|
Russian Peasants' Uprising Of 1905–1906
The Russian peasants' uprising of 1905–1906, also known as the Jaquerie of 1905–1906 or the agrarian revolt of 1905–1906, was a series of peasant uprisings and violence that broke out throughout the Russian Empire in the years of 1905–1906. Background The peasants uprising was connected to the 1905 Revolution and the October Manifesto, as the country was gripped by a revolutionary and rebellious atmosphere following Tsar Nicholas II reactionary policies. After Bloody Sunday in January, large instances of rebellion exploded throughout the country, initiating the 1905 Revolution. The revolution forced the reactionary Tsar to make concessions, and in October he issued a manifesto granting some civil liberties to prevent the nation from slipping into chaos, trying to 'pacify' the country. The revolt The general 'mood of rebellion' riding the country quickly spread to the provinces and the countryside. Seeing the weakness of the government, they started organising rent s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
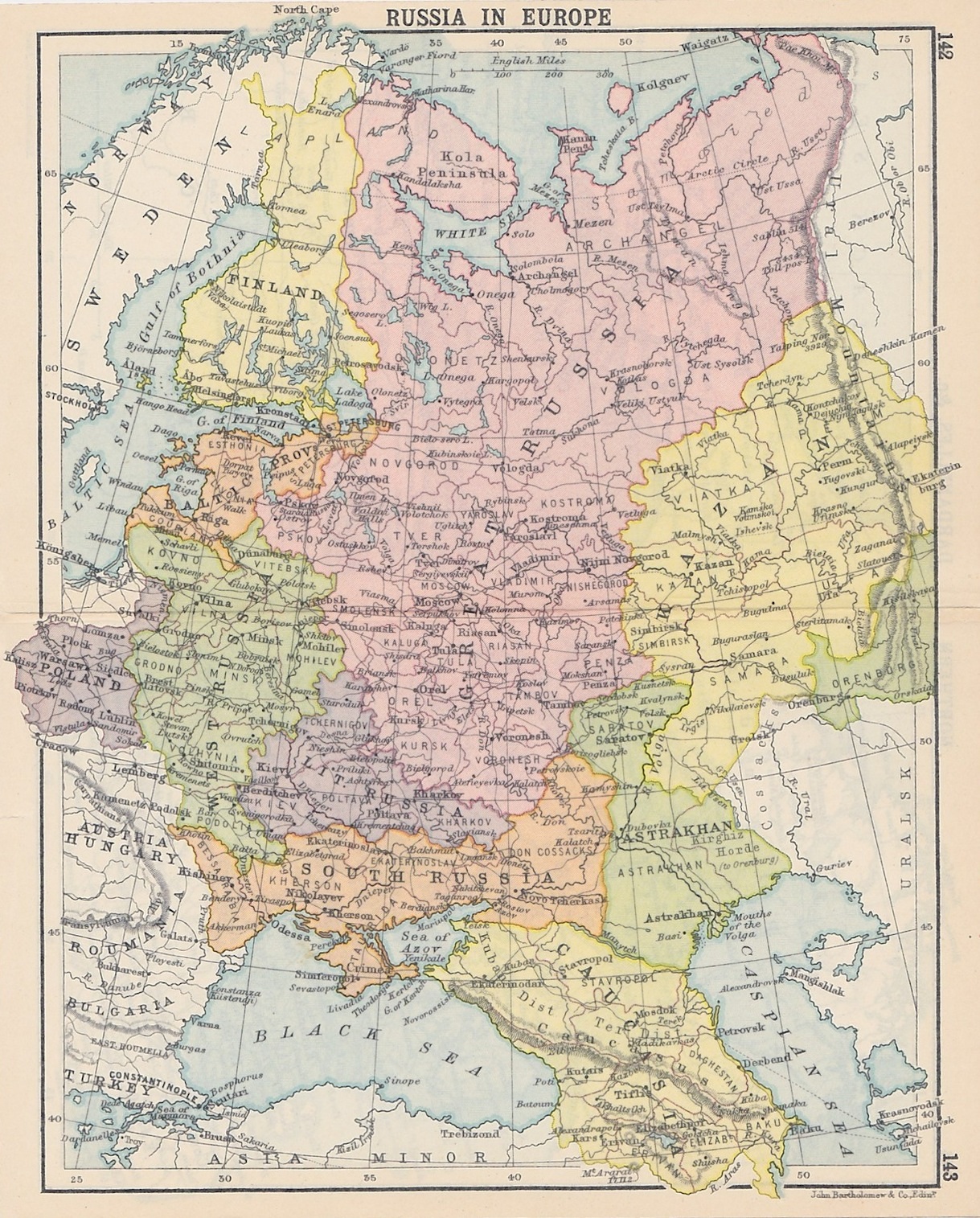
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughly one-sixth of the world's landmass, making it the list of largest empires, third-largest empire in history, behind only the British Empire, British and Mongol Empire, Mongol empires. It also Russian colonization of North America, colonized Alaska between 1799 and 1867. The empire's 1897 census, the only one it conducted, found a population of 125.6 million with considerable ethnic, linguistic, religious, and socioeconomic diversity. From the 10th to 17th centuries, the Russians had been ruled by a noble class known as the boyars, above whom was the tsar, an absolute monarch. The groundwork of the Russian Empire was laid by Ivan III (), who greatly expanded his domain, established a centralized Russian national state, and secured inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peasant Uprising
This is a chronological list of revolts organized by peasants. Background The history of peasant wars spans over two thousand years. A variety of factors fueled the emergence of the peasant revolt phenomenon, including: * Tax resistance * Social inequality * Religious war * Wars of national liberation, National liberation * Resistance against serfdom * Land reform * External factors such as Black Death, plague and Great Famine of 1315-1317, famine Later peasant revolts such as the Telangana Rebellion were also influenced by Agrarian socialism, agrarian socialist ideologies such as Maoism. The majority of peasant rebellions ended prematurely and were unsuccessful. Peasants suffered from limited funding and lacked the training and organisational capabilities of professional armies. Chronological list The list gives the name, the date, the peasant allies and enemies, and the result of these conflicts following this legend: : : : : See also * Servile Wars * Peasant mov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1905 Revolution
The Russian Revolution of 1905, also known as the First Russian Revolution, was a revolution in the Russian Empire which began on 22 January 1905 and led to the establishment of a constitutional monarchy under the Russian Constitution of 1906, the country's first. The revolution was characterized by mass political and social unrest including worker strikes, peasant revolts, and military mutinies directed against Tsar Nicholas II and the autocracy, who were forced to establish the State Duma legislative assembly and grant certain rights, though both were later undermined. In the years leading up to the revolution, impoverished peasants had become increasingly angered by repression from their landlords and the continuation of semi-feudal relations. Further discontent grew due to mounting Russian losses in the Russo-Japanese War, poor conditions for workers, and urban unemployment. On , known as " Bloody Sunday", a peaceful procession of workers was fired on by guards outside the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
October Manifesto
The October Manifesto (), officially "The Manifesto on the Improvement of the State Order" (), is a document that served as a precursor to the Russian Empire's first Constitution, which was adopted the following year in 1906. The Manifesto was issued by Tsar Nicholas II (1868–1918, ruled 1894–1917), under the influence of Sergei Witte (1849–1915), on as a response to the Russian Revolution of 1905. Nicholas strenuously resisted these ideas, but gave in after his first choice to head a military dictatorship,''Scenarios of Power, From Alexander II to the Abdication of Nicholas II'' by Richard Wortman, p. 398 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porcelain
Porcelain (), also called china, is a ceramic material made by heating Industrial mineral, raw materials, generally including kaolinite, in a kiln to temperatures between . The greater strength and translucence of porcelain, relative to other types of pottery, arise mainly from Vitrification#Ceramics, vitrification and the formation of the mineral mullite within the body at these high temperatures. End applications include tableware, ceramic art, decorative ware such as figurines, and products in technology and industry such as Insulator (electricity), electrical insulators and laboratory ware. The manufacturing process used for porcelain is similar to that used for earthenware and stoneware, the two other main types of pottery, although it can be more challenging to produce. It has usually been regarded as the most prestigious type of pottery due to its delicacy, strength, and high degree of whiteness. It is frequently both glazed and decorated. Though definitions vary, po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Agricultural Zone
The Central Agricultural Zone is a traditional region of Russia. Historically it was the centre of agriculture and colonisation in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, and was one the most densely populated area of the Russian Empire. It was also the poorest. Before the emancipation of serfs, it was home to most of the Russian serf population, and later it was also the centre of the communal system, which contributed to the areas relative poverty compared to the rest of Russia. During the revolutionary years it was the centre of most agrarian violence, and later the centre of the Red Movement and Red Army during the Russian Revolution. Overview The Central Agricultural Zone was marked by lower living standards for peasants, and an extremely dense and poor rural population.Figes, p. 103–104Shanin, p. 93–94 It was surrounded by areas where commercial farming was prevalent: in the Baltic were capitalist farms able to hire wage-labour due to the Emancipation in 1817 with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saratov Governorate
Saratov Governorate () was an administrative-territorial unit (''guberniya'') of the Russian Empire and the Russian SFSR. History On December 25, 1769, the Saratov province was established as part of the Astrakhan Governorate. On January 11, 1780, Empress Catherine the Great issued a decree of the establishment of the Saratov governorship of the northern districts of the Astrakhan Governorate to begin on November 7 of that year, followed by a decree on who will lead the new governorship. For the grand opening of the Saratov governorship, on February 3, 1781, the Astrakhan governor, along with lieutenant-general Jacobi and Bishop Anthony arrived from Astrakhan. On August 23, 1781 the Empress issued a decree approving the emblems of the city of Saratov and several Saratov governorship county-level cities (Atkarsk, Balashov (town), Balashov, Kamyshin, Khvalynsk, Kuznetsk, Petrovsk, Saratov Oblast, Petrovsk, Serdobsk, Tsaritsyn, and Volsk). In 1796, 41 of the governorships which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trepov
Trepov is a Russian surname. Notable people with the name include: * Alexander Trepov (1862–1928), Prime Minister of the Russian Empire * Dmitri Feodorovich Trepov (1850–1906), Head of Moscow police and Governor-General of St. Petersburg * Fyodor Trepov (other), multiple people, including: **Fyodor Trepov (senior) (1809–1889), Russian government official **Fyodor Trepov (junior) Fyodor Fyodorovich Trepov (; – 27 March 1938) was a Russian military and government figure, General of the cavalry, governor general of the General Government of Galicia and Bukovina. He was a son of Fyodor Trepov (senior), Fyodor Tre ... (1854–1938), Russian military and government official {{surname Russian-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergey Witte
Count Sergei Yulyevich Witte (, ; ), also known as Sergius Witte, was a Russian statesman who served as the first prime minister of the Russian Empire, replacing the emperor as head of government. Neither liberal nor conservative, he attracted foreign capital to boost Russia's industrialization. Witte's strategy was to avoid the danger of wars. Witte served under the final two emperors of Russia, Alexander III () and Nicholas II ().Harcave, Sidney. (2004)''Count Sergei Witte and the Twilight of Imperial Russia: A Biography,'' p. xiii./ref> During the Russo-Turkish War (1877–78), he had risen to a position in which he controlled all the traffic passing to the front along the lines of the Odessa Railways. As finance minister from 1892–1903, Witte presided over extensive industrialization and achieved government monopoly control over an expanded system of railroad lines. Following months of civil unrest and outbreaks of violence in what became known as the 1905 Russian Rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Russian Army
The Imperial Russian Army () was the army of the Russian Empire, active from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was organized into a standing army and a state militia. The standing army consisted of Regular army, regular troops and two forces that served on separate regulations: the Cossacks, Cossack troops and the Islam in Russia, Muslim troops. A regular Russian army existed after the end of the Great Northern War in 1721.День Сухопутных войск России. Досье [''Day of the Ground Forces of Russia. Dossier''] (in Russian). TASS. 31 August 2015. During his reign, Peter the Great accelerated the modernization of Russia's armed forces, including with a decree in 1699 that created the basis for recruiting soldiers, military regulations for the organization of the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacquerie
The Jacquerie () was a popular revolt by peasants that took place in northern France in the early summer of 1358 during the Hundred Years' War. The revolt was centred in the valley of the Oise north of Paris and was suppressed after over two months of violence. This rebellion became known as "the Jacquerie" because the nobles derided peasants as "Jacques" or "Jacques Bonhomme" for their padded surplice, called a " jacque". The aristocratic chronicler Jean Froissart and his source, the chronicle of Jean le Bel, referred to the leader of the revolt as Jacque Bonhomme ("Jack Goodfellow"), though in fact the Jacquerie 'great captain' was named Guillaume Cale. The word ''jacquerie'' became a synonym of peasant uprisings in general in both English and French. Background After the capture of the French king ( John II, Froissart's ''bon roi Jean'' "good king John") by the English during the Battle of Poitiers in September 1356, power in France devolved fruitlessly among the Es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nobility
United Nobility (; ''Ob'yedinennoye dvoryanstvo'') was a political association active in the Russian Empire from 1906 to 1917. The organisation consisted of the Russian nobility and gentry. United Nobility was one of several landowners' organisations which were established in the wake of the Russian Peasants' uprising of 1905–1906, and the largest estates joined these groups as a part of a larger "gentry reaction" to the violence directed towards Russian squires.Figes, p. 206 Its leader was Count Aleksei Bobrinsky, brother-in-law of later Prime Minister Georgy Lvov. It was established to defend the property rights and the domination in local politics of the gentry. The organisation had a strong presence in the State Council, with one third of all seats being held by a member, and prevented the passing of liberal reforms from the Duma.Figes, p. 216 It had powerful supporters in the State Council, the Civil Service and the Tsar's court. The organisation led a campaign against t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |