|
Rutuli
The Rutuli or Rutulians were an ancient people in Italy. The Rutuli were located in a territory whose capital was the ancient town of Ardea, located about 35 km southeast of Rome. Thought to have been descended from the Umbri and the Pelasgians, according to modern scholars they were more probably connected with the Etruscan or Ligurian peoples. Mythological history In Virgil's ''Aeneid'', and also according to Livy, the Rutuli are led by Turnus, a young prince to whom Latinus, king of the Latins, had promised the hand of his daughter Lavinia in marriage. When the Trojans arrived in Italy, Latinus decided to give his daughter to Aeneas instead because of instructions he had received from the gods to marry his daughter to a foreigner. Turnus was outraged and led his people as well as several other Italian tribes against the Trojans in war. Virgil's text ends when Aeneas defeats Turnus in single combat and therefore confirms his right to marry Lavinia. In some other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeneid
The ''Aeneid'' ( ; or ) is a Latin Epic poetry, epic poem that tells the legendary story of Aeneas, a Troy, Trojan who fled the Trojan War#Sack of Troy, fall of Troy and travelled to Italy, where he became the ancestor of the Ancient Rome, Romans. Written by the Roman poet Virgil between 29 and 19 BC, the ''Aeneid'' comprises 9,896 lines in dactylic hexameter. The first six of the poem's twelve books tell the story of Aeneas' wanderings from Troy to Italy, and the poem's second half tells of the Trojans' ultimately victorious war upon the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins, under whose name Aeneas and his Trojan followers are destined to be subsumed. The hero Aeneas was already known to Greco-Roman legend and myth, having been a character in the ''Iliad''. Virgil took the disconnected tales of Aeneas' wanderings, his vague association with the foundation of Ancient Rome, Rome and his description as a personage of no fixed characteristics other than a scrupulous ''pietas'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turnus
Turnus () was the legendary King of the Rutuli in Roman history, and the chief antagonist of the hero Aeneas in Virgil's ''Aeneid''. According to the ''Aeneid'', Turnus is the son of Daunus and the nymph Venilia and is brother of the nymph Juturna. Historical tradition While there is limited information in historical sources about Turnus, some key details about Turnus and the Rutuli differ significantly from the account in the Aeneid. The only source predating the Aeneid is Marcus Porcius Cato's ''Origines''. Turnus is also mentioned by Livy in his ''Ab Urbe Condita'' and by Dionysius of Halicarnassus in his (''Rômaïkê Archaiologia'', "''Roman Antiquities''"), both of which come later than the ''Aeneid''. Turnus is mentioned in the Pseudo-Jasher, along with Angeas of Africa. In all of these historical sources, Turnus' heritage is unclear. Dionysius calls him ''Tyrrhenus'', which means " Etruscan", while other sources suggest a Greek ancestry. In all of these sourc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
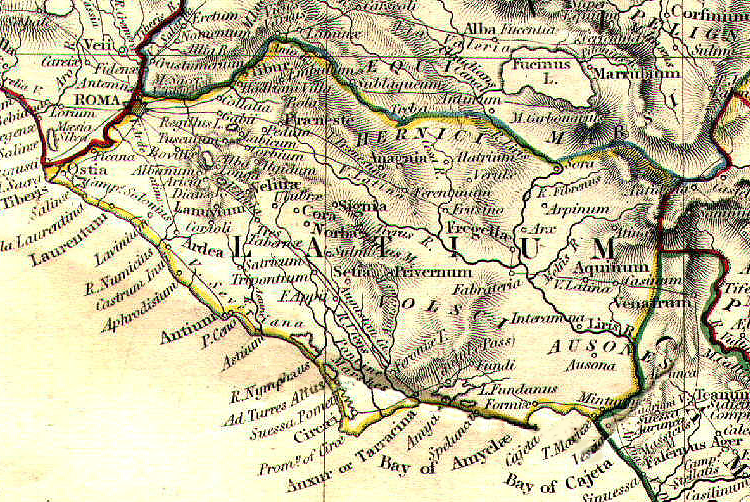
Ancient Latium
or ' () is a region of the Italian Peninsula bounded to the north by the Tiber River, to the east by the central Apennine Mountains, to the west by the Mediterranean Sea and to the south by Monte Circeo. It was the territory of the Latins, an Italic tribe which included the early inhabitants of the city of Rome. Later it was also settled by various Italic tribes such as the Rutulians, Volscians, Aequi, and Hernici. The region was referred to as "old" to distinguish it from the expanded region, Latium, that included the region to the south of Old Latium, between Monte Circeo and the river Garigliano – the so-called Latium adiectum ("attached Latium"). It corresponded to the central part of the modern administrative region of Lazio, Italy, and it covered an area measuring of roughly 50 Roman miles. It was calculated by Mommsen that the region's area was about 1860 square kilometres. Settlement Literary tradition Dionysius of Halicarnassus has preserved extensive informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucius Tarquinius Superbus
Lucius Tarquinius Superbus (died 495 BC) was the legendary seventh and final king of Rome, reigning 25 years until the popular uprising that led to the establishment of the Roman Republic.Livy, ''ab urbe condita libri'', wikisource:From_the_Founding_of_the_City/Book_1, I He is commonly known as Tarquin the Proud, from his cognomen ''Superbus'' (Latin for "proud, arrogant, lofty"). Ancient accounts of the Roman Kingdom, regal period mingle history and legend. Tarquin was said to have been either the son or grandson of Lucius Tarquinius Priscus, the fifth king of Rome, and to have gained the throne through the murders of both his wife and his elder brother, followed by the assassination of his predecessor, Servius Tullius. His reign has been described as a tyranny that justified the abolition of Roman Kingdom, the monarchy. Background The most ancient sources, such as that of Quintus Fabius Pictor, assert Tarquin was the son of Tarquinius Priscus, but modern historians believ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; 15 October 70 BC21 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Rome, ancient Roman poet of the Augustan literature (ancient Rome), Augustan period. He composed three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: the ''Eclogues'' (or ''Bucolics''), the ''Georgics'', and the Epic poetry, epic ''Aeneid''. A number of minor poems, collected in the ''Appendix Vergiliana'', were attributed to him in ancient times, but modern scholars generally regard these works as spurious, with the possible exception of a few short pieces. Already acclaimed in his own lifetime as a classic author, Virgil rapidly replaced Ennius and other earlier authors as a standard school text, and stood as the most popular Latin poet through late antiquity, the Middle Ages, and early modernity, exerting inestimable influence on all subsequent Western literature. Geoffrey Chaucer assigned Virgil a uniquely prominent position among all the celebrities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeneas
In Greco-Roman mythology, Aeneas ( , ; from ) was a Troy, Trojan hero, the son of the Trojan prince Anchises and the Greek goddess Aphrodite (equivalent to the Roman Venus (mythology), Venus). His father was a first cousin of King Priam of Troy (both being grandsons of Ilus (son of Tros), Ilus, founder of Troy), making Aeneas a second cousin to Priam's List of children of Priam, children (such as Hector and Paris (mythology), Paris). He is a minor character in Greek mythology and is mentioned in Homer's ''Iliad''. Aeneas receives full treatment in Roman mythology, most extensively in Virgil's ''Aeneid'', where he is cast as an ancestor of Romulus and Remus. He became the first true hero of Rome. Snorri Sturluson identifies him with the Norse god Víðarr of the Æsir.The Prose Edda of Snorri Sturlson Translated by Arthur Gilchrist Brodeur [1916] Prologue II at Internet Sacred Texts Archive. Accessed 11/14/17 Etymology Aeneas is the Romanization of Greek, Romanization of the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ancient Peoples Of Italy
This list of ancient peoples living in Italy (geographical region), Italy summarises the many different Italian populations that existed in antiquity. Among them, the Roman people, Romans succeeded in Romanization (cultural), Romanizing the entire Italian peninsula following the Roman expansion in Italy, which provides the time-window in which most of the names of the remaining ancient Italian peoples first appear in existing written documentation. Many names are exonyms assigned by the ancient writers of works in ancient Greek and Latin, while others are scholarly inventions. Nearly all of these peoples and tribes spoke Indo-European language, Indo-European languages: Italic peoples, Italics, Celts, Ancient Greeks, and tribes likely occupying various intermediate positions between these language groups. On the other hand, some Italian peoples (such as the Rhaetians, Camuni, Etruscans) likely spoke Pre-Indo-European languages, non- or pre-Indo-European languages. In addition, peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Kingdom
The Roman Kingdom, also known as the Roman monarchy and the regal period of ancient Rome, was the earliest period of Ancient Rome, Roman history when the city and its territory were King of Rome, ruled by kings. According to tradition, the Roman Kingdom began with the Founding of Rome, city's founding , with settlements around the Palatine Hill along the river Tiber in central Italy, and ended with the Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, overthrow of the kings and the establishment of the Republic . Little is certain about the kingdom's history as no records and few inscriptions from the time of the kings have survived. The accounts of this period written during the Roman Republic, Republic and the Roman Empire, Empire are thought largely to be based on oral tradition. Origin The site of the founding of the Roman Kingdom (and eventual Roman Republic, Republic and Roman Empire, Empire) included a ford (crossing), ford where one could cross the river Tiber in central Roman Italy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latinus
Latinus (; Ancient Greek: Λατῖνος, ''Latînos'', or Λατεῖνος, ''Lateînos'') was a figure both in Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology. He is often associated with the heroes of the Trojan War, namely Odysseus and Aeneas. Although his appearance in the ''Aeneid'' is irreconcilable with his appearance in Greek mythology, the two pictures are so different that he cannot be seen as one character. Greek mythology In Hesiod's ''Theogony'', Latinus was the son of Odysseus and Circe who ruled the Tyrrhenians with his brothers Agrius and Telegonus (son of Odysseus), Telegonus. According to the Byzantine author John the Lydian, Hesiod, in the ''Catalogue of Women'', considered Latinus to be the brother of Graecus, who is described as the son of Zeus by Pandora (daughter of Deucalion), Pandora, the daughter of Deucalion and Pyrrha. In his ''Fabularum Liber'' (or ''Fabulae''), Gaius Julius Hyginus recorded the myth that Latinus was a son of Circe and Telemachus (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ardea, Lazio
Ardea () is an ancient town and ''comune ''(municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Rome Capital, south of Rome and about from today's Mediterranean coast. The economy is mostly based on agriculture, although, starting from the 1970s, industry has played an increasingly important role. Foundation legends The city's foundation is attributed to different sources. Some writers suggest it was established by Ardeas, a son of Odysseus and Circe, while the more widely accepted tradition attributes it to Danaë, the mother of Perseus. Both versions imply a Pelasgic origin. Barthold Georg Niebuhr considers Ardea to have been the chief city of the Pelasgian segment of the Latin nation. He also connects its king, Turnus, to the Tyrrhenians. In the Aeneid, Ardea is portrayed as the capital of the Rutuli, a people who either vanished or merged into the Latin population. Despite this, King Turnus is depicted as being under Latinus authority while maintaining his own sovereignty. Additi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lavinia
In Roman mythology, Lavinia ( ; ) is the daughter of Latinus and Amata, and the last wife of Aeneas. Creation It has been proposed that the character was in part intended to represent Servilia Isaurica, Emperor Augustus's first fiancée. Story Lavinia, the only child of the king and "ripe for marriage", had been courted by many men who hoped to become the king of Latium. Turnus, ruler of the Rutuli, was the most likely of the suitors, having the favor of Queen Amata. In Virgil's account, King Latinus is warned by his father Faunus in a dream oracle that his daughter is not to marry a Latini, Latin: Lavinia has what is perhaps her most, or only, memorable moment in Book 7 of the ''Aeneid'', lines 94–104: during a sacrifice at the altars of the gods, Lavinia's hair catches fire, an omen promising glorious days to come for Lavinia and war for all Latins: Not long after the dream oracle and the prophetic moment, Aeneas sends emissaries bearing several gifts for King Latinus. K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Italy
The prehistory of Italy began in the Paleolithic period, when members of the genus ''Homo'' first inhabited what is now modern Italian territory, and ended in the Iron Age, when the first written records appeared in Italy. Paleolithic In prehistoric times, the landscape of the Italian Peninsula was significantly different from its modern appearance. During glaciations, for example, the sea level was lower and the islands of Elba and Sicily were connected to the mainland. The Adriatic Sea began at what is now the Gargano Peninsula, and what is now its surface up to Venice was a fertile plain with a humid climate. The arrival of the first known hominins was 850,000 years ago at Monte Poggiolo. The presence of ''Homo neanderthalensis'' has been demonstrated in archaeological findings dating to c. 50,000 years ago (late Pleistocene). There are about 20 unique sites, the most important being that of the Grotta Guattari at San Felice Circeo, on the Tyrrhenian Sea south of Rome; a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |