coronavirus OC43 * ''Betacoronavirus hongkongense'', Human coronavirus HKU1 * ''Betacoronavirus muris'', Murine hepatitis virus * ''Betacoronavirus myodae'', Myodes rufocanus vole coronavirus 2/JL2014 * ''Betacoronavirus ratti'', Betacoronavirus HKU24 Structure The viruses of this subgenus, like other coronaviruses, have a lipid bilayer envelope in which the membrane (M), envelope (E) and spike (S) structural proteins are anchored. Unlike other coronaviruses, viruses in this subgenus also have an additional shorter spike-like structural protein c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Taxon
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of Genus, genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. Theoretical implications Monotypic taxa present several important theoretical challenges in biological classification. One key issue is known as "Gregg's Paradox": if a single species is the only member of multiple hierarchical levels (for example, being the only species in its genus, which is the only genus in its family), then each level needs a distinct definition to maintain logical structure. Otherwise, the different taxonomic ranks become effectively identical, which creates problems for organizing biological diversity in a hierarchical o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicines
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and relies on the science of pharmacology for continual advancement and on pharmacy for appropriate management. Drugs are classified in many ways. One of the key divisions is by level of control, which distinguishes prescription drugs (those that a pharmacist dispenses only on the medical prescription) from over-the-counter drugs (those that consumers can order for themselves). Medicines may be classified by mode of action, route of administration, biological system affected, or therapeutic effects. The World Health Organization keeps a list of essential medicines. Drug discovery and drug development are complex and expensive endeavors undertaken by pharmaceutical companies, academic scientists, and governments. As a resu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaccines
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious or malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins. The agent stimulates the body's immune system to recognize the agent as a threat, destroy it, and recognize further and destroy any of the microorganisms associated with that agent that it may encounter in the future. Vaccines can be prophylactic (to prevent or alleviate the effects of a future infection by a natural or "wild" pathogen), or therapeutic (to fight a disease that has already occurred, such as cancer). Some vaccines offer full sterilizing immunity, in which infection is prevented. The administration of vaccines is called vaccination. Vaccination is the most effective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagnostic Tests
A medical test is a medical procedure performed to detect, diagnose, or monitor diseases, disease processes, susceptibility, or to determine a course of treatment. Medical tests such as, physical and visual exams, diagnostic imaging, genetic testing, chemical and cellular analysis, relating to clinical chemistry and molecular diagnostics, are typically performed in a medical setting. Types of tests By purpose Medical tests can be classified by their purposes, including diagnosis, screening or monitoring. Diagnostic A diagnostic test is a procedure performed to confirm or determine the presence of disease in an individual suspected of having a disease, usually following the report of symptoms, or based on other medical test results. This includes posthumous diagnosis. Examples of such tests are: * Using nuclear medicine to examine a patient suspected of having a lymphoma. * Measuring the blood sugar in a person suspected of having diabetes mellitus after periods of increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western African Ebola Virus Epidemic
The 2013–2016 epidemic of Ebola virus disease, centered in West Africa, was the most widespread outbreak of the disease in history. It caused major loss of life and socioeconomic disruption in the region, mainly in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone. The first cases were recorded in Guinea in December 2013; the disease spread to neighbouring Liberia and Sierra Leone, with minor outbreaks occurring in Nigeria and Mali. Secondary infections of medical workers occurred in the United States and Spain. Isolated cases were recorded in Senegal, the United Kingdom and Italy. The number of cases peaked in October 2014 and then began to decline gradually, following the commitment of substantial international resources. It caused significant mortality, with a considerable case fatality rate. By the end of the epidemic, 28,616 people had been infected; of these, 11,310 had died, for a case-fatality rate of 40%. , the World Health Organization (WHO) and respective governments reporte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of hosts in a given population within a short period of time. For example, in meningococcal infections, an attack rate in excess of 15 cases per 100,000 people for two consecutive weeks is considered an epidemic. Epidemics of infectious disease are generally caused by several factors including a change in the ecology of the host population (e.g., increased stress or increase in the density of a vector species), a genetic change in the pathogen reservoir or the introduction of an emerging pathogen to a host population (by movement of pathogen or host). Generally, an epidemic occurs when host immunity to either an established pathogen or newly emerging novel pathogen is suddenly reduced below that found in the endemic equilibrium and the transmission threshold is exceeded. An epidemic may be restricted to one location; however, if it sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, and has 6 regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide. Only sovereign states are eligible to join, and it is the largest intergovernmental health organization at the international level. The WHO's purpose is to achieve the highest possible level of health for all the world's people, defining health as "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity." The main functions of the World Health Organization include promoting the control of epidemic and endemic diseases; providing and improving the teaching and training in public health, the medical treatment of disease, and related matters; and promoting the establishment of international standards for biologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Betacoronavirus
''Betacoronavirus'' (β-CoVs or Beta-CoVs) is one of four genera (''Alphacoronavirus, Alpha''-, ''Beta-'', ''Gammacoronavirus, Gamma-'', and ''Deltacoronavirus (genus), Delta-'') of coronaviruses. Member viruses are Viral envelope, enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses that infect mammals, including humans. The natural reservoir for betacoronaviruses are bats and rodents. Rodents are the reservoir for the subgenus ''Embecovirus'', while Bat virome, bats are the reservoir for the other subgenera. The coronavirus genera are each composed of varying viral lineages with the betacoronavirus genus containing four such lineages: A, B, C, D. In older literature, this genus is also known as "group 2 coronaviruses". The genus is in the subfamily ''Orthocoronavirinae'' in the family ''Coronaviridae'', of the order ''Nidovirales''. The betacoronaviruses of the greatest clinical importance concerning humans are Human coronavirus OC43, OC43 and Human coronavirus HKU1, HKU1 (which can cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |