|
Ruegeria Pomeroyi
''Ruegeria pomeroyi'' is a species of Gram-negative, rod-shaped, aerobic dimethylsulfoniopropionate- demethylating bacterium. Its type strain is DSS-3T (=ATCC 700808T =DSM 15171T). Its genome has been sequenced. Discovery ''Ruegeria pomeroyi'' was discovered off the coast of the Eastern United States in the laboratory of Mary Ann Moran, Ph.D. at the University of Georgia. ''R. pomeroyi'' was named after Lawrence "Larry" Pomeroy, the marine microbial ecologist who notably established in 1974 that marine bacteria play a substantial and pivotal role in ocean food web dynamics. Pomeroy was also a researcher at the University of Georgia. Genome The genome of the ''Ruegeria pomeroyi'' type strain (DSS-3) was completed in 2004. The genome is 4,109,442 base pairs long with a megaplasmid that is 491,611 base pairs long. Ecology ''Ruegeria pomeroyi'' is a coastal ocean bacterium in a lineage of bacteria commonly considered ecological "generalists." The relatively large genome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomonadota
Pseudomonadota (synonym Proteobacteria) is a major phylum of Gram-negative bacteria. The renaming of phyla in 2021 remains controversial among microbiologists, many of whom continue to use the earlier names of long standing in the literature. The phylum Proteobacteria includes a wide variety of pathogenic genera, such as '' Escherichia'', '' Salmonella'', '' Vibrio'', '' Yersinia'', '' Legionella'', and many others.Slonczewski JL, Foster JW, Foster E. Microbiology: An Evolving Science 5th Ed. WW Norton & Company; 2020. Others are free-living (non parasitic) and include many of the bacteria responsible for nitrogen fixation. Carl Woese established this grouping in 1987, calling it informally the "purple bacteria and their relatives". Because of the great diversity of forms found in this group, it was later informally named Proteobacteria, after Proteus, a Greek god of the sea capable of assuming many different shapes (not after the Proteobacteria genus ''Proteus''). In 2021 the In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphaproteobacteria
Alphaproteobacteria is a class of bacteria in the phylum Pseudomonadota (formerly Proteobacteria). The Magnetococcales and Mariprofundales are considered basal or sister to the Alphaproteobacteria. The Alphaproteobacteria are highly diverse and possess few commonalities, but nevertheless share a common ancestor. Like all ''Proteobacteria'', its members are gram-negative and some of its intracellular parasitic members lack peptidoglycan and are consequently gram variable. Characteristics The Alphaproteobacteria are a diverse taxon and comprises several phototrophic genera, several genera metabolising C1-compounds (''e.g.'', ''Methylobacterium'' spp.), symbionts of plants (''e.g.'', '' Rhizobium'' spp.), endosymbionts of arthropods (''Wolbachia'') and intracellular pathogens (''e.g. Rickettsia''). Moreover, the class is sister to the protomitochondrion, the bacterium that was engulfed by the eukaryotic ancestor and gave rise to the mitochondria, which are organelles in eukaryoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodobacterales
Rhodobacterales are an order of the Alphaproteobacteria. Gene transfer agents are viruslike elements produced by Rhodobacterales which transfer DNA and may be an important factor in their evolution. Etymology From Greek ''rhodon'', the rose A rose is either a woody perennial flowering plant of the genus ''Rosa'' (), in the family Rosaceae (), or the flower it bears. There are over three hundred species and tens of thousands of cultivars. They form a group of plants that can b ..., and ''bakterion'', a rod. This refers to the colour of aerobic phototrophic cultures of this order of bacteria which can be pink or red due to the production of carotenoids. References Further reading Scientific journals * * Scientific books * External links Alphaproteobacteria {{Rhodobacterales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodobacteraceae
The Rhodobacteraceae are a family of Pseudomonadota in the order Rhodobacterales within the alpha subgroup.See the NCBIbr>webpage on Rhodobacteraceae Data extracted from the Like all Pseudomonadota, they are gram-negative. It contains chemoorganotrophs and photoheterotrophs bacteria. Many occur in aquatic habitats. Genera Accepted Genera The following genera have been effectively and validly published: * ''Acidimangrovimonas'' Ren ''et al''. 2019 * ''Actibacterium'' Lucena ''et al''. 2012 * '' Aestuariibius'' Park ''et al''. 2018 * '' Aestuariicoccus'' Feng ''et al''. 2018 * '' Aestuariihabitans'' Yoon ''et al''. 2014 * '' Aestuariivita'' Park ''et al''. 2014 * ''Aestuarium'' Yu ''et al''. 2019 * ''Agaricicola'' Chu ''et al''. 2010 * '' Albibacillus'' Hördt ''et al''. 2020 * ''Albidovulum'' Albuquerque ''et al''. 2003 * '' Albimonas'' Lim ''et al''. 2008 * ''Albirhodobacter'' Nupur ''et al''. 2015 * ''Aliiroseovarius'' Park ''et al''. 2015 * ''Aliishimia'' Kim ''et al'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruegeria
In taxonomy, ''Ruegeria'' is a genus of the Rhodobacteraceae. This genus was formerly known as the marine ''Agrobacterium'' before they were reclassified in 1998. It bears in fact the name of Hans-Jürgen Rüger, a German microbiologist, for his contribution to the taxonomy of marine species of ''Agrobacterium''. Characteristics The genus is characterised by members who are: * Gram-negative (like all Proteobacteria) * ovoid to rod-shaped cells 0.6–1.6 × 1.0–4.0 µm * motile by polar flagella, or nonmotile * non-sporeformers * aerobic * oxidase and catalase positive * are incapable of photosynthetic growth * bacteriochlorophyll a is absent * major quinone is ubiquinone 10 * GC-content, mol% G+C of the DNA is 55–59 * member of the family ''Rhodobacteraceae'', which is phenotypically, metabolically, ecologically diverse and defined based on 16S sequences data Phylogenetically it is very close to the genus ''Silicibacter'', but the two remain separate species due to phe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner cytoplasmic cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane. Gram-negative bacteria are found in virtually all environments on Earth that support life. The gram-negative bacteria include the model organism ''Escherichia coli'', as well as many pathogenic bacteria, such as '' Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', '' Chlamydia trachomatis'', and '' Yersinia pestis''. They are a significant medical challenge as their outer membrane protects them from many antibiotics (including penicillin), detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and lysozyme, an antimicrobial enzyme produced by animals that forms part of the innate immune system. Additionally, the outer leaflet of this membrane comprises a complex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethylsulfoniopropionate
Dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP), is an organosulfur compound with the formula (CH3)2S+CH2CH2COO−. This zwitterionic metabolite can be found in marine phytoplankton, seaweeds, and some species of terrestrial and aquatic vascular plants. It functions as an osmolyte as well as several other physiological and environmental roles have also been identified. DMSP was first identified in the marine red alga ''Polysiphonia fastigiata''. Biosynthesis In higher plants, DMSP is biosynthesized from ''S''-methylmethionine. Two intermediates in this conversion are dimethylsulfoniumpropylamine and dimethylsulfoniumpropionaldehyde. In algae, however, the biosynthesis starts with the replacement of the amino group in methionine by hydroxide. Degradation DMSP is broken down by marine microbes to form two major volatile sulfur products, each with distinct effects on the environment. One of its breakdown products is methanethiol (CH3SH), which is assimilated by bacteria into protein su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demethylation
Demethylation is the chemical process resulting in the removal of a methyl group (CH3) from a molecule. A common way of demethylation is the replacement of a methyl group by a hydrogen atom, resulting in a net loss of one carbon and two hydrogen atoms. The counterpart of demethylation is methylation. In biochemistry In biochemical systems, the process of demethylation is catalyzed by demethylases. These enzymes oxidize N-methyl groups, which occur in histones and some forms of DNA: :R2N-CH3 + O → R2N-H + CH2O One such oxidative enzyme family is the cytochrome P450. Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases are active for demethylation of DNA, operating by a similar pathway. These reactions exploit the weak C-H bond adjacent to amines. In particular, 5-methylcytosines in DNA can be demethylated by TET enzymes as illustrated in the figure. TET enzymes are dioxygenases in the family of alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases. A TET enzyme is an alpha-ketoglut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Bacteria
Marine prokaryotes are marine bacteria and marine archaea. They are defined by their habitat as prokaryotes that live in marine environments, that is, in the saltwater of seas or oceans or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. All cellular life forms can be divided into prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells have a nucleus enclosed within membranes, whereas prokaryotes are the organisms that do not have a nucleus enclosed within a membrane. The three-domain system of classifying life adds another division: the prokaryotes are divided into two domains of life, the microscopic bacteria and the microscopic archaea, while everything else, the eukaryotes, become the third domain. Prokaryotes play important roles in ecosystems as decomposers recycling nutrients. Some prokaryotes are pathogenic, causing disease and even death in plants and animals. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
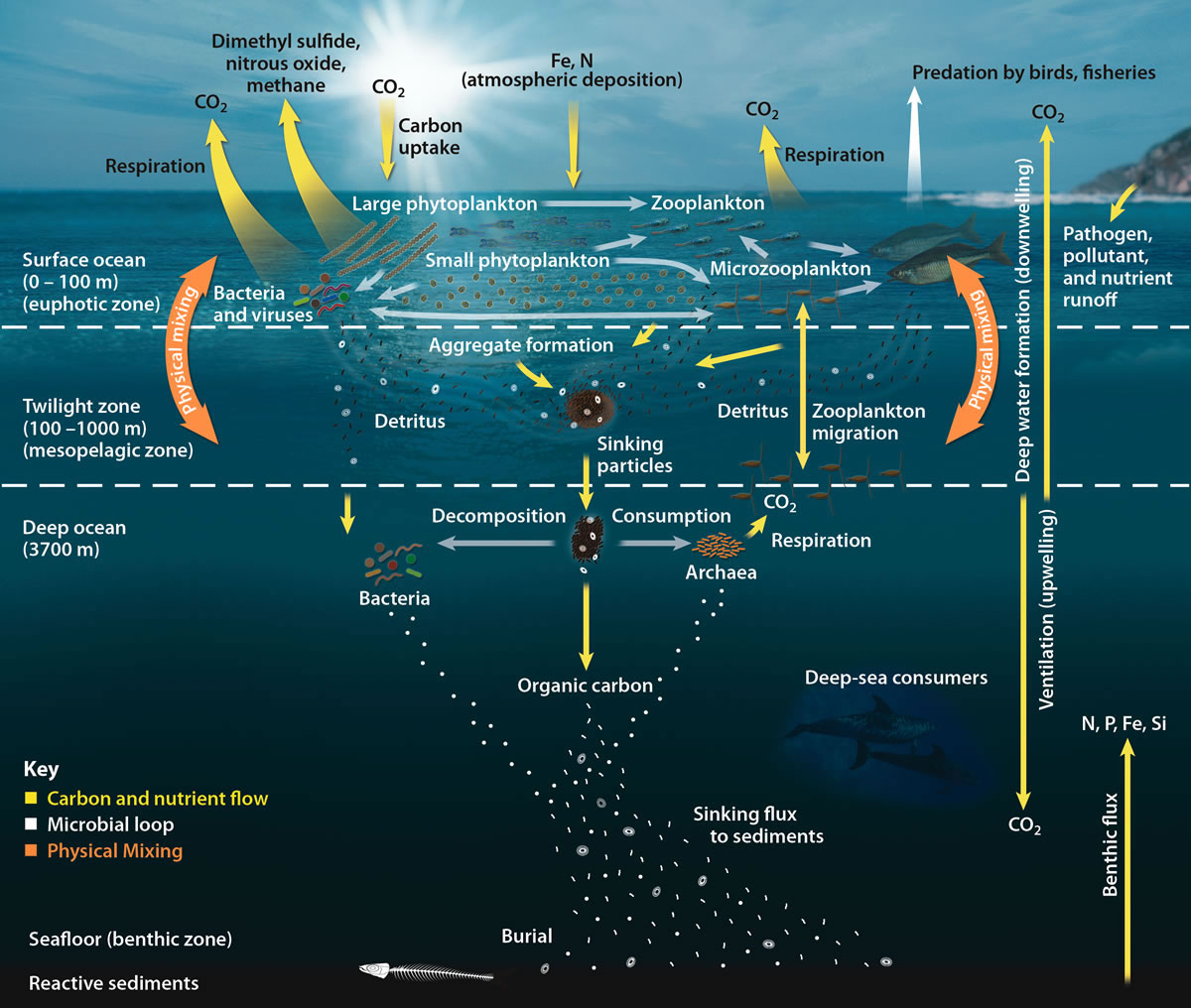
Ocean Food Web
Compared to terrestrial environments, marine environments have biomass pyramids which are inverted at the base. In particular, the biomass of consumers (copepods, krill, shrimp, forage fish) is larger than the biomass of primary producers. This happens because the ocean's primary producers are tiny phytoplankton which grow and reproduce rapidly, so a small mass can have a fast rate of primary production. In contrast, many significant terrestrial primary producers, such as mature forests, grow and reproduce slowly, so a much larger mass is needed to achieve the same rate of primary production. Because of this inversion, it is the zooplankton that make up most of the marine animal biomass. As primary consumers, zooplankton are the crucial link between the primary producers (mainly phytoplankton) and the rest of the marine food web (secondary consumers). If phytoplankton dies before it is eaten, it descends through the euphotic zone as part of the marine snow and settles into t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Sequestration
Carbon sequestration is the process of storing carbon in a carbon pool. Carbon dioxide () is naturally captured from the atmosphere through biological, chemical, and physical processes. These changes can be accelerated through changes in land use and agricultural practices, such as converting crop land into land for non-crop fast growing plants. Artificial processes have been devised to produce similar effects, including large-scale, artificial capture and sequestration of industrially produced using subsurface saline aquifers, reservoirs, ocean water, aging oil fields, or other carbon sinks, bio-energy with carbon capture and storage, biochar, enhanced weathering, direct air capture and water capture when combined with storage. Forests, kelp beds, and other forms of plant life absorb carbon dioxide from the air as they grow, and bind it into biomass. However, these biological stores are considered volatile carbon sinks as the long-term sequestration cannot be guarant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |